Taxonomic Classification PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Taxonomic Classification
1
(No Transcript)
2
Taxonomic Classification
- Domain Eukarya (Cells have true nuclei)
- Kingdom Mycetae (Fungae) ie. Fungi
- Phylum
- Zygomycota
- Ascomycota
- Basidiomycota
- Deutermycota (Anamorphs)
Teleomorphs and Anamorphs
Teleomorphs sexual form (perfect
state) Anamorphs asexual form (imperfect
state)
3
Summary of Fungal Characteristics
Phylum Sexual
Asexual Growth Common name Propagules
Propagules Characterics Zygomycota
Zygospores Sporangia Molds,
Non- bread molds
Sporangiospores septate hyphae
Ascospores
Septate hyphae Ascomycota Cleistothecia
Conidia Yeast, Molds sac fungi
Dimorphic
Septate hyphae Basidiomycota
Basidiospore Conidia Yeast,
Mush- club fungi rooms, Smuts,
Deutermycota Septate hyphae fungi
imperfecti None Conidia
Yeast, Molds black fungi (anamorphs)
Dimorphic
4
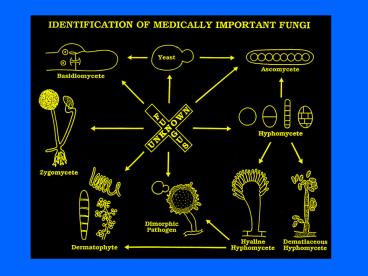
Deuteromycetes
5
(No Transcript)
6
Refer also to tables 19-3 19-4 , pg 986, 987
7
Taxonomic Classification
- Characteristics of Zygomycota
- Reproduce sexually (teleomorphic form) by
zygospores - Reproduce asexually (anamorphic form) by
sporangiospores that develop within a sporangium - Possess hyphae that rarely produce septae
(partially or non-septate or coenocytic) - Uncommon cause of human mycoses
- Mostly environmental saprophytes (e.g. bread
molds)
8
Taxonomic Classification
- Characteristics of Zygomycota
- Mostly opportunistic pathogens
- Clinical infection known as zygomycosis
(singular) or zygomycoses (plural)
9
489
Non- Septate Hyphae
Sporangium of a Zygomycete (Asexual
Spore)
10
006
Zygospores of Zygomycetes (Sexual Spore)
Nonseptate Hyphae
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.