Cervical Spine - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 60
Title:
Cervical Spine
Description:
A change in sensation, such as numbness or tingling. *Evidence of a broken bone on X-Rays ... Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response (BAER) Subdural Hematoma on MRI ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:112
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cervical Spine
1
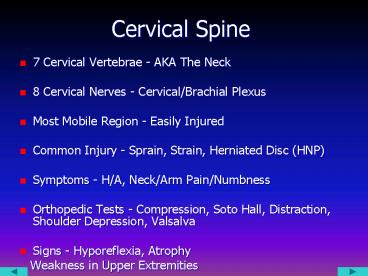
Cervical Spine
- 7 Cervical Vertebrae - AKA The Neck
- 8 Cervical Nerves - Cervical/Brachial Plexus
- Most Mobile Region - Easily Injured
- Common Injury - Sprain, Strain, Herniated Disc
(HNP) - Symptoms - H/A, Neck/Arm Pain/Numbness
- Orthopedic Tests - Compression, Soto Hall,
Distraction, Shoulder Depression, Valsalva - Signs - Hyporeflexia, Atrophy
- Weakness in Upper Extremities
2
SPINAL ANATOMY
3
(No Transcript)
4
Thoracic Spine
- 12 Thoracic Vertebrae - AKA Dorsal Spine
- 12 Thoracic Nerves - Between the Ribs
- Least Mobile Region - Less Injured
- Injuries - Dorsalgia, Fx Ribs
- Orthopedic Tests None
- Signs - Fx on X-Ray,
- Bruised Sternum, Dyspnea
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Lumbar Sacral Spine
- 5 Lumbar Vertebrae, 5 Fused Sacral Vert. - The
Low Back - 5 Lumbar Nerves - Lumbar Plexus
- 5 Sacral Nerves - Sacral Plexus
- Weight Bearing - Easily Injured
- Common Injury - HNP, Sprain Strain
- Symptoms - LBP, Sciatica
- Signs - Hyporeflexia, Atrophy
- Weakness in Lower Extremities
- Orthopedic Tests - SLR, WLR, Kemps, Elys
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
Diagnostic Testing
- X-RAY
- MRI
- EMG/NCV
11
X-Rays
- Rule Out
- Fractures
- Dislocations
- Osteoarthritis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Bone Tumors
- Infections
12
Fractures
- A pop or snap felt or heard at the time of the
injury. - Mild to severe pain
- Severe swelling and bruising (often, but not
always). - An unstable joint (feels wobbly or loose).
- A grating sound or feeling.
- A bulge (sometimes) at the site of a complete
tear. - A change in sensation, such as numbness or
tingling. - Evidence of a broken bone on X-Rays
13
Normal Cervical Spine X-Ray
14
C6-C7 Vertebral Dislocation
15
C2-C3 Fracture/Dislocation
16
Skull Fracture X-Ray
17
Normal Elbow (X-Ray)
18
Fractured Humerus (X-Ray)
19
OA at L2-L3 (Deg Disc Disease)
20
Lumbar Spine Compression Fxs
21
Fibula Fracture X-Ray
22
Tibia Fibular Fracture
23
Pelvic Fracture X-Ray
24
Patella Fracture/Dislocation X-Ray
The patella should be here
25
Finger Dislocation X-Ray
26
(No Transcript)
27
MRI
- Herniated Disc (HNP)
- Posterior
- Anterior
- Lateral
- Bulging Disc
- Clinical Significance ?
- Spinal Stenosis
- Foraminal Stenosis
- Surgery Required
- Pre-Existing
- Sequestered (Prolapsed)
- Surgery Required
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
Cervical Herniated Disc (MRI)
36
Lumbar Herniated Disc (MRI)
37
Cervical Spinal Stenosis (MRI)
38
Thoracic Spine Compression Fx MRI
39
EMG (Electromyography)
- Needle Insertion
- Diagnosis of Myopathy
- Diagnosis of Radiculopathy
- Symptom Muscle Weakness
- Sign Atrophy
- Silent at Rest Normal
- Fibrillations/Fasiculations at rest Pathology
40
(No Transcript)
41
Electromyography Trace (EMG)
42
Normal EMG (Insertional Activity)
43
Orbicularis Oculi Fasiculation
44
Deltoid Muscle Fibrillation
45
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV)
46
(No Transcript)
47
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
48
Soft Tissue Injuries Due to MVA
- Cervical Spine Sprain/Strain Whiplash
- Thoracic Spine Sprain/Strain Dorsalgia
- Lumbar Spine Sprain/Strain Lumbalgia
- Shoulder Sprain/Strain
- Knee Sprain/Strain
- Wrist Sprain/Strain
49
(No Transcript)
50
(No Transcript)
51
(No Transcript)
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
Both open and closed head injuries may result
in A concussion.
A brain bruise
(contusion). If the injury was caused by a strong
force, a brain
contusion or bleeding within or around the brain
may occur. Bleeding
within or around the brain, which can be a
life-threatening
injury. Initial symptoms of this type of injury
may be the same as
those of a concussion. More serious symptoms
usually develop
within 24 hours after the injury. In rare cases,
if the bleeding is slow,
symptoms will take longer to develop. Dx
Testing Skull X-Ray to R/O Fracture CT or MRI
to R/O Subdural Hematoma If Positive Craniotomy
(Surgery) to Evacuate Hematoma
55
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response (BAER)
56
Subdural Hematoma on MRI
57
Indisputable Signs of Traumatic Injuries
- Fracture on X-Ray, MRI or CT scan
- Dislocation on X-Ray, MRI or CT scan
- Abnormal Reflexes
- Hyporeflexia
- Hypereflexia
- Positive Babinsky
- Muscular Atrophy
- Severe Swelling and Ecchymosis (Bruising)
- Severe Lacerations
- If none of the above are present, it is a
soft-tissue injury
58
P M R Opinion on EMG/NCV/SSEP
- According to the recommendations published by
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of
North America May 1998, the strict indications
for neurodiagnostic studies ordered in patients
with less than 8 weeks of treatment were fever,
chills, weight loss, tumor, infection, high
energy trauma, cauda equina syndrome, severe
motor deficit, long tract signs, or progressive
neurologic loss.
59
Thank you for your attention!
- We hope this presentation was educational.
- You may access this information on our web site
www.arrowclaims.com beginning in November of 2002.
60
Arrow Claims Services , Inc.
Straight to the point IMEs Peers