Creating Patterns PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title: Creating Patterns
1
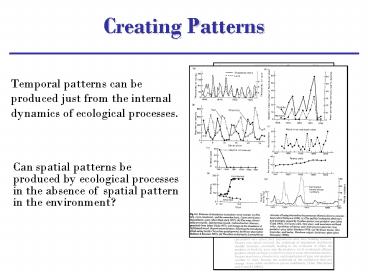
Creating Patterns
- Temporal patterns can be produced just from the
internal dynamics of ecological processes.
Can spatial patterns be produced by ecological
processes in the absence of spatial pattern in
the environment?
2
The Belousov-Zhabotinskiireaction-diffusion
systems
- What is the BK reaction?
- Self organization (spontaneous spatial pattern)
exists when, for each location, three conditions
may occur - A refractory state where the system recovers
from some event - A period of potential where some event could
occur but has not yet happened - An event occurs dependent on local conditions
and the ability of the event to migrate or
diffuse to that particular location - Example 1. Accumulation of flammable litter
in a grassland. 2. A period with enough litter
to sustain a fire. 3. A fire and repeat
Potential State
Refractory State
Excited State
3
Ecology as a BK Reaction
- Can a trophic interaction be analogous to a
chemical reaction? - Satoh, K. 1990? Single and multiarmed spiral
patterns in a cellular automaton model for an
ecosystem. Physical Society of Japan 35
4204-4207.
4
Complex and Dynamic Patterns in Uniform
Environments
X
5
Simulated Patterns with Small Anomalies or
Stochastic Properties
6
Dispersal Rates and Pattern
Hassel, M.P., Comins, H.N., and May, R.M. 1991.
Spatial structure and chaos in insect population
dynamics. Nature 353 255-258.
7
Could BK analogies apply to other levels of
ecological organization?
- Multispecies competitive-replacement communities?
- A out competes B out competes C
- Successional series or disturbance-prone
communities? - Crop-pest outbreaks?
- Human epidemics?
- What about stochastic processes will they still
work?
8
Conclusions 1. Patchiness does not NECESSARILY
lead to stable coexistence 2. Differential
dispersal ability of predators and prey are
important.
9
Other Ways that Heterogeneity may Affect
Predator- Prey Stability
See for summary/review Holt, R. D.1993. Ecology
at the mesoscale Rickleffs and Schluter (eds).
Species Diversity in Ecological Communities. U.
Chicago Press.
- In general,
- Where prey exist in source-sink types of habitat,
predation is destabilizing where predation limits
prey well below carrying capacity - Where patches are variable in quality to the
predator or prey, predator dispersal is always
stabilizing - In general source-sink dynamics for predator or
prey can be stabilizing due to buffering effect
of prey back migration to source. There are
exceptions
Type III functional response
Higher density due to additional sink-supported
population could lead to higher predator response
Predation
Prey Density
Low density stable prey population w/o sinks
10
Predation-Induced Patterns
Belousov-Zhabotinskii (BZ) reactions
Potentially excitable
Cell cycle
Unexcitable
Excited
Satoh, K. 1990. Single and multiarmed patterns
in a cellular automaton model for an ecosystem J.
Physic. Soc. Jap. 59 4204-4207
Plant Herbivore Predator Empty Plant
Excited Unexcitable Potential Potential Herbivore
Potential Excited Unexcitable Unexcitable
Predator Unexcitable Potential Excited Unexcita
ble
11
Hassel, M.P., Comins, HN, and May, RM. 1991.
Spatial Structure and chaos in insect population
dynamics. Nature 353 255-258.
12
Into the Real World
13
Cats and Rabbits Revisited
14
Of voles, weasels, and raptors in Scotland
15
Predicting outbreaks
16
And Lynxes and Hares and Sunspots