Potentiometric Methods PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title: Potentiometric Methods
1
- Potentiometric Methods
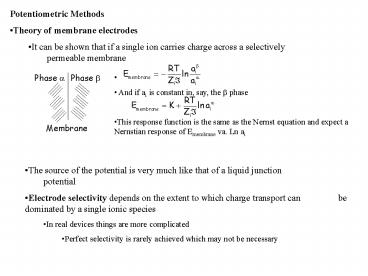
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- It can be shown that if a single ion carries
charge across a selectively permeable membrane
- And if ai is constant in, say, the b phase
- This response function is the same as the Nernst
equation and expect a Nernstian response of
Emembrane va. Ln ai
- The source of the potential is very much like
that of a liquid junction potential - Electrode selectivity depends on the extent to
which charge transport can be dominated by a
single ionic species - In real devices things are more complicated
- Perfect selectivity is rarely achieved which may
not be necessary
2
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Glass electrodes
- Glass membrane sealed to the end of another
material - 100 - 500 mm thick
- Inside the bulb is a Ag/AgCl electrode
- Cell AgAgCl(sat.), HCl(0.1M)
KCl(sat.), Hg2Cl2Hg - internal ref
external ref - glass electrode
(const. E)
Glass Memb.
Test Soln
- Cross section of membrane system
- Charge transport in dry glass is Na or other
alkali metal ion - The hydrated layers consist of a silicate
polymer that has an affinity for a particular
ion or ions - Serve as an ion exchanger
- Produce a charge separation as is in a liquid
junction
3
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Glass electrodes
- At the a - m or b - m interface there exists an
adsorption equilibrium
- At the m - m, m - m, similar kinds of
equilibria involving Na - The total potential across the membrane is
- EmembEbm Emm Emm Ema
- Ebm and Ema result from a selective charge
exchange across the respective interfaces - For H, the Donnan equilibrium occurs HGl
H Gl - Resulting in the Donnan boundary potential
- Eisenman has shown
4
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Glass electrodes
5
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Glass electrodes
- Emembrane is responsive to both H and Na
- If is small, the response is
only to H - Other types of electrodes
- Cations
- If the electrode is connected to the negative
terminal of the voltmeter, one observes an
increase in Ecell with pM
6
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Other types of electrodes
- Anions
- Inherent error in potentiometric measurements of
activity - Assume K is constant from the analytical
solutions to the analytical solutions - But this is not true as the electrolyte
concentration not the same - Junction potentials contained in K change because
of changes in electrolyte concentrations - Ecell Ethermo ELJ EIR
- The uncertainty in Ecell is at least ? 0.001 V
7
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Inherent error in potentiometric measurements of
activity
- Example for a solution whose pH is 4.00,
H1.00 x 10-4 - 4Zi 0.04 so H could be 1.04 x 10-4 or pH
3.98 or - H could be 0.96 x 10-4
or pH 1.02 - Thus the pH is in the range of 4.00 ? 0.02 this
uncertainty cannot be
eliminated
8
- Potentiometric Methods
- Theory of membrane electrodes
- Other errors associated with glass electrodes
- Alkaline error at pH gt 9 or 10, glasses become
sensitive to Na - Must take into account
- This is given as a nomograph in the box with the
electrode - The result is a negative error in pH the pH is
less than measured - Acid error at very low pH (around 0 or 1, or
less) a positive error is observe - The origin of this error is not understood
- ISEs measure activity, not concentration
- Since activity coefficients change with ionic
strength, this must be taken into account - Standard Additions method (for cations)
- Solve these two equations for K and M
- Titration curves see Skoog, West and Holler for
an example including how to calculate the
discrete 1st and 2nd derivative curves