Speed of light PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: Speed of light
1
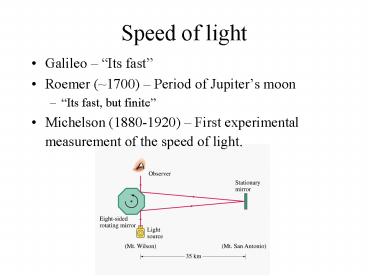
Speed of light
- Galileo Its fast
- Roemer (1700) Period of Jupiters moon
- Its fast, but finite
- Michelson (1880-1920) First experimental
measurement of the speed of light.
2
Speed of light in materials
For free space (vacuum) we showed
We expect in any other material
3
Speed of light in materials (dielectrics)
For a dielectric material we showed
We observe
4
Index of refraction
We will see later that n varies with frequency of
light
5
Ray model of light
Incident Ray
Reflected Ray
ni
nt
Transmitted Ray
Rays are a construct to show the direction the
wave is traveling
Rays are generally perpendicular to the surfaces
of equal phase (wave fronts).
6
The Laws that are Empirically Observed
- Law of reflection.
- Snells Law of Refraction.
7
Reflection Definitions
- External
- Internal
- Specular - Reflection off a smooth surface
- Diffuse - Reflection off a rough surface
e.g. air to glass
e.g. glass to air
8
Plane Mirrors
Virtual Image
9
How big does your bathroom mirror have to be?
h
Shift your observation point to a top view and
observe the right-left inversion of an image in a
plane mirror.
10
Corner Reflectors
- The reflected light ray is always parallel to the
incident ray. - Implication for stealth technology.
11
A More Physical View of the Law of Reflection
C
B
ni
A
D
nt
12
A More Physical View of the Law of Reflection
C
B
ni
A
D
nt
13
Paraxial rays
14
Refraction
- The bending of a light ray at the boundary
between two media.
Snells Law
15
Refraction Basics
- Incident, reflected, and refracted rays are all
in the plane of incidence. - A ray entering a higher index medium bends toward
the normal. - A ray entering a lower index medium bends away
from the normal. - Relative index of refraction
- Vacuum wavelength
16
Example
- A light ray is incident on a water surface at an
angle of 30 degrees w.r.t. the normal to the
surface. What is the angle of the refracted ray
relative to the normal to the surface? - Does the frequency of the light change at the
water boundary? - Does the wave length change in the water?
- How much?
17
Fermats Principle
- The actual path between two points taken by a
beam of light is the one that is traversed in the
least time.
S
h
ni
O
x
nt
b
P
a-x
a
18
Total Internal Reflection
There will always be an angle such that
(even though it cant be physically)
We define a critical angle for the limiting case
19
Fiberoptics
nc
ni
nf
How big can be?
20
Fiberoptics
nc
ni
nf
How big can be?
21
Dispersion
- Difference in wave speed (n) in a material due to
frequency
(or wavelength)