Molecular Evolution - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 68
Title:
Molecular Evolution
Description:
GENERAL POPULATION NEWBORN COHORT (NECs) Followed to the ... Roach et al, Am J Human Genetics, Volume 79, Oct 2006. Aly et al. Diabetes 55:1265-1269, 2006 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Molecular Evolution
1
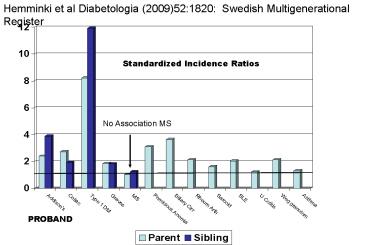
Hemminki et al Diabetologia (2009)521820
Swedish Multigenerational Register
Standardized Incidence Ratios
No Association MS
PROBAND
2
Genome-wide Associations in Type 1 Diabetes
Modified from Concannon, Rich, Nepom NEJM
3601646 2009
3
GENERAL POPULATION NEWBORN COHORT (NECs) Followed
to the Development of Anti-islet Autoantibodies
and then Diabetes HIGH RISKDR3/4DQ2/DQ8 lacking
protective DP and DR4 alleles Baschal et al
Diabetes 562405, 2007
4
Haplotype Sharing
Father
Mother
Father
Father
Mother
Mother
5
Extreme Risk for Diabetic Autoimmunity
inDR3-DQB10201/DR4-DQB10302 Siblings
Share 2 MHC haplotypes 29 (16 cases) Share 0 or
1 19 (3 cases) p0.03 HR3.4, 95 CI (1.1, 7.0)
Share 2 MHC haplotypes 29 (11 cases) Share 0 or
1 19 (1 case) p0.04 HR6.1, 95 CI (1.04, 11.81)
Aly TA. Extreme genetic risk for type 1A
diabetes. PNAS. September 2006.
6
Human Type 1 diabetes susceptibility
regions http//www.t1dbase.org/cgi-bin/dispatcher.
cgi/Welcome/display
8/4/08
IL2RA
INS
ERBB3
HLA
(IFIh1)
PTPN22
(IL2)
(PTPN11)
(CTLA4)
KIAA0350
PTPN2
7
ODDS RATIO
Modified from Todd et al. Robust Associations of
four new chromosome regions from genome-wide
anlayses of type 1 diabetes Nature Genetics
June 6 2007
8
Expanded Reference Group for Type 1 Diabetes
2,000 cases and 7,670 controls
E-41 6 7 8 7 13 14
10 6 7 6
Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases and
seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls
WTCCC Nature June 2007 661-677
9
Modified from Genome-Wide Analysis Todd et al
Nature Genetics June 2007
10
Type 1A Diabetes( ) Odds Ratios
- MHC(6.9) DQgtDRgtDPgtgtHLA-A,B
- Insulin(2.3)
- PTPN22(1.89) Lymphocyte Tyrosine Phosphatase
- CTLA-4(.85),PTPN2(1.30),KIAA0350(.81),RBM17-CD25(.
75) - ERBB3e(1.22),12q13(1.28)
- IFIH1(.82)?, CD226(1.17)?
- Other
? MHC LINKED GENE(S) X
11
Extreme Risk for Type 1A Diabetes
High risk cohort DR3/4-DQ8 siblings that share
both MHC haplotypes identical-by-descent with
their proband, N29 Low risk cohort DR3/4-DQ8
siblings that do not share both MHC
haplotypes identical-by-descent with their
proband, N19
Updated 5/7/07
Aly T et al. PNAS 2006
12
Genetic Mapping at 3-Kilobase Resolution Revelas
Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor 3 as risk
Factor for type 1 Diabetes in Sweden
- 2,360 Illumina snp analysis MHC and centromere
- ITPR3 Intronic snp (rs2296336) identified as
associated DM in survey and confirmatory Swedish
population - DR/DQ linkage present but does not obviate
association - Patient 107/643 snp C/C, Control 35/481 C/C
Roach et al, Am J Human Genetics, Volume 79, Oct
2006
13
Aly et al. Diabetes 551265-1269, 2006Analysis
of 656 SNPs of case (N17) and control (N15)
HLA-DR3-B8-haplotypes with Illumina technology
- The HLA-DR3-B8-A1 haplotype is a common (carried
in 7 of Caucasians), conserved (gt99.9 by SNP
assay comparison), and extended (?3 Mb)
haplotype. - HLA-DR3-B8-Al haplotype, genotyped at 656 SNPs in
the MHC - Control and Case (islet autoantibody positive
and/or diabetic) had remarkable conservation
approximately 3 million base pairs. - Provides excellent genomic segment to analyze
relation to diabetes centromeric and telomeric to
region for DR3 haplotypes.
14
Columns Haplotypes HLA-DR3-B8-A1
HLA-DR3-non-B8
HLA-A
HLA-B
MICA
Rows represent SNPs in the MHC region Figure
is Xcel spreadsheet with 656 miniturized rows
or SNPs Major allele grey Minor allele
yellow Unknown allele blue (phase not
determined)
DRB1
DQB1
DPB1
Aly et al, Diabetes 55 1265, 2006
15
Smyth et al Nature Genetics 38617-619, 2006
Genome wide assocaition study of nonsynonymous
SNPS Interferon-induced helicase (IFIH1) region
- O.R. .82 and .87 G allele A946T of IFIH1cases
2,0292,471 controls 1,7554,593 - TDT 46.8 transmission of G alleleTransmitted
912 versus 1,037 not (expected with null
hypothesis 975) - Genes in region not distinguishable fibroblast
activation protein (FAP), IFIH1, granacalcin
(GCA), potassium channel KCNH7
16
Interferon Induced Helicase SNP (IFIH1 A946T)
association type 1 DMSmyth et al, Nature
Genetics 2006 rs1990760
17
Natural peptides selected by diabetogenic DQ8 and
murine I-Ag7 molecules show common sequence
homology Suri et al JCI 1152268, 2005Structure
of Human insulin peptide DQ8, Lee et al Nature
Immunology 6501, 2001
Crystal DQ8B9-23 S H L V E A L Y L
V C G E R G
Wiley Nat Immunol
P1
P4
P9
P6
Preferred AA in Bound Peptides
I-Ag7 v,e,q
I,L A,s D,E
12 20
30,11 45
DQ8 E,d
A,S A,V,s E,D
27,17 19 20 60,25
amino acid at position
18
Type 1A Diabetes
- Monogenic Single gene defect.
APS-I AIRE autosomal recessive
XPID Scurfy Gene X-linked - Polygenic Summation of small effects of
multiple genes creating diabetes
susceptibility (e.g. NOD mouse) - Oligogenic MHCfew major genes
Genetic heterogeneity with
different major non-MHC genes for different
families (e.g. BB rat)
BDC-July01
19
Type 1A Diabetes
- PolygenicNOD Mouse?APS-II?Type
1A?Polygenic/Heterogeneous
- MonogenicAPS-I (AIRE)XPID (ScurfinFoxp3)
- OligogenicBB rat (Ian4/5MHC)LETL Rat
(CblbMHC)IDDM17
BDC
20
Spontaneous Animal Models
- BB rat Homozygosity Lymphopenia (Ch4Ian) RT1-U
class II (Ch 20) Additional Loci (Ch2,18,X) - NOD mouse Polygenic class II class I loci
IL-2 linked polymorphism gt12 iddm loci - Long-EvansTokushima Rat RT1-U MHC Homozygosity
Chr 11-Cblb gene
BDC
21
APS-I
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type 1
- Autosomal Recessive mutations AIRE (Autoimmune
Regulator) gene - Mucocutaneous Candidiasis/Addisons
Disease/Hypoparathyroidism - 18 Type 1 Diabetes
- Transcription Factor in Thymus
BDC
22
XPID X-linked polyendocrinopathy, immune
dysfunction and diarrhea
- XLAAD Autoimmunity Allergic Dysreg
- Scurfin gene (Foxp3/JM2)
- Immunopathogenesis Th2 Cytokines, abnormal
activation (Il-4,5,13)-ScurfyNude No
Autoimmunity-CD4 into Nude Disease-Bone
Marrow into irradiated No Disease-Require
Antigen Stimulation for Disease-Mixed Chimera
No Disease
BDC
23
Foxp3/JM2 Gene
Fork Head Homology
Zn
Zip
ORF
X
XLAAD-100
D
XLAAD-200
Scurfy
X
Zn Zinc-finger domain, Zip Zip Motif ORF
Predicted Open Reading Frame
BDC
24
Other Genes
- Insulin Gene VNTR Type 1A DiabetesProtection
with greater thymic messenger RNA - AIRE gene APS-I syndromeAutosomal recessive 18
Diabetes - Scurfy gene of XPID SyndromeNeonatal death
overwhelming autoimmunity - Ian 4/5 recessive lymphopenia gene BB rat
- Cblb recessive autoimmune gene LETL rat
- LYP inhibitor T cell activation and CTLA-4 gene
in man
25
HLA
J. Noble
Human Leukocyte Antigen human MHC cell-surface
proteins important in self vs. nonself
distinction present peptide antigens to T cells
CLASS I A,B,C
CLASS II DR,DQ,DP
26
(No Transcript)
27
The Major Histocompatibility Complex
LMP7
DQA1
DPA1
DRB1
DQB1
TAP1
DPB1
TAP2
DRA
LMP2
MHC Class II Region
0 base pairs
1 million
MICA
CYP 21B
B
C
E
A
C4A
HSP70
TNF
1 million
Class I Region
Class III Region
4 million
28
DQB10402
? -chain
Leu56?
?-chain
Asp57?
BDC
29
HLA-Peptide TCR
NH3
?2 Helix
a1 Helix
CDR1
TCR alpha
CDR3
CDR2
CDR2
CDR3
TCR beta
CDR1
BDC
COO-
30
HLA nomenclature
J. Noble
Format Gene locusSerologic specificity 2
digits Allele 2 digits Silent polymorphism (if
present) 1 digit examples DRB10405 DQB103
02 A68012 B2701
31
TERMINOLOGY
J. Noble
Allele
DRB10401
Haplotype
DQB10302
DRB10401
DRB10401
DQB10302
Genotype
DRB102
DRB10301
DQB102
32
WHICH HLA LOCI ARE INVOLVED?
J. Noble
DP
DQ
DR
B
C
A
?
?
33
HLA POLYMORPHISM
J. Noble
34
HLA Class I and II Alleles (January 2001)
412
271
207
NUMBER OF ALLELES
100
93
45
20
19
2
A B1 A1 B1 A1 B1 A B C
DR DQ DP
Class II Alleles
Class I Alleles
35
Alleles and Haplotypes in HBDI Type 1 Diabetes
Families
J. Noble
36
TYPE 1 DIABETES
J. Noble
Overall incidence 1/300
Incidence for DR3/DR4 (DQB10302) 1/15
37
DR4 SUBTYPES
J. Noble
38
Common HLA Haplotypes
DQB1
DRB1
6p
DRA
DQA1
- High RiskDR3 DQB10201, DQA10501, DRB10301
DR4 DQA10301, DQB10302, DRB10401 - ProtectiveDR2 DQB10602, DQA10102,, DRB11501
BDC
39
Diabetes Risk by HLADQ and DR Haplotypes
BDC
40
HBDI Series Transmission from Parents with
second haplotype not DQ2 or DQ8
N 406/333/33/ 79/ 72/ 55/ 55/ 44/ 42/ 38/ 29/
37/ 4
41
BDC
42
Paul et al. Absolute Risk of childhood DM by HLA
class II Genotype Lambert et al J. Clin Endocr
Metab 894037-4043, 2004
43
Myth of Protection by DQB 57 AspEight Highest
Risk Genotypes DQbeta
Paul et al. Absolute Risk of Childhood-Onset Type
1 Diabetes J Clin Endocr Metab 894037-4043,
2004
44
DRB11401 and DQB10602Dominant Protection
TDT Transmission to Diabetic
N4
N11
N307
N6
N37
JCEM853793-3797,2000
45
HLA-Defined IDDM Risk GroupsDenver Population,
n9,338
BDC
46
Proportion of Twins Without Diagnosis of DM
6 and younger n 38
7-10 n 33
11-14 n 42
15-24 n 37
25 and older n 37
Difference significant (log-rank and gen'ld
wilcoxon p 0.001 , 0.001 )
Years Since DM Diagnosis in Index Twin
Redondo, Diabetologia
47
Developing in Twin
Incidence or Hazard of IDDM
0.05
0.04
6 and younger n 38
7-10 n 33
11-14 n 42
0.03
15-24 n 37
25 and older n 37
Incidence
0.02
0.01
0.0
0
10
20
30
40
Redondo, Diabetologia
Discordance Time
48
AFBAC Affected Family-Based Controls
J. Noble
49
The IDDM2 Locus
Insulin Gene (INS)
IDDM2
Predisposing
Class I VNTR 26-63 repeats 21 alleles
Insulin Gene (INS)
IDDM2
Protective
Class III VNTR 140-200 repeats 15 alleles
VNTR Variable Number of Tandem Repeats
50
IDDM2 Genotypes in U.S. Caucasians
Pugliese et al., J. Autoimm 7 687- 694, 1994
51
Transmission of VNTR Alleles to the Affected
Offspring
- Parent-of-origin effects influence the
transmission of IDDM2 alleles - Parent-of origin effects may be mediated by
imprinting (repression of expression of one of
the parental alleles, usually by methylation)
Pugliese et al., J. Autoimm 7 687- 694, 1994
52
(No Transcript)
53
VNTR Effectson Pancreatic INS Transcription
- VNTR stimulates INS steady-state transcription in
ß-cells - VNTR length inversely correlates with INS mRNA
steady-state levels in ß-cells in vivo
- Protective class III VNTR alleles are associated
with LOWER (30) INS transcription than
diabetes-predisposing class I VNTR alleles
Pancreas INS Transcription
Predisposing Class I VNTR
Protective Class III VNTR
54
INS is transcribed in Human Thymus
-No RNA -Skin -Lung -Intestinal Mucosa -Islet
Cells (undiluted) -Islet Cell (12500) -Thymus
-Thymus
ß-actin mRNA
INS mRNA
-No RNA -Skin -Lung -Intestinal Mucosa -Islet
Cells (undiluted) -Thymus -Thymus
Pugliese et al. Nature Genetics 15293-297, 1997
55
VNTR alleles affect INS transcription in thymus
Thymus INS Transcription
cDNA
cDNA
DNA
DNA
Predisposing Class I VNTR
Protective Class III VNTR
Class I VNTR
Pancreas INS Transcription
Class III VNTR
Pugliese et al. Nature Genetics 15293-297, 1997
Predisposing Class I VNTR
Protective Class III VNTR
56
Parental Effects at the IDDM2 LocusImprinting
(INS Monoallelic Expression)in Human Thymus
Genomic cDNA
Class I VNTR
Class III VNTR
- INS Monoallelic expression observed in 15-20 of
heterozygous thymus specimens - Class III VNTR always the non-expressed
allele(5/5 thymi 2 fetal 3 post-natal cases 5
8 months, 3 yrs old)
Pugliese et al. Vafiadis et al. Nature Genetics
15293-297 15 289-292, 1997
57
IDDM2 Effects in the Thymus
- Allelic Variation Effects in the thymus,
protective class III VNTR alleles are associated
with higher INS transcription (2-3 fold) than
predisposing alleles - Parental Effects may prevent the expression of
class III VNTR alleles and cause loss of
protection - Hypothesis INS expression in the thymus and its
regulation affect diabetes risk by modulating
thymic selection processes and in turn tolerance
to insulin
A. Pugliese
58
Percent BabyDiab (Offspring) Autoantibody
Positive at age 5 yearsHLA and Insulin Gene VNTR
Walter et al, Diabetologia (2003) 46712-720
59
Minimal Influence CTLA-4 Polymorphisms Human
Type 1 DM in Contrast to Graves DiseaseUeda et
al, Nature 2003 423506
- CTLA-4 susceptible G allele transmitted 53.3
to affected offspring in 3,671 Diabetic families
(RR1.14) - G/G A/G
A/AGraves Disease 41 46
23Control 29 48 14 - G/G Genotype Associated with ½ soluble CTLA-4
Splice Variant - Idd5.1 Of NOD Mouse Possibly CTLA-4 variant at
Position 77 with G allele increasing exon 2
deleted splice variant, ligand independent form
60
with Genotype
LYP Gene (PTPN22) Polymorphism
Plt.001
Plt.05
Denver
Sardinia
Bottini et al. Nature Genetics 36 337-338
61
Transmitted LYP(PTPN22) Alleles Diabetes 2004,
533020 Replication of an Association Between the
LYP Locus with Type 1 DM
62
LYPPTPN22-PEP in Mouse
Modified from Mustelin T and Tasken K, Biochem.J.
Bottini
63
Autoimmune-associated lymphoid tyrosine
phosphatase is a gain-of-function
variantVang,..Bottini, Nature Genetics Nov 2005
- Tryptophan Replacing Arginine R620W PTPN22 gene,
increases risk diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis,
etc. - LYP-Trp620 inhibits T cells greater than
LYP-Arg620-Less IL-2 secretion from genotype
Trp/Arg vs Arg/Arg-Transfection T lymphocytes
LYP-R gene greater inhibition IL-2 secretion - Early TCR signaling inhibited more by disease
associated LYP-Trp620 variant - Gain of function variant associated with
autoimmunity suggests possibility of
pharmacologic inhibition of PTPN22 as therapeutic
64
LYP polymorphismAutoimmunity
A C to T transition in position 1861 of Lyp cDNA
leads to an Arg-Trp polymorphism in position 620,
within the P1 domain of the final protein
Bottini
65
Hypothesis LYP mutation
Bottini
66
Functional Variant LYP associated with Type 1
Diabetes Bottini, Nature Gen36337
TCR
CD4
CD45
CD28
LYP-Csk Inhibition
67
SUMO4 SNP M55V IDDM5
Not Confirmed Kosoy et al, Genes Immun 2005
6231 Smth et al Nat Genet 2005, 37110 Confirmed
Japan See Ikegami slide set
Guo et al, Nature Genetics 2004,
36837-841 Functional Variant of SUMO4, new
IkBalpha modifier
68
Pax4 Transcription Factor A (residue 1168) or C
(Proline/Histidine P321H)
RR3.75!, plt.0001
Not Confirmed Maier et al Diabetologia 482180
2005 Gylvin et al Diabetologia 482183 2005
Biason-Lauber et al, Diabetologia 2005,
48900-905Association of childhood type 1 DM with
a variant of PAX4 possible link to beta cell
regenerative capacity