OctNov 2003 Superstorms PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 3
Title: OctNov 2003 Superstorms
1
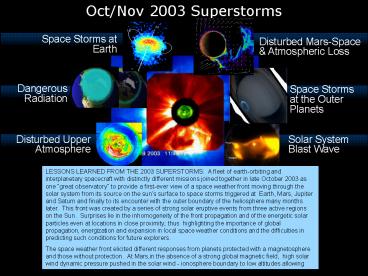
Oct/Nov 2003 Superstorms
Space Storms at Earth
Disturbed Mars-Space Atmospheric Loss
Dangerous Radiation
Space Storms at the Outer Planets
Disturbed Upper Atmosphere
Solar System Blast Wave
LESSONS LEARNED FROM THE 2003 SUPERSTORMS A
fleet of earth-orbiting and interplanetary
spacecraft with distinctly different missions
joined together in late October 2003 as one
great observatory to provide a first-ever view
of a space weather front moving through the solar
system from its source on the suns surface to
space storms triggered at Earth, Mars, Jupiter
and Saturn and finally to its encounter with the
outer boundary of the heliosphere many months
later. This front was created by a series of
strong solar eruptive events from three active
regions on the Sun. Surprises lie in the
inhomogeneity of the front propagation and of the
energetic solar particles even at locations in
close proximity thus highlighting the
importance of global propagation, energization
and expansion in local space weather conditions
and the difficulties in predicting such
conditions for future explorers. The space
weather front elicited different responses from
planets protected with a magnetosphere and those
without protection. At Mars,in the absence of a
strong global magnetic field, high solar wind
dynamic pressure pushed in the solar wind -
ionosphere boundary to low altitudes allowing
2
solar wind electromagnetic fields to strip away
and carry off oxygen ions in a replay of
processes that may have produced significant
water loss over the course of solar system
history. High levels of solar energetic
particles, caused failure of the XXX instrument
on Mars Global Surveyor designed to measure this
radiation. A complex arrangement of remnant
magnetic fields in the rocks on Mars will make
the local radiation environment challenging to
predict. On Earth, within the protection of a
strong magnetic field, these same dynamic
pressures and associated southward interplanetary
magnetic field disrupted the shielding currents
in the inner magnetosphere and allowed solar wind
electric fields to penetrate all the way to the
equator, lifting up and redistributing
ionospheric plasma in a strong equatorial
fountain, while allowing dense plumes of plasma
to be drawn from mid-latitudes up over the polar
cap. The coupling between geospace conditions,
and midlatitude electrodynamics is a major
frontier area in space science research where new
discoveries are being made based on superstorm
observations. The severe southward interplanetary
magnetic fields in the space weather front joined
the Earths field to the Suns for a time,
opening the polar cap and pushing its boundary to
mid-latitudes. High energy solar particles
penetrated freely into the Earths atmosphere
along the open field lines in the expanded polar
cap forcing the astronauts to take shelter on the
space station and airline flights to be rerouted.
These high energy particles combined with the
energy inputs from the auroral storms to increase
the nitric oxide in the upper atmosphere,
accelerating the cooling of the storm-heated
atmosphere but ultimately disrupting
stratospheric ozone distributions at lower
altitudes, possibly for months. These new
observations from the superstorms highlight one
of the potential pathways for coupling between
space weather and terrestrial climate, which are
normally difficult to identify against a highly
variable background signal of tides, planetary
and gravity waves, propagating upward from the
dense lower atmosphere. As the space weather
front moved over Jupiter and Saturn, radio
signals revealed a sharp rise in the energetic
particles trapped in their magnetic fields. In
these rapidly rotating magnetospheres,
accumulated evidence indicates that auroral
storms are driven largely by internal forces
associated with the rotation or with plasma loss
from certain moons. Recent observations indicate
that strong dynamic pressure fronts in the solar
wind can produce new auroral features though
instruments were not in place to document these
during the superstorms. A better understanding
of magnetospheric dynamics at the giant planets
triggered by solar wind shock fronts awaits
future coordinated observations. Need paragraph
here on propagation out to heliospheric boundary
.. Coordinated global observations , like
these, are an important national need for space
research. Without such observation sets, our
understanding of the processes governing the
large-scale interaction between the sun and
planetary environments in our solar system
(including Earth) will remain limited,
restricting the range of useful prediction needed
for scientific progress, as well as for
protection of space assets and for human
exploration beyond Earth. The information
available from the superstorms will help define
requirements for future missions and coordination
between mission and lay the foundation for new
discoveries in sun-Earth system science as well
as in comparative planetary environments.
3
Comprehensive observations , like these, are an
important new direction for space research.
Without such observation sets, our understanding
of the processes governing the global interaction
between the sun and planetary environments in our
solar system (including Earth) will remain
limited, restricting the range of useful
prediction needed for scientific progress, as
well as for protection of space assets and for
human exploration beyond Earth. The information
available from the superstorms will help define
needs for future missions and coordination
between mission and lay the foundation for new
discoveries in sun-Earth system science as well
as in comparative planetary environments.