16.360 Lecture 3 PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: 16.360 Lecture 3
1
16.360 Lecture 3
Last lecture
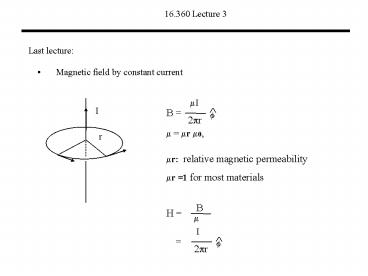
- Magnetic field by constant current
? ?r ?0,
?r relative magnetic permeability
?r 1 for most materials
2
16.360 Lecture 3
Last lecture
- Traveling wave
y(x,t) Acos(2?t/T-2?x/?),
y(x,t) Acos?(x,t),
?(x,t) 2?t/T-2?x/?,
3
16.360 Lecture 3
Last lecture
- Traveling wave
y(x,t) Acos(2?t/T2?x/?),
Velocity 0.6?/0.6T ?/T
Phase velocity
Vp dx/dt - ?/T
4
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor
VR(t)
Vs(t) V0Sin(?t?0),
VR(t) i(t)R,
Vs(t) VR(t) VC(t),
V0Sin(?t?0)
i(t)dt/C i(t)R,
Integral equation,
Using phasor to solve integral and differential
equations
5
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor
Vs(t) V0Sin(?t?0)
j(?0 - ?/2)
)
Re(V0 e
6
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor
1
),
Re(I
j?
time domain equation
V0Sin(?t?0)
i(t)dt/C i(t)R,
phasor domain equation
7
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor domain
V
I R
,
I
R 1/(j?C)
,
R 1/(j?C)
Back to time domain
j?t
Re (
e
)
R 1/(j?C)
8
16.360 Lecture 3
- An Example
VR(t)
Vs(t) V0Sin(?t?0),
VR(t) i(t)R,
Vs(t)
VL(t)
i (t)
Ldi(t)/dt,
VL(t)
Vs(t) VR(t) VL(t),
V0Sin(?t?0)
Ldi(t)/dt i(t)R,
differential equation,
Using phasor to solve the differential equation.
9
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor
j?t
di(t)/dt
Re(d I e
)/dt
j?
),
Re(I
time domain equation
V0Sin(?t?0)
Ldi(t)/dt i(t)R,
phasor domain equation
j?
)L
Re(I
10
16.360 Lecture 3
- Phasor domain
I R
j?L
V
I
,
I
R (j?L)
,
R j?L)
Back to time domain
j?t
Re (
e
)
R (j?L)
11
16.360 Lecture 3
- Steps of transferring integral or differential
equations to linear - equations using phasor.
- Express time-dependent variables as phsaor.
- Rewrite integral or differential equations in
phasor domain. - Solve phasor domain equations
- Change phasors variable to their time domain value
12
16.360 Lecture 3
- Electromagnetic spectrum.
Recall relation ?f v.
- Some important wavelength ranges
- Fiber optical communication ? 1.3 1.5?m.
- Free space communication 700nm 980nm.
- TV broadcasting and cellular phone 300MHz
3GHz. - Radar and remote sensing 30GHz 300GHz
13
16.360 Lecture 3
- Transmission lines
- Transmission line parameters, equations
- Wave propagations
- Lossless line, standing wave and reflection
coefficient - Input impedence
- Special cases of lossless line
- Power flow
- Smith chart
- Impedence matching
- Transients on transmission lines
14
16.360 Lecture 3
- Today
- Transmission line parameters, equations
B
A
VBB(t)
Vg(t)
VAA(t)
L
A
B
VAA(t) Vg(t) V0cos(?t),
Low frequency circuits
VBB(t) VAA(t)
Approximate result
VBB(t) VAA(t-td) VAA(t-L/c)
V0cos(?(t-L/c)),
15
16.360 Lecture 3
- Transmission line parameters, equations
Recall ??c, and ? 2??
VBB(t) VAA(t-td) VAA(t-L/c)
V0cos(?(t-L/c)) V0cos(?t- 2?L/?),
If ?gtgtL, VBB(t) ? V0cos(?t) VAA(t),
If ?lt L, VBB(t) ?VAA(t), the circuit theory
has to be replaced.
16
16.360 Lecture 3
- Next lecture
- Types of transmission lines
- Lumped-element model
- Transmission line equations
- Wave propagation
17
(No Transcript)