Variola Virus PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 80
Title: Variola Virus
1
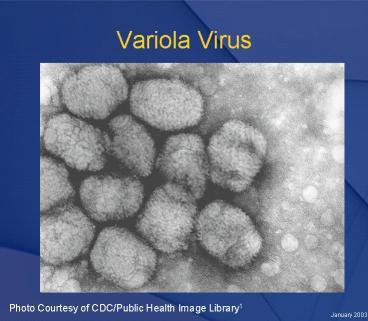
Variola Virus
Photo Courtesy of CDC/Public Health Image Library1
2
History
- Ancient scourge many millions killed
- Global eradication in 1977
3
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
4
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization2
5
Bioweapon Potential
- Precedence
- Prior use in French-Indian War
- Produced by USSR
6
Bioweapon Potential
- Reality of the risk
- Viral stocks exist
- Non-immune population
7
Photo Courtesy of CDC3
8
Epidemiology
- No animal reservoir/vector
- Mortality 25-30
- Person-to-person transmission
- Via respiratory droplets
- Household and face-to-face contacts
- High risk of nosocomial spread
- Secondary attack rate 25-40
- Up to 20 contacts infected per case
9
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization4
10
Epidemiology
- Aerosol route of transmission
- Likely in bioterrorism setting
11
Virology
- Orthopoxviridae DNA Viruses
- Variola variants
- Variola major high mortality
- Variola minor low mortality, 20th Century
- Vaccinia
- Current smallpox vaccine
12
Virology
- Orthopoxviridae DNA Viruses
- Other pox viruses
- Cowpox
- Monkeypox
13
Pathogenesis
Virus contacts respiratory mucosa Carried to
lymph nodes Primary viremia Organ
seeding WBCs infected Dermal
invasion Vesicle Sepsis
14
Clinical Features
- Incubation Stage
- Asymptomatic
- 10-12 days (range 7-17)
15
Clinical Features
- Prodromal Stage
- Sudden nonspecific flu-like illness
- High fevers
- Headache
- Backache
- Prostration
- 2-5 days duration
16
Clinical Features
- Eruptive Stage
- Characteristic rash
- Centrifugal location
- Grouping
- Depth of lesions
17
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization5
18
Clinical Features
- Distribution of the rash
19
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization6
20
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization7
21
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
22
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
23
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization8
24
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization9
25
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization10
26
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization11
27
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization12
28
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization13
29
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization14
30
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization15
31
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization16
32
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization17
33
Photo Courtesy of CDC/James Hicks18
34
Photo Courtesy of CDC19
35
Clinical Features
- Severity of the classical rash
- Discrete (lt10 mortality)
- Semi-confluent (25-50)
- Confluent (50-75)
36
Discrete Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
37
Semi-Confluent Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization20
38
Confluent Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
39
Smallpox Complications
- Eye infection or blindness
- Arthritis
- Encephalitis
- Secondary bacterial infections
40
Differential Diagnosis
- Varicella (chickenpox)
- Monkeypox
- Drug eruptions
- Generalized vaccinia
- Multiple insect bites
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Secondary syphilis
- Viral exanthems (e.g. HHV-6, Cocksackie, etc)
41
Chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization21
42
Monkey Pox
Photo Courtesy of CDC22
43
Erythema Multiforme
Photo Courtesy of New England Journal of
Medicine23
44
Generalized Vaccinia
Photo Courtesy of CDC24
45
Generalized Vaccinia
Photo Courtesy of CDC25
46
Molluscum Contagiosum
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics26
47
Secondary Syphilis
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics27
48
Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease(Enterovirus Infection)
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics28
49
Differential Diagnosis
- Chickenpox (varicella virus)
- Distribution of rash
- Grouping of lesions
- Asynchronous development
- Vesicle appearance
- Shallow
- Short Prodrome
50
Chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization29
51
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization30
52
smallpox
chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization31
53
Chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics32
54
Chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics33
55
Non-Classical Rash Presentations
- Modified variant of smallpox
- Seen in 25 of cases who were previously
vaccinated - Much lower mortality, milder disease
- Harder to distinguish from chickenpox
- May be predominant form seen if cases appear in a
vaccinated population
56
Modified Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of National Archives
57
Flat (Malignant) Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization34
58
Non-Classical Rash Presentations
- Flat (Malignant) variant of smallpox
- 5-10 of smallpox cases in outbreak setting
- Severe systemic disease
- Flat, leathery lesions
- Lesions coalesce, no discrete pustules
- Mortality 97
- May be associated with compromised hosts
59
Flat (Malignant) Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization35
60
Hemorrhagic Smallpox
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization36
61
Non-Classical Rash Presentations
- Hemorrhagic variant of smallpox
- lt5 of all cases
- Rapidly progressive fulminant illness
- Lesions become hemorrhagic before pustules form
- Predilection for pregnant women
- May be difficult to diagnose
- Differential diagnosis
- Menigococcemia
- DIC
- Hemorrhagic Chickenpox
62
Meningococcemia
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics37
63
Hemorrhagic Chickenpox
Photo Courtesy of American Academy of Pediatrics38
64
Diagnosis
- Clinical
- Classic rash is sufficient in outbreak setting
- Must have high index of suspicion
65
Photo Courtesy of World Health Organization39
66
Diagnosis
- Smallpox should be ruled out if
- Classic rash is present
- Suspicious rash with severe systemic illness
67
Diagnosis
- From vesicle/pustule fluid
- Traditional confirmation
- Electron microscopy
- Culture
- Newer rapid tests
- PCR
- Immunohistochemistry
- Reference labs (e.g. CDC)
68
Diagnosis
Photo Courtesy of CDC/Dr. Fred Murphy, Sylvia
Whitfield40
69
Management
- Isolation of suspected cases
- No effective antivirals
- Supportive care
- Fluid, electrolyte balance
- Hemodynamic, ventilatory support
- Antibiotics for secondary infections
- /- vaccination with smallpox vaccine
70
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
- For exposure to aerosol or suspected case
- Household or face-to-face contacts
71
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
- Vaccine
- Protective within 3-4 days of exposure
- Reduces incidence 2-3 fold
- Decreases mortality gt50
- Cidofovir
- Effective vs other poxviruses
- Nephrotoxic antiviral agent
72
Vaccination
- Vaccinia live virus vaccine
- U.S. stock
- gt20 years old, still viable
- 10 fold dilution still gt95 effective
- Jennerian pustule protection
Photo Courtesy of CDC41
73
Vaccination
- Efficacy
- 10 fold reduction 2o attack rate
- Full protection for 3-10 years
- Modest protection from mortality up to 20 yr
- Multiple vaccinations boost duration
74
Vaccination
- Adverse Effects
- 3/100,000 vaccinees
- Death
- 1/million vaccinees historically
- Highest risk
- Infants
- Primary vaccinees
- Absolute contraindications
- None in outbreak setting
75
Vaccination
- Relative contraindications
- Age lt1 year old
- Pregnancy
- Immunocompromised
- Skin Disorders
- Eczema
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Contact with high-risk persons
76
Vaccination
- Serious complications
- Encephalitis
- 1300,000 primary vaccinees
- 25 mortality
- No treatment
- Often permanent neurological defects
- Progressive Vaccinia
- (a.k.a. vaccinia gangrenosum/necrosum)
- Untreated mortality near 100
- Eczema vaccinatum
- History of eczema or chronic skin disorder
- 40 mortality in young children
77
Vaccination
- Mild complications
- Generalized vaccinia
- Autoinoculation
- VIG can treat or prevent
78
Infection Control
- Isolation of Cases
- Contact precautions
- Gloves, gowns
- Airborne precautions
- Negative pressure HEPA filtered room, N95 masks
- Home isolation an option
- Immunized persons should provide care
79
Infection Control
- Management of Case Contacts
- Period of infectiousness
- Oral lesions all scabs
- Fever precedes rash
- Fever Isolation
- Contact identification
- Exposure to case after fever onset
- Face-to-face contact
- lt 3 meters
- Immediate vaccination
- 17 day observation
- Isolate if gt 38o
80
Infection Control
- Nosocomial transmission
- All patients and staff in hospital with a case
should be vaccinated - Quarantine may be necessary