190019201940195019601970198019902000 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
190019201940195019601970198019902000
Description:
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000. MODERNISM 1600 1950 ... Wren - 1987. Pugh - 1989. Argyris - 1960. McGregor 1960. Maslow 1943. Weber 1924 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:37
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 190019201940195019601970198019902000
1
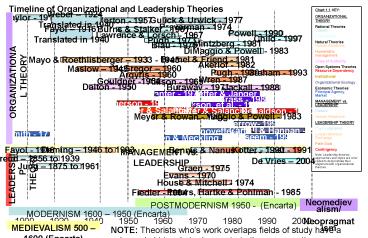
Timeline of Organizational and Leadership Theories
Chart 1.1 KEY ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY Rational
Theories Classic Contingency Natural Theories
Human Relations Humanistic management Lines of
Authority Open Systems Theories Resource
Dependency Institutional Organizational
Ecology Economic Theories Principal Agency,
Market MANAGEMENT vs. LEADERSHIP Classic Human
Relations LEADERSHIP THEORY Psychodynamic Leader-M
ember Exchange Path-Goal Contingency Note
Leadership theories, approaches and styles are
color coded to demonstrate their alignment with
organizational theories.
Weber 1924 Translated in 1940
Taylor - 1911
Gulick Urwick - 1977
Merton - 1957
Braverman - 1974
Burns Stalker - 1961
Fayol 1916 Translated in 1940
Powell - 1990
Lawrence Lorsch - 1967
Child - 1997
Pugh - 1973
Mintzberg - 1981
Blau - 1976
DiMaggio Powell - 1983
Bramel Friend - 1981
Mayo Roethlisberger 1933 - 1945
Akerlof - 1982
McGregor 1960
Maslow 1943
Pugh - 1989
Argyris - 1960
Wren - 1987
ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY
Allison - 1969
Dalton - 1950
Buraway - 1979
Schaeffer Janger - 1982
Brass - 1984
Emerson - 1962
Pfeffer Salancik - 1978
Pfeffer Salancik - 1983
Donaldson - 1990
Perrow- 1996
Granovetter - 1983
Smith - 1776
Useem - 1993
Jensen Meckling - 1976
MANAGEMENT vs. LEADERSHIP
Deming 1946 to 1993
Fayol - 1916
Bennis Nanus - 1985
Rost - 1991
Kotter - 1990
Freud 1856 to 1939
De Vries 2004
Jung 1875 to 1961
Graen - 1975
Evans - 1970
LEADERSHIP THEORY
House Mitchell - 1974
Peters, Hartke Pohlman - 1985
Fiedler - 1964
POSTMODERNISM 1950 - (Encarta)
Neomedievalism/ Neopragmatism
MODERNISM 1600 1950 (Encarta)
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
MEDIEVALISM 500 1600 (Encarta)
NOTE Theorists whos work overlaps fields of
study have a color coded triangle to demonstrate
those connections
2
Timeline of Organizational and Leadership Theories
Chart 1.1 KEY ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY Rational
Theories Classic Contingency Natural Theories
Human Relations Humanistic management Lines of
Authority Open Systems Theories Resource
Dependency Institutional Organizational
Ecology Economic Theories Principal Agency,
Market MANAGEMENT vs. LEADERSHIP Classic Human
Relations LEADERSHIP THEORY Psychodynamic Leader-M
ember Exchange Path-Goal Contingency Note
Leadership theories, approaches and styles are
color coded to demonstrate their alignment with
organizational theories.
Weber 1924 Translated in 1940
Taylor - 1911
Gulick Urwick - 1977
Merton - 1957
Braverman - 1974
Fayol 1916 Translated in 1940
ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY
Freud 1856 to 1939
Jung 1875 to 1961
LEADERSHIP APPROACHES
KEY LEADERSHIP APPROACHES Trait Skills Style Situ
ational LEADERSHIP STYLES Authoritarian Transacti
onal Transformational Laissez-Faire Values-Based D
emocratic Team Leadership Emotional
Quotient Note Leadership theories, approaches
and styles are color coded to demonstrate their
alignment with organizational theories.
Bird - 1940
LEADERSHIP APPROACHES
Zaleznik - 1977
Mann - 1959
Lord, et al. - 1986
Stogdill - 1948
Argyris -1954
Katz - 1955
Mumford - 1991
LEADERSHIP STYLES
De Vries 2004
POSTMODERNISM 1950 - (Encarta)
Neomedievalism/ Neopragmatism
MODERNISM 1600 1950 (Encarta)
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
MEDIEVALISM 500 1600 (Encarta)
NOTE Theorists whos work overlaps fields of
study have a color coded triangle to demonstrate
those connections
3
Timeline of Organizational and Leadership Theories
Chart 1.1 KEY ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY Rational
Theories Classic Contingency Natural Theories
Human Relations Humanistic management Lines of
Authority Open Systems Theories Resource
Dependency Institutional Organizational
Ecology Economic Theories Principal Agency,
Market MANAGEMENT vs. LEADERSHIP Classic Human
Relations LEADERSHIP THEORY Psychodynamic Leader-M
ember Exchange Path-Goal Contingency Note
Leadership theories, approaches and styles are
color coded to demonstrate their alignment with
organizational theories.
Bramel Friend - 1981
Mayo Roethlisberger 1933 - 1945
Akerlof - 1982
ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY
McGregor 1960
Maslow 1943
Pugh - 1989
Argyris - 1960
Wren - 1987
LEADERSHIP APPROACHES
Graen - 1975
Evans - 1970
House Mitchell - 1974
Stogdill - 1974
Blake Mouton - 1985
Kahn - 1956
Bass - 1985
Kuhnert -1994
Blake Mouton - 1991
Bass - 1985
LEADERSHIP STYLES
Downton - 1973
Tichy DeVanna - 1986
House - 1976
Bennis Nanus - 1978
Burns - 1978
POSTMODERNISM 1950 - (Encarta)
Neomedievalism/ Neopragmatism
MODERNISM 1600 1950 (Encarta)
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
MEDIEVALISM 500 1600 (Encarta)
NOTE Theorists whos work overlaps fields of
study have a color coded triangle to demonstrate
those connections
4
Timeline of Organizational and Leadership Theories
Chart 1.1 KEY ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY Rational
Theories Classic Contingency Natural Theories
Human Relations Humanistic management Lines of
Authority Open Systems Theories Resource
Dependency Institutional Organizational
Ecology Economic Theories Principal Agency,
Market MANAGEMENT vs. LEADERSHIP Classic Human
Relations LEADERSHIP THEORY Psychodynamic Leader-M
ember Exchange Path-Goal Contingency Note
Leadership theories, approaches and styles are
color coded to demonstrate their alignment with
organizational theories.
ORGANIZATIONAL THEORY
Pfeffer Salancik - 1978
Emerson - 1962
Pfeffer Salancik - 1983
Donaldson - 1990
LEADERSHIP APPROACHES
Peters, Hartke Pohlman - 1985
Fiedler - 1964
Hersey Blanchard - 1969
Tannenbaum 1958/1971
Graef - 1983
Bass Avolio - 1990
LEADERSHIP STYLES
Havron McGrath - 1962
Larson LaFasto - 1989
Barge - 1996
Parker - 1990
Zacarro et. Al. - 2001
Hill - 2004
Stewert Manz - 1995
POSTMODERNISM 1950 - (Encarta)
Neomedievalism/ Neopragmatism
MODERNISM 1600 1950 (Encarta)
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
MEDIEVALISM 500 1600 (Encarta)
NOTE Theorists whos work overlaps fields of
study have a color coded triangle to demonstrate
those connections
5
Timeline of Organizational and Leadership Theories
Weber 1924 Translated in 1940
Taylor - 1911
Fayol 1916 Translated in 1940
Wood - 1995
Chandler 1977/1997
Porter - 2002
Brooks - 1999
Powell - 1990
Weiner - 1940
Shannon - 1948
Keen - 1994
KEY Chart 1.2 Evolutionary Theories
PostFordism Network Organizations Information Age
and the Market Driven Org. Decision Making
Culture Diversity LEADERSHIP APPROACHES Trait Ski
lls Style Situational LEADERSHIP STYLES
Authoritarian Transactional Transformational Lais
sez-Faire Values-Based Democratic Team
Leadership Emotional Quotient Note Leadership
theories, approaches and styles are color coded
to demonstrate their alignment with
organizational theories.
Lucas Baroudi - 1994
March Simon - 1950
Mintzberg Waters - 1990
Lindblom - 1957
Butler - 1990
Edwards - 1979
Etzioni - 1964
Ouchi - 1980
Kunda - 1992
Kanter - 1979
GENDER
Acker - 1990
Rothschild Whitt - 1979
Reskin, McBrier et al. - 1999
RACE
Collins - 1980
DIVERSITY
Class - 1979
CLASS
Block - 1987
Clawson, et al. - 1992
POLITICS
Piven Cloward - 1977
Vogel - 1989
Martin - 2000
Morris - 1981
Burns - 1978
French Raven 1959
Bird - 1940
Trait Approaches
Smith Foti - 1998
Zaleznik - 1977
Lord, et al. - 1986
Mann - 1959
Stogdill - 1948
LEADERSHIP APPROACHES
Skill Approaches
Katz - 1955
Argyris -1954
Mumford - 1991
Stogdill - 1974
Blake Mouton - 1985
Kahn - 1956
Tannenbaum - 1958
Hersey Blanchard - 1969
Graef - 1983
Bass - 1985
Kuhnert -1994
Bass Avolio - 1990
Downton - 1973
Goleman - 1995
Blake Mouton - 1991
Salovey Mayer - 1990
Tichy DeVanna - 1986
House - 1976
Cloke Goldsmith - 2002
Bennis Nanus - 1978
LEADERSHIP STYLES
Romme - 2004
Bass Avolio - 1990
Burns - 1978
Lines - 2004
Havron McGrath - 1962
Larson LaFasto - 1989
Barge - 1996
Parker - 1990
Zacarro et. Al. - 2001
Hill - 2004
Stewert Manz - 1995
POSTMODERNISM 1950 - (Encarta)
Neomedievalism/ Neopragmatism
MODERNISM 1600 1950 (Encarta)
1900 1920 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000
MEDIEVALISM 500 1600 (Encarta)