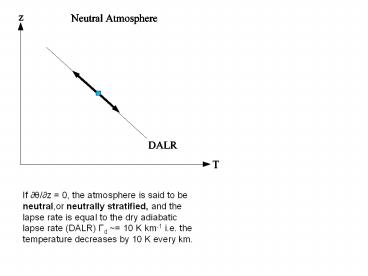
If ??/?z = 0, the atmosphere is said to be neutral,or neutrally stratified, and the lapse rate is equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) Gd ~= 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature decreases by 10 K every km. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
If ??/?z = 0, the atmosphere is said to be neutral,or neutrally stratified, and the lapse rate is equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) Gd ~= 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature decreases by 10 K every km.
Description:
If ?/z = 0, the atmosphere is said to be neutral,or neutrally stratified, and ... to the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) Gd ~= 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: If ??/?z = 0, the atmosphere is said to be neutral,or neutrally stratified, and the lapse rate is equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) Gd ~= 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature decreases by 10 K every km.
1
If ??/?z 0, the atmosphere is said to be
neutral,or neutrally stratified, and the lapse
rate is equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate
(DALR) Gd 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature
decreases by 10 K every km.
2
If ??/?z gt 0, i.e. ? increases with height, the
atmosphere is said to be stable, statically
stable, or stably stratified. If an air parcel is
moved upwards adiabatically, it will follow the
DALR, so be colder (therefore denser) than its
environment and so sink back down. Conversely if
an air parcel is moved downwards adiabatically,
it will follow the DALR, so be warmer (therefore
less dense) than its environment and so rise back
up. In other word, the atmosphere is stable to
small perturbations.
3
If ??/?z lt 0, i.e. ? decreases with height, the
atmosphere is said to be unstable, statically
unstable, or unstably stratified. If an air
parcel is moved upwards adiabatically, it will
follow the DALR, be warmer (less dense) than its
environment and so keep on rising. Conversely if
an air parcel is moved downwards adiabatically,
it will follow the DALR, so be cooler (therefore
denser) than its surroundings and so carry on
sinking. In other word, the atmosphere is
unstable to small perturbations.
4
If ??/?z 0, the atmosphere is said to be
neutral,or neutrally stratified, and the lapse
rate is equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate
(DALR) Gd 10 K km-1 i.e. the temperature
decreases by 10 K every km.
If ??/?z gt 0, i.e. ? increases with height, the
atmosphere is said to be stable, statically
stable, or stably stratified.
If ??/?z lt 0, i.e. ? decreases with height, the
atmosphere is said to be unstable, statically
unstable, or unstably stratified.
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
The lines are isotherms (lines of constant
temperature) and isobars (lines of constant
pressure)
11
plus isentropes (lines of constant potential
temperature), also known as dry adiabats.
12
plus saturated adiabatics (lines of constant
equivalent potential temperature).
13
plus lines of constant mixing ratio r mass of
water vapour/mass of dry air (usually written in
g/kg)
14
Plus the international standard atmosphere.
15
Plus a radiosonde sounding from Arizona, wind
barbs are shown on the right, each full barb is
10 knots.