BACTERIA - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
BACTERIA
Description:
live in hot springs, can survive in pH of 2 and temp of 230o F. Domain Eubacteria ... bacilli-rod shaped. spirilla-spiral. Classification of Bacteria ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:23
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BACTERIA
1
BACTERIA
2
Classification of Monera
3
Archaea
- These prokaryotes are classified separately due
to unusual lipids in their cell membranes - Their cell walls do not contain the compound
peptidoglycan (protein carbohydrate compound)
found in eubacteria. - Heterotrophs Autotrophs - often
chemiautotrophic - ancestors of eukaryotes and chloroplasts
Thermoacidophile
4
Types of Archaea
- Methanogens
- create methane,
- live in sewage and animal intestines (cows)
- Halophiles
- live in Great Salt Lake and Dead Sea, salt
lovers, - use salt to make ATP
- Thermoacidophiles
- live in hot springs,
- can survive in pH of 2 and temp of 230o F
5
Domain Eubacteria
- most successful group by numbers, mass, and
habitats - ancestors of mitochondria
6
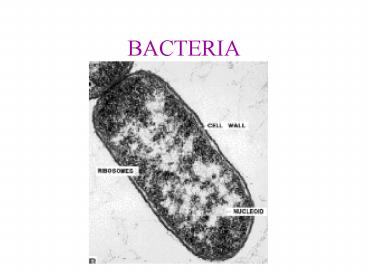
Bacteria Structure
- DNA Plasmids
- Cytoplasm Ribosomes
- Cell Membrane
- Peptidoglycan cell wall
- Capsule
- Pili
7
(No Transcript)
8
Cell Wall (Gram staining technique)
- Gram Positive ()
- has a thick peptidoglycan cell wall surrounding
plasma membrane - Gram Negative(-)
- has thin peptidoglycan cell wall around plasma
membrane - AND an outer membrane (lipid - lipopolysaccharide
) layer around that
9
(No Transcript)
10
Classification of Bacteria
- By shape and number
- cocci-spherical
- bacilli-rod shaped
- spirilla-spiral
11
(No Transcript)
12
Classification of Bacteria
- Characteristic Groups
- diplo-pairs (diplococcus)
- staphylo-clusters (staphylococcus)
- strepto-chains (streptobacillus)
13
Classification of Bacteria
- Methods of obtaining energy
- AUTOTROPHS
- a) Photosynthetic Bacteria
- all use suns energy
- classified by pigments
- cyanobacteria, green and purple sulfur bacteria
- b) Chemoautotrophic Bacteria
- remove high energy electrons from inorganic
compounds (NH4, CH4, H2S) - some cause nitrification (NH3 to NO3 form
usable by plants) - HETEROTROPHS
- largest group of decomposers
- include nitrogen fixers (N2 to NO3)
14
Classification of Bacteria
- Types of Locomotion
- sliding over slimy surfaces
- twisting through fluid
- propelling with flagella
- non-motile
15
Classification of Bacteria
- By adaptation
- -endospore
- -toxin
16
Bacteria Reproduction
- Cell Division
- Binary fission one cell pinches into two cells
- Asexual Reproduction
- Conjugation
- hollow pili grow from one bacteria to another
then plasmids are passed - Sexual Reproduction
17
Kingdom Eubacteria
- Phylum Cyanobacteria (Anabaena)
- bacilli and cocci
- gram negative
- aerobic, photosynthetic, autotrophic
- Phylum Spirochetes (Treponema pallidum-causes
syphilis) - spirilla
- gram negative
- aerobic and anaeobic, heterotrophic
- Phylum Proteobacteria (Escherichia coli)
- all three shapes
- gram negative
- anaerobic and aerobic, heterotrophic and
autotrophic
18
Phylum Cyanobacteria
- bacilli and cocci
- gram negative
- aerobic, photosynthetic, autotrophic
19
Helpful bacteriaE. coli in our intestines
helps with digestionoil eaterssewage
eatersmakers of yogurt, cheese, sour cream,
etc.makers of beer and winedecomposers recycle
nutrients of dead matternitrogen fixers recycle
nitrogencopper miners help get copper from the
grounddrug makers (insulin)