What does language do? - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 93
Title:
What does language do?
Description:
... form-meaning pair whose properties may not be strictly ... Linguistic input is converted into a mental simulation based on bodily-grounded structures. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:24
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: What does language do?
1
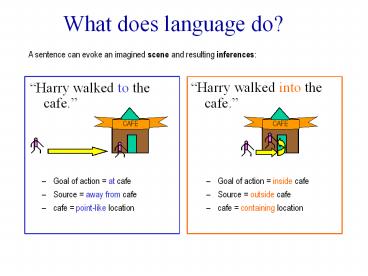
What does language do?
A sentence can evoke an imagined scene and
resulting inferences
- Harry walked to the cafe.
- Harry walked into the cafe.
- Goal of action at cafe
- Source away from cafe
- cafe point-like location
- Goal of action inside cafe
- Source outside cafe
- cafe containing location
2
Language understanding
(Utterance, Situation)
Linguistic knowledge
Conceptual knowledge
Analysis
Interpretation
3
Language understanding analysis simulation
Harry walked to the cafe.
Utterance
Lexicon
Constructicon
Analysis Process
General Knowledge
Semantic Specification
Schema Trajector Goal walk Harry cafe
Belief State
Simulation
4
Interpretation x-schema simulation
- Constructions can
- specify which schemas and entities are involved
in an event, and how they are related - profile particular stages of an event
- set parameters of an event
walker at goal
energy
goalhome
walkerHarry
Harry is walking home.
5
Traditional Levels of Analysis
Pragmatics
Semantics
Syntax
Morphology
Phonetics
6
Harry walked into the cafe.
Pragmatics
Semantics
Utterance
Syntax
Morphology
Phonetics
7
Construction Grammar
A construction is a form-meaning pair whose
properties may not be strictly predictable from
other constructions. (Construction Grammar,
Goldberg 1995)
Form
Meaning
block
walk
to
8
Form-meaning mappings for language
Linguistic knowledge consists of form-meaning
mappings
- Meaning
- event structure
- sensorimotor control
- attention/perspective
- social goals...
- Form
- phonological cues
- word order
- intonation
- inflection
9
Constructions as maps between relations
Complex constructions are mappings between
relations in form and relations in meaning.
Form
Meaning
Mover Motion before(Mover, Motion)
MotionEvent mover(Motion, Mover)
is Action ing before(is,
Action) suffix(Action, ing)
ProgressiveAction aspect(Action, ongoing)
DirectedMotionEvent direction(Motion,
Direction) mover(Motion, Mover)
Mover Motion Direction before(Motion,
Direction) before(Mover, Motion)
10
Embodied Construction Grammar
- Embodied representations
- active perceptual and motor schemas
- situational and discourse context
- Construction Grammar
- Linguistic units relate form and
meaning/function. - Both constituency and (lexical) dependencies
allowed. - Constraint-based (Unification)
- based on feature structures (as in HPSG)
- Diverse factors can flexibly interact.
11
Representing image schemas
schema name
schema Source-Path-Goal roles source path g
oal trajector
schema Container roles interior exterior po
rtal boundary
role name
Boundary
Interior
Trajector
Portal
Source
Goal
Path
Exterior
These are abstractions over sensorimotor
experiences.
12
Inference and Conceptual Schemas
- Hypothesis
- Linguistic input is converted into a mental
simulation based on bodily-grounded structures. - Components
- Semantic schemas
- image schemas and executing schemas are
abstractions over neurally grounded perceptual
and motor representations - Linguistic units
- lexical and phrasal construction representations
invoke schemas, in part through metaphor - Inference links these structures and provides
parameters for a simulation engine
13
Embodied Construction GrammarECG(Formalizing
Cognitive Linguisitcs)
- Linguistic Analysis
- Computational Implementation
- Test Grammars
- Applied Projects Question Answering
- Map to Connectionist Models, Brain
- Models of Grammar Acquisition
14
ECG Structures
- Schemas
- image schemas, force-dynamic schemas, executing
schemas, frames - Constructions
- lexical, grammatical, morphological, gestural
- Maps
- metaphor, metonymy, mental space maps
- Spaces
- discourse, hypothetical, counterfactual
15
ECG Schemas
- schema Hypotenuse subcase of Line-Segment
- evokes Right-Tri as rt
- roles
- lower-left Point
- upper-right Point
- constraints
- self ? rt.long-side
- schema ltnamegt subcase of ltschemagt evokes
ltschemagt as - ltlocal namegt
- roles lt local role gt
- ltrole restrictiongt
- constraints
- ltrolegt ? ltrolegt
- ltrolegt ? ltvaluegt
- ltpredicategt
16
Source-Path-Goal Container
- schema Container
- roles
- interior Bounded-Region boundary Curve
portal Bounded-Region
- schema SPG
- subcase of TrajLandmark
- roles
- source Place
- path DirectedCurve
- goal Place
- trajector Entity
- landmark Bounded-
- Region
17
Referent Descriptor Schemas
- schema RD
- roles
- category
- gender
- count
- specificty
- resolved Ref
- modifications
- schema RD5 // Eve
- roles
- HumanSchema
- Female
- one
- Known
- Eve Sweetser
- none
18
ECG Constructions
- construction ltnamegt
- subcase of ltconstructiongt
- constituents
- ltnamegtltconstructiongt
- form
- constraints
- ltnamegt before/meets ltnamegt
- meaning
- constraints
- // same as for schemas
- construction SpatialPP
- constituents
- prep SpatialPreposition
- lm NP
- form
- constraints
- prep meets lm
- meaning TrajectorLandmark
- constraints
- selfm ? prep
- landmark ? lm.category
19
Into and The CXNs
- construction Into subcase of SpatialPreposition
- form WordForm constraints
- orth ? "into"
- meaning SPG
- evokes Container as c constraints
- landmark ? c
- goal ? c.interior
- construction The subcase of Determiner
formWordForm - constraints
- orth ? "the"
- meaning
- evokes RD as rd
- constraints rd.specificity ? known
20
Two Grammatical CXNs
- construction DetNoun subcase of NP
constituents - dDeterminer
- nNoun
- form constraints
- d before n
- meaning constraints
- selfm ? d.rd
- category ? n
- construction NPVP subcase of S constituents
- subj NP
- vp VP
- form constraints
- subj before vp
- meaning constraints
- profiled-participant ?
- subj
21
- construction ActiveSelfMotionPath subcase of
ActiveMotionPath constituents - v verb
- ppSpatialPP
- form constraints
- v before pp
- meaningSelfMotionPathEvent
- constraints spg ? pp
profiled-participant ? mover
profiled-process ? motion
profiled-process ? v
- Construction WalkedVerb
- subcase of PastPerfectiveVerb form
constraints orth ?"walked"
meaningWalkAction
22
Competition-based analyzer
- An analysis is made up of
- A constructional tree
- A semantic specification
- A set of resolutions
Johno Bryant
Bill gave Mary the book
23
Combined score determines best-fit
- Syntactic Fit
- Constituency relations
- Combine with preferences on non-local elements
- Conditioned on syntactic context
- Antecedent Fit
- Ability to find referents in the context
- Conditioned on syntax match, feature agreement
- Semantic Fit
- Semantic bindings for frame roles
- Frame roles fillers are scored
24
0Eve1walked2into3the4house5
- Constructs
- --------------
- NPVP0 (0,5)
- Eve3 (0,1)
- ActiveSelfMotionPath
- 2 (1,5)
- WalkedVerb57 (1,2)
- SpatialPP56 (2,5)
- Into174 (2,3)
- DetNoun173 (3,5)
- The204 (3,4)
- House205 (4,5)
- Schema Instances
- -------------------
- SelfMotionPathEvent1
- HouseSchema66
- WalkAction60
- Person4
- SPG58
- RD177 house
- RD5 Eve
25
Unification chains and their fillers
- SelfMotionPathEvent1.mover
- SPG58.trajector
- WalkAction60.walker
- RD5.resolved-ref
- RD5.category
- Filler Person4
- SpatialPP56.m
- Into174.m
- SelfMotionPathEvent1.spg
- Filler SPG58
- SelfMotionPathEvent1
- .landmark
- House205.m
- RD177.category
- SPG58.landmark
- FillerHouseSchema66
- WalkedVerb57.m
- WalkAction60.routine
- WalkAction60.gait
- SelfMotionPathEvent1
- .motion
- FillerWalkAction60
26
Summary ECG
- Linguistic constructions are tied to a model of
simulated action and perception - Embedded in a theory of language processing
- Constrains theory to be usable
- Frees structures to be just structures, used in
processing - Precise, computationally usable formalism
- Practical computational applications, like MT and
NLU - Testing of functionality, e.g. language learning
- A shared theory and formalism for different
cognitive mechanisms - Constructions, metaphor, mental spaces, etc.
27
A Best-Fit Approach for Productive Analysis of
Omitted Arguments
- Eva Mok John Bryant
- University of California, Berkeley
- International Computer Science Institute
28
Simplify grammar by exploiting the language
understanding process
- Omission of arguments in Mandarin Chinese
- Construction grammar framework
- Model of language understanding
- Our best-fit approach
29
Productive Argument Omission (in Mandarin)
- Mother (I) give you this (a toy).
ma1ma gei3 ni3 zhei4ge
mother give 2PS thisCLS
1
- You give auntie the peach.
2
ni3 gei3 yi2
2PS give auntie
- Oh (go on)! You give auntie that.
3
ao ni3 gei3 ya
EMP 2PS give EMP
4
gei3
give
- I give you some peach.
CHILDES Beijing Corpus (Tardiff, 1993 Tardiff,
1996)
30
Arguments are omitted with different probabilities
- All arguments omitted 30.6 No arguments
omitted 6.1
31
Construction grammar approach
- Kay Fillmore 1999 Goldberg 1995
- Grammaticality form and function
- Basic unit of analysis construction, i.e. a
pairing of form and meaning constraints - Not purely lexically compositional
- Implies early use of semantics in processing
- Embodied Construction Grammar (ECG) (Bergen
Chang, 2005)
32
Problem Proliferation of constructions
Subj Verb Obj1 Obj2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
Verb Obj1 Obj2
? ? ?
Transfer Recipient Theme
Subj Verb Obj2
? ? ?
Giver Transfer Theme
Subj Verb Obj1
? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient
33
If the analysis process is smart, then...
Subj Verb Obj1 Obj2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
- The grammar needs only state one construction
- Omission of constituents is flexibly allowed
- The analysis process figures out what was omitted
34
Best-fit analysis process takes burden off the
grammar representation
Constructions
Utterance
incremental, competition-based,
psycholinguistically plausible
Semantic Specification image schemas, frames,
action schemas
Simulation
35
Competition-based analyzer finds the best analysis
- An analysis is made up of
- A constructional tree
- A set of resolutions
- A semantic specification
The best fit has the highest combined score
36
Combined score that determines best-fit
- Syntactic Fit
- Constituency relations
- Combine with preferences on non-local elements
- Conditioned on syntactic context
- Antecedent Fit
- Ability to find referents in the context
- Conditioned on syntactic information, feature
agreement - Semantic Fit
- Semantic bindings for frame roles
- Frame roles fillers are scored
37
Analyzing ni3 gei3 yi2 (You give auntie)
Two of the competing analyses
ni3 gei3 yi2 omitted
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
ni3 gei3 omitted yi2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
- Syntactic Fit
- P(Theme omitted ditransitive cxn) 0.65
- P(Recipient omitted ditransitive cxn) 0.42
(1-0.78)(1-0.42)0.65 0.08
(1-0.78)(1-0.65)0.42 0.03
38
Using frame and lexical information to restrict
type of reference
The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme
Manner Means Place Purpose Reason Time
Lexical Unit gei3 Giver (DNI) Recipient (DNI) Theme (DNI)
39
Can the omitted argument be recovered from
context?
- Antecedent Fit
ni3 gei3 yi2 omitted
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
ni3 gei3 omitted yi2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
?
40
How good of a theme is a peach? How about an
aunt?
- Semantic Fit
ni3 gei3 yi2 omitted
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
ni3 gei3 omitted yi2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
The Transfer Frame Giver (usually animate) Recipient (usually animate) Theme (usually inanimate)
41
The argument omission patterns shown earlier can
be covered with just ONE construction
Subj Verb Obj1 Obj2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
P(omittedcxn)
0.78
0.42
0.65
- Each cxn is annotated with probabilities of
omission - Language-specific default probability can be set
42
Leverage process to simplify representation
- The processing model is complementary to the
theory of grammar - By using a competition-based analysis process, we
can - Find the best-fit analysis with respect to
constituency structure, context, and semantics - Eliminate the need to enumerate allowable
patterns of argument omission in grammar - This is currently being applied in models of
language understanding and grammar learning.
43
Best-fit example with theme omitted
Subj Verb Obj1 Obj2
? ? ? ?
Giver Transfer Recipient Theme
2
ni3 gei3 yi2
2PS give auntie
You give auntie the peach.
Verb
?
Transfer
Subj
?
Giver
Obj1
?
Recipient
Obj2
?
Theme
local? omitted?
local? omitted?
local? omitted?
local
local
omitted
local? omitted?
local
44
How to recover the omitted argument, in this case
the peach?
The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme
Manner Means Place Purpose Reason Time
Obj2
?
Theme
omitted
Lexical Unit gei3 Giver Recipient Theme
(DNI) (DNI) (DNI)
45
Best-fit example with theme omitted
3
ao ni3 gei3 ya
EMP 2PS give EMP
Oh (go on)! You give auntie that.
Verb
?
Transfer
Subj
?
Giver
Obj1
?
Recipient
Obj2
?
Theme
local? omitted?
local? omitted?
local? omitted?
local
omitted
omitted
local? omitted?
local
46
How to recover the omitted argument, in this case
the aunt and the peach?
Obj1
?
Recipient
The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme The Transfer Frame Giver Recipient Theme
Manner Means Place Purpose Reason Time
omitted
Obj2
?
Theme
Lexical Unit gei3 Giver Recipient Theme
(DNI) (DNI) (DNI)
omitted
47
Embodied Compositional Semantics
- after
- Ellen Dodge
- edodge_at_berkeley.edu
48
Questions
- What is the nature of compositionality in the
Neural Theory of Language? - How can it be best represented using Embodied
Construction Grammar?
49
Examples
- He bit the apple
- He was bitten (by a toddler)
- He bit into the apple
- His white teeth bit into the apple.
- He shattered the window
- The window was shattered
- The window shattered
50
Compositionality
- Put the parts together to create the meaning of
the whole. - Questions
- what is the nature of the parts?
- How and why do they combine with one another?
- What meaning is associated with this composition?
51
Short answers
- Parts constructions, schemas
- Combination binding, unification
- Meaning of the whole simulation of unified
parts
52
Constructions
- Construction Grammar
- Constructions are form-meaning pairings
- A given utterance instantiates many different
constructions - Embodied Construction Grammar
- Construction meaning is represented using schemas
- Meaning is embodied
53
Key assumptions of NTL
- Language understanding is simulation
- Simulation involves activation of neural
structures
54
Comments
- Language understanding
- Understanding process is dynamic
- Redundancy is okay
55
Conceptual structure
- Embodied
- Schematic
- (Potentially) language-independent
- Highly interconnected
56
Simulation parameters
- Constructions unify to create semantic
specification that supports a simulation - Two types of simulation parameters for event
descriptions - Event content
- Event construal
57
Putting the parts together
- Bindings
- Unification
58
Pre-existing structure
schema
Cxn
schema
schema
Cxn
schema
Cxn
schema
59
Unification
schema
Cxn
schema
schema
Cxn
schema
Cxn
schema
60
Summary
- Parts constructions, schemas
- Combination binding, unification
- Meaning of the whole simulation of the combined
parts
61
First example
- He bit the apple.
62
Schemas
schema MotorControl subcase of Process
roles Actor ? Protagonist Effector
Effort Routine constraints Actor ?
animate
63
schema Contact subcase of SpatialRelation
roles Entity1 entity Entity2
entity
schema MotorControl subcase of Process
roles Actor ? Protagonist Effector
Effort Routine constraints Actor ?
animate
schema ForceTransfer evokes Conact as C
roles Supplier ? C.entity1 Recipient ?
C.entity2 Force
schema ForceApplication subcase of MotorControl
evokes ForceTransfer as FT roles
Actor ? FT.Supplier ? Protagonist Acted
Upon? FT.Recipient Effector Routine
Effort ? FT.Force.amount
64
Schema networks
Contact
MotorControl
ForceTransfer
Motion
Effector Motion
SelfMotion
ForceApplication
CauseEffect
MotionPath
Effector MotionPath
SelfMotion Path
SPG
SpatiallyDirectedAction
Agentive Impact
Contact
65
Verb Constructions
Construction BITE1 subcase of Verb form
bite meaning ForceApplication
constraints Effector ? teeth
Routine ? bite // close mouth
schema ForceApplication subcase of MotorControl
evokes ForceTransfer as FT roles
Actor ? FT.Supplier ? Protagonist Acted
Upon ? FT.Recipient Effector
Routine Effort ? FT.Force.amount
66
Verb Constructions
cxn BITE meaning ForceApplication
schema MotorControl
cxn GRASP meaning ForceApplication
schema ForceApplication subcase of
MotorControl
cxn PUSH meaning ForceApplication
cxn SLAP meaning AgentiveImpact
schema Agentive Impact subcase of
ForceApplication
cxn KICK meaning AgentiveImpact
cxn HIT meaning AgentiveImpact
67
Argument Structure Construction
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Affected ? NPm
68
Argument Structure Construction
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Affected ? NPm
69
CauseEffect schema
schema CauseEffect subcase of
ForceApplication Process roles Causer ?
Actor Affected ? ActedUpon ?
Process.Protagonist Instrument ? Effector
70
Schema Network
Contact
MotorControl
ForceTransfer
Process
Motion
Effector Motion
SelfMotion
ForceApplication
CauseEffect
MotionPath
Effector MotionPath
SelfMotion Path
SPG
SpatiallyDirectedAction
Agentive Impact
Contact
71
Argument Structure Construction
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Affected ? NPm
72
Schema Network
Contact
MotorControl
ForceTransfer
Process
Motion
Effector Motion
SelfMotion
ForceApplication
CauseEffect
MotionPath
Effector MotionPath
SelfMotion Path
SPG
SpatiallyDirectedAction
Agentive Impact
Contact
73
Important points
- Compositionality does not require that each
component contain different information. - Shared semantic structure is not viewed as an
undesirable redundancy
74
Argument Structure Construction
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Affected ? NPm
75
Event Descriptor schema
schema EventDescriptor roles
EventType Process ProfiledProcess
Process ProfiledParticipant Entity
ProfiledState(s) State SpatialSetting
TemporalSetting
76
Argument Structure Construction
Construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Affected ? NPm
77
Bindings with other cxns
construction NPVP1 constituents Subj NP
VP VP form Constraints Subj f
before VPf meaning EventDescriptor
ProfiledParticipant ? Subjm
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V NP form VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED constraints
Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant Affected ? NPm
78
Bindings with other cxns
Construction NPVP1 constituents Subj NP
VP VP form constraints Subj f
before VPf meaning EventDescriptor
ProfiledParticipant ? Subjm
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V NP form VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED constraints
Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant Affected ? NPm
schema EventDescriptor roles
EventType ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant ProfiledState(s)
SpatialSetting TemporalSetting
79
Bindings with other cxns
construction NPVP1 constituents Subj NP
VP VP form Constraints Subj f
before VPf meaning EventDescriptor
ProfiledParticipant ? Subjm
construction ActiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V NP form VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED constraints
Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant Affected ? NPm
schema EventDescriptor roles
EventType ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant ProfiledState(s)
SpatialSetting TemporalSetting
80
Unification
Meaning
Constructions
EventDescriptor EventType ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
NPVP1
CauseEffect causer affected
TransitiveAction2
ForceApplication actor actedupon
BITE
NP2
ReferentDescriptor
THE
APPLE
NP1
ReferentDescriptor
HE
81
Unification
Meaning
Constructions
EventDescriptor EventType ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
NPVP1
CauseEffect causer affected
TransitiveAction2
ForceApplication actor actedupon
BITE
NP2
ReferentDescriptor
THE
APPLE
NP1
ReferentDescriptor resolved referent
HE
82
Unification
Meaning
Constructions
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
NPVP1
CauseEffect causer affected
TransitiveAction2 Verb
ForceApplication actor actedupon
BITE
NP2
ReferentDescriptor
THE
APPLE
NP1
ReferentDescriptor resolved referent
HE
83
Unification
Meaning
Constructions
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
NPVP1 subj
CauseEffect causer affected
TransitiveAction2
ForceApplication actor actedupon
BITE
NP2
ReferentDescriptor
THE
APPLE
NP1
ReferentDescriptor
HE
84
Unification
Meaning
Constructions
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
NPVP1
CauseEffect causer affected
TransitiveAction2 NP
ForceApplication actor actedupon
BITE
NP2
ReferentDescriptor
THE
APPLE
NP1
ReferentDescriptor
HE
85
Semantic SpecificationHe bit the apple
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
CauseEffect causer affected
ForceApplication actor actedupon routine ?
bite effector ? teeth
RD27 category
Person
RD55 category
Apple
86
Simulation - He bit the apple
CauseEffect
Protagonist Causer ? Actor
ForceApplication
Process
Protagonist Affected ? ActedUpon
87
Simulation - He bit the apple
CauseEffect
Protagonist Causer ? Actor
ForceApplication
Process
Protagonist Affected ? ActedUpon
88
Passive voice
- He was bitten (by a toddler)
89
Argument Structure ConstructionHe was bitten (by
a toddler)
construction PassiveTransitiveAction2 subcase
of VP constituents V PassiveVerb
(PP agentivePP) form constraints
VF before PPF meaning
CauseEffectAction evokes EventDescriptor as
ED ForceApplication as FA constraints
Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Affected ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm
Causer ? FA.Actor Affected ? FA.ActedUpon
Causer ? PP.NPm
90
Semantic SpecificationHe was bitten (by a
toddler)
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
CauseEffect causer affected
ForceApplication actor actedupon routine ?
bite effector ? teeth
RD27 category
Person
RD48 category
Person
91
Simulation - He was bitten (by a toddler)
CauseEffect
Action Bite
Protagonist Causer ? Actor
Effect Process
Protagonist Affected ? ActedUpon
92
Variations on a theme
- He shattered the window
- The window was shattered
- The window shattered
93
Verb Construction -- shatter
Construction SHATTER1 subcase of Verb
form shatter meaning StateChange
constraints Initial Undergoer.state
? whole Final Undergoer.state ?
shards
schema StateChange subcase of Process
roles Undergoer ? Protagonist
94
Argument Structure ConstructionHe shattered the
window
construction ActiveTransitiveAction3 subcase
of VP constituents V verb NP NP
form constraints VF
before NPF meaning CauseEffect evokes
EventDescriptor as ED StateChange as SC
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess Causer ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant SC ? Vm
Affected ? SC.Undergoer Affected ? NPm
95
Semantic SpecificationHe shattered the window
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
CauseEffect causer affected
StateChange Undergoer state ? wholeness
RD27 category
Person
RD189 category
Window
96
Simulation - He shattered the window
CauseEffect
Protagonist Causer
Action
Process
Protagonist Affected ? Undergoer
97
Argument Structure ConstructionThe window was
shattered
construction PassiveTransitiveAction3 subcase
of VP constituents V PassiveVerb
(PP agentivePP) form constraints
VF before NPF meaning CauseEffect
evokes EventDescriptor as ED StateChange as
SC constraints Selfm ?
ED.EventType Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess
Affected ? ED.ProfiledParticipant
SC ? Vm Affected ? SC.Undergoer
Causer ? PP.NPm
98
Semantic SpecificationThe window was shattered
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
CauseEffect causer affected
StateChange Undergoer state ? wholeness
RD175 category
Window
99
Simulation - The window was shattered
CauseEffect
Protagonist Causer
Action
Process
Protagonist Affected ? Undergoer
100
Argument Structure ConstructionThe window
shattered
construction ActiveIntransitiveAction1
subcase of VP constituents V verb
form meaning Process evokes
EventDescriptor as ED StateChange as SC
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType
Vm ? ED.ProfiledProcess
Protagonist ? ED.ProfiledParticipant SC ?
Vm Protagonist ? SC.Undergoer
101
Semantic SpecificationThe window shattered
EventDescriptor eventtype ProfiledProcess
ProfiledParticipant
Process protagonist
StateChange Undergoer state ? wholeness
RD177 category
Window
102
Simulation - The window shattered
Process
Process
Protagonist Undergoer
103
Some more variations on a theme
- He bit the apple
- He bit into the apple
- His white teeth bit into the apple.
104
Argument Structure ConstructionHe bit into the
apple
construction ActiveEffectorMotionPath2
subcase of VP constituents
V verb PP Spatial-PP
form constraints VF before PPF meaning
EffectorMotionPath evokes EventDescriptor
as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Actor ? ED.ProfiledParticipa
nt FA ? Vm Actor ? FA.Actor Effector ?
FA.Effector // INI Target ? FA.ActedUpon SPG
? PPm Target ? PPm .Prep.LM
105
Schema
schema EffectorMotionPath subcase of
EffectorMotion subcase of SPG // or evokes SPG
roles Actor ? MotorControl.protagoni
st Effector ? SPG.Tr ? M.Mover ?
Motion.protagonist Target ? SPG.Lm
106
Schema Network
Contact
MotorControl
ForceTransfer
Process
Motion
Effector Motion
SelfMotion
ForceApplication
CauseEffect
MotionPath
Effector MotionPath
SelfMotion Path
SPG
SpatiallyDirectedAction
Agentive Impact
Contact
107
Argument Structure Construction He bit into the
apple
construction ActiveEffectorMotionPath2
subcase of VP constituents
V verb PP Spatial-PP
form constraints VF before PPF meaning
EffectorMotionPath evokes EventDescriptor
as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Actor ? ED.ProfiledParticipa
nt FA ? Vm Actor ? FA.Actor Effector ?
FA.Effector // INI Target ? FA.ActedUpon SPG
? PPm Target ? PPm .Prep.LM
108
EffectorMotionPath
Action
Protagonist Actor
Effector Motion
Protagonist Effector
Source
Path
Goal
109
Argument Structure Construction He bit into the
apple
construction ActiveEffectorMotionPath2
subcase of VP constituents
V verb PP Spatial-PP
form constraints VF before PPF meaning
EffectorMotionPath evokes EventDescriptor
as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Actor ? ED.ProfiledParticipa
nt FA ? Vm Actor ? FA.Actor Effector ?
FA.Effector // INI Target ? FA.ActedUpon SPG
? PPm Target ? PPm .Prep.LM
110
Simulation He bit into the apple
Action
Protagonist Actor
Effector Motion
Protagonist Effector
Source
Path
Goal
111
Argument Structure ConstructionHis white teeth
bit into the apple
construction ActiveEffectorMotionPath3
subcase of VP constituents
V verb PP Spatial-PP
form constraints VF before PPF meaning
EffectorMotionPath evokes EventDescriptor
as ED ForceApplication as FA
constraints Selfm ? ED.EventType Vm ?
ED.ProfiledProcess Effector ?
ED.ProfiledParticipant FA ? Vm Actor ?
FA.Actor // INI Effector ? FA.Effector Target
? FA.ActedUpon SPG ? PPm Target ? PPm
.Prep.LM
112
Simulation His white teeth bit into the apple
Action
Protagonist Actor
Effector Motion
Protagonist Effector
Source
Path
Goal
113
Non-agentive biting
- He landed on his feet, hitting the narrow
pavement outside the yard with such jarring
impact that his teeth bit into the edge of his
tongue. BNC - The studs bit into Trent's hand. BNC
- His chest burned savagely as the ropes bit into
his skin. BNC
114
Schema Network
Contact
MotorControl
ForceTransfer
Process
Motion
Effector Motion
SelfMotion
ForceApplication
CauseEffect
MotionPath
Effector MotionPath
SelfMotion Path
SPG
SpatiallyDirectedAction
Agentive Impact
Contact
115
Simulation His teeth bit his tongue
Motion
Protagonist Mover
Source
Path
Goal
116
Summary
- Small set of constructions and schemas
- Composed in different ways
- Unification produces specification of parameters
of simulation - Sentence understanding is simulation
- Different meanings different simulations
117
Concluding Remarks
- Complexity
- Simulation
118
Concluding Remarks
- Complexity
- Simulation
- Language understanding is simulation
- Simulation involves activation of conceptual
structures - Simulation specifications should include
- which conceptual structures to activate
- how these structures should be activated
119
Extra slides follow
120
Prototypes and extensions?
- CauseMotion Path
- He threw the ball across the room
- He kicked the ball over the table
- He sneezed the napkin off the table
- He coughed the water out of his lungs
121
Key points
- In prototypical verb-argument structure
construction combinations, verb meaning is very
similar to argument structure meaning. - Verbs whose meaning partially overlaps that of a
given argument structure constructions may also
co-occur with that argument structure
construction - These less prototypical combinations may motivate
extensions to the central argument structure
constructions