Pr - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Pr
Description:
Thanks to in silico analysis and genome sequencing. How to ... development in xenopus. Bicoid: anteroposterior. axis in drosophila) Cap-independent inhibition ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:52
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Pr
1
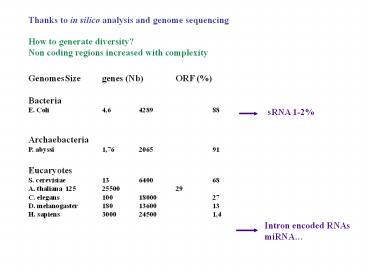
Thanks to in silico analysis and genome
sequencing
How to generate diversity? Non coding regions
increased with complexity
Genomes Size genes (Nb) ORF () Bacteria E.
Coli 4,6 4289 88 Archaebacteria P.
abyssi 1,76 2065 91 Eucaryotes S.
cerevisiae 13 6400 68 A. thaliana 125 25500 29
C. elegans 100 18000 27 D. melanogaster 180 1360
0 13 H. sapiens 3000 24500 1,4
2
(No Transcript)
3
Regulation of translation (and degradation) in
prokaryotes
A rapid way to adapt the bacteria to the
environment
4
Transcription-translation-degradation coupling
ribosome
5
Initiation of translation in procaryotes a key
step for regulation
From Laursen et al. 2005 Microbiol. Mol Biol Rev.
69101
6
mRNA structure modulates the efficiency of
translation
7
Protein-mediated translational control
8
Threonyl-tRNA synthetase regulates its own
expression
Romby Springer (2003) TIG 19155
9
Mimicry and translational control
Romby Springer (2003) TIG 19155
10
The ribosome accomodates secondary structure
upstream from the SD sequence of mRNA
Jenner et al. (2005) Science 308120
11
Conserved operator in eubacteria suggests a
conserved regulatory mechanism
Other tRNA-like structure in mRNA ?
12
B. Subtilis uncharged tRNA induced
antitermination of transcription of the cognate
aaRS gene
Thr starvation
Putzer et al. 2002 NARes. 303026 and ref therein
13
Protein-mediated translational control
14
Ribosomal S15 protein entraps the 30S subunit
into a dead-end initiation complex
Nikulin et al. 2000 NSB 7273 Serganov et al.
2002 JMB 320963
15
Diversity of S15-dependent regulatory mechanisms
Serganov et al. 2002 JMB 320963 Serganov et al.
2003 EMBO J 221898 Mathy et al. 2004 Mol.
Microbiol. 52661
16
sRNAs - Regulatory RNAs An heterogeneous class
of RNA Diversity of regulatory mechanisms Regulate
directly or indirectly multiple genes Coupling
the structure and the regulatory activity
17
Chromosomally encoded sRNAs - biological roles
sRNAs
target(s)
response/ biological role
encodes
MicF
ompF mRNA
membrane stress
porin
MicC
ompC mRNA
membrane stress
porin
MicA
ompA mRNA
membrane stress?
porin
DsrA
hns mRNA
thermoregulation
transcriptional regulator
RprA
rpoS mRNA
stress response sS
general stress
OxyS
fhlA mRNA
oxidative stress
transcriptional activator
RyhB
iron-storage proteins
sodB mRNA etc
iron homeostasis
IstR
SOS response
tisAB mRNA
toxin
ldrD mRNA
RdlD
killing peptide
purine metabolism?
GadY
gadX mRNA
transcriptional activator
acid stress
ftsZ mRNA
DicF
cell division protein
cell division
GcvB
oppAdppA mRNA?
peptide transport
periplasmic bind. proteins
Spot42
galK mRNA etc
gal operon enzyme
sugar metabolism
?
6S RNA
stationary phase survival
Sigma factor
s70
CsrB CsrC
carbon metabolism, virulence
CsrA protein
regulator
(from Wagner EGH et al.)
18
How do regulatory RNAs regulate?
Wagner et al. (2002) Adv in Genetics 46, 361-396
19
Gottesman (2004) Annu Rev Microbiol 58303
20
The binding pathway of the antisense RNA involves
different steps in a hierarchical way
Kolb et al. 2000 RNA 6 311. EMBO J 19 5905 Kolb
et al. 2001 JMolBiol 309 605. NAR 29 3145
21
Homologous antisense and target RNA structure and
sequences highlight similar topology for the
resulting complexes
6-7 nts loop
Presence of bulged nts
Stable helix
22
Sensory mRNAs - Riboswitches (alternative
conformers...)
Repression
Activation
Self-induced mRNA degradation
Narberhaus F. (2002) Arch. Microbio. 178,
404 Mandal M. Breaker R. (2003) Cell 113,
577 Nudler E. Mironov A. (2004) TBS 29, 11
23
Translational control in eukaryotes
more widespread than expected
24
Initiation of translation in eukaryotes
43S Pre-initiation complex
From Gebauer Hentze (2004) Nature Rev Moll Cell
Biol. 5827
25
Elements that influence translation of mRNA
26
mRNP-specific regulation of the initiation
complex assembly
Steric blockage
(iron metabolism)
Gebauer Hentze (2004) Nature Rev Moll Cell
Biol. 5827
27
Eukaryotic post-transcriptional operons ?
One regulatory protein targets functionally
related mRNAs (Keene 2003 Mol Cell 12 1347)
Iron regulatory protein
28
Eukaryotic miRNAs regulate translation
RISC
29
Some remarks
- Multiple roles of RNA in gene regulation all
steps of the mRNA are submitted to control
(splicing, transport, localization, translation,
degradation) - Characterization of mRNP,
expression pattern of the small RNAs
(miRNA sRNA
- Search for structured elements (conserved or
not..) in leader regions of mRNA (involved in
function dependent of environmental cues,
metabolism, riboswitches, target for miRNA,
sRNA)
- Regulation and kinetics kinetic folding of
the RNA
- Annotation of the known regulatory elements in
mRNA (riboswitches, translational operators)
- ARN-dependent regulatory networks