Models of Memory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Models of Memory
Description:
All the brain structures identified here have been implicated in efforts to ... Formation of amyloid plaques. Abnormal protein that deposits in prefrontal cortex ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:39
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Models of Memory
1
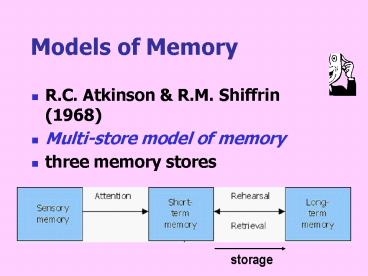
Models of Memory
- R.C. Atkinson R.M. Shiffrin (1968)
- Multi-store model of memory
- three memory stores
storage
2
short-term memory
long-term memory
Fig 7.25 The anatomy of memory. All the brain
structures identified here have been implicated
in efforts to discover the anatomical structures
involved in memory. Although its exact
contribution to memory remains the subject of
considerable debate, the hippocampus is thought
to play an especially central role in memory.
3
Models of Memory
- Sensory memory
- iconic - visual (.5-1 sec.)
- echoic - auditory (4-5 sec.)
- Short-term (working) memory
- capacity 7 2 items
- duration 20 sec. without rehearsal
- serial position effect (primacy and recency)
- chunking to improve capacity
- location prefrontal cortex
4
Chunking
- GEX
- FOL
- MUN
- BEP
- RAJ
- TEV
- KIG
- PET
- TUG
- KEY
- MAP
- LEG
- SEE
- WIN
- FBI
- CBS
- MCI
- CIA
- MTC
- CNN
- PTA
5
Models of Memory
- Long-term memory
- unlimited capacity lifetime duration
- three processes of LTM
- consolidation
- storage
- retrieval
- location hippocampus, amygdala
- Types of long-term memory
- declarative (explicit) vs. procedural (implicit)
- declarative can be semantic or episodic
6
Models of Memory
- F. Craik and R. Lockhart (1972)
- Levels of processing approach
- not a where but a how
- shallow vs. deep processing
- maintenance vs. elaborative rehearsal
- examples of elaborative rehearsal
- generation effect
- self-reference effect
7
Information Loss
- Interference
- proactive and retroactive
- Amnesia
- retrograde and anterograde
- Partial retrieval
- tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon (TOT)
- False retrieval
- Loftus research on memory
- influence of wording
8
Fig 7.26 Retrograde versus anterograde amnesia.
In retrograde amnesia, memory for events that
occurred prior to the onset of amnesia is lost.
In anterograde amnesia, memory for events that
occur subsequent to the onset of amnesia suffers.
9
Alzheimers Disease
- Symptoms
- Memory loss confusion
- Brain abnormalities
- Formation of amyloid plaques
- Abnormal protein that deposits in prefrontal
cortex - Formation of neurofibrillary tangles
- Abnormal tangling of proteins within neurons
- Begins in entorhinal cortex (base of frontal lobe)
10
Progression of Alzheimers Disease