system PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: system
1
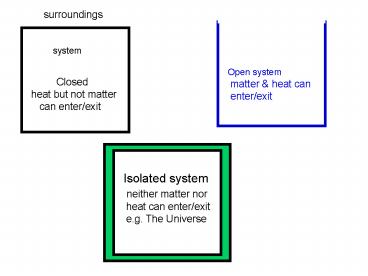
surroundings
system
Closed heat but not matter can
enter/exit
2
The 1st Law of Thermodynamics The energy of the
universe is constant DEuniv
0
Heat (q)
Work (w)
DEsys q w
surroundings
Heat (q) and work (w) are the means of
transferring energy to/from a system.
3
Potential Energy - unrealized energy due to
position in force field, e.g. gravity,
charge
Kinetic Energy energy due to motion of object
½mv2
4
Specific Heat (see page 461) The amount of heat
that must be added to a substance to raise the
T by 1ºC. units cal g-1 ºC-1 symbol c.
q m c DT
Alternate form called heat capacity CP ( cal
mol-1 ºC-1)
The Hope Diamond weighs 9.10 g. How much heat
would be required change the T From 20.0ºC to
100.ºC?
5
A Calorimeter measures q.
qCu qH2O qcal
Cu 0.092 cal g-1 K-1 H2O 1.00 cal g-1 K-1
(150 g) Ccal ????? Ti 17.0 C Tf
19.2 C
23.0 cal ºC-1
If the Hope diamond is boiled and placed in this
same calorimeter, what is Tf?
6
Thermochemical Equations ..
CH4 2O2 ? CO2 2H2O ???
energy
heat
What else does this reaction produce?
What form does this energy take?
Where does this energy come from?
Standard conditions P 1atm T
25C Enthalpy (H) qP or DHrx (Internal Energy
(E) qV)
CH4 2O2 ? CO2 2H2O 890 kJ mol-1
or
DHrx -890 kJ mol-1
exothermic heat is a product DHrx lt 0
endothermic heat is a reactant DHrx gt 0
Thermochemical equations and stoichiometry How
much heat is produced by the combustion of 47g of
CH4?
7
DHrx qrx/mol A J mol-1 or kJ mol-1
qrx qH2O qcal
A calorimeter can be used to determine the heat
given off by a chemical reaction or DHrx.
A B ? C D qP
What happens to Twater if reaction is exothermic?
8
Standard Heat of Formation DH?f DHrx for the
formation of a compound from its elements as
they would exist in their standard state 1 atm
25?C. DH?f lt 0 if the reaction is exothermic
and gt 0 if endothermic.
Elements in standard states (DHºf 0) solid
nonmetals Cgr (graphite) Si, P, S,
I2 Gases H2, N2, O2, Cl2, F2, etc. Solid metals
most Liquid metals Hg, Ga,
Formation of . CH4 NH3 SO2 C2H6O
Cgr O2 ? CO2 393.5 kJ mol-1
DH?f - 393.5 kJ mol-1
9
Cgr ½O2 ? CO ??? kJ mol-1
Why cant DH?f be measured for this reaction in a
bomb calorimeter?
Hess Law The heat of a reaction is the sum of
the heats of formation of all the products
minus the heats of formation of all the
reactants. or .. DHrx Si ni DHf,i (products)
- Si ni DHºf.i (reactants)
where ni is the stoiciometric coefficient
CO ½O2 ? CO2 DHºrx DHºf,CO2 - DHºf,CO2 -
½DHºf,O2
10
Reactions for which DH can be measured in
calorimeter
CO ½O2 ? CO2 DHrx -283.0 kJ mol-1
C(gr) O2 ? CO2 DHf -393.5 kJ
mol-1
Since O2 is the standard state for oxygen then
DHf 0 This is true for any element in its
standard state, e.g. C(gr)
Cgr ½O2 ? CO DHf ??? kJ mol-1
Hess Law DHrx (CO ? CO2) DHf (CO2) -
DHf (CO) - ½DHf (O2) -283.0
-393.5 - x - 0
x -393.5 (-283.0) 0 -110.5 kJ mol-1
see appendix K
32 page 595
11
CH4 2O2 ? CO2 2H2O DHrx -890
kJ mol-1
4 C-H 2 OO ? 2 CO 4 O-H
DHrx Sum of reactant bond energies Sum of
Product bond energies
Not as accurate as Thermodynamic tables
because C-H bonds (etc.) not the same in all
compounds
12
Spontaneous Merriam-Webster
1 proceeding from natural feeling or native
tendency without external constraint 2 arising
from a momentary impulse 3 controlled and
directed internally SELF-ACTING 4 produced
without being planted or without human labor
INDIGENOUS 5 developing or occurring without
apparent external influence, force, cause, or
treatment 6 not apparently contrived or
manipulated
Will Na2CO3 dissolve in hexane?
Will Na2CO3 dissolve in water?
Will water flow downhill?
Will it happen?
13
Spontaneity Factors
- Reduce Enthalpy (H)
- (release heat)
- (form bonds that are stronger than the ones
broken) - (processes for which DH is (-) are favored.)
- Increase Entropy (S)
- (make a system more disordered)
Entropy (S) is the thermodynamic function that
indicates the degree of disorder inherent in a
system.
14
1st Law of Thermodynamics The Energy of the
Universe is constant. DEsys DEsurr
constant DEsys q w
2nd Law of Thermodynamics The Entropy of the
Universe is increasing. DSsys DSsurr gt 0
15
As ice ? water the DSsys? but DSsurr?. The 2nd
Law says that DSsys DSsurr gt 0. The process is
spontaneous if T is gt Tnmp
water
As water ? ice the DSsys? but DSsurr?. The
process is spontaneous, DSsys DSsurr gt 0,
only if Tsurr lt Tnmp, in which case the
increased order of ice is compensated by
decreased order of surr.
16
3rd Law of Thermodynamics The Entropy of a pure
substance is 0 at 0K. A substance will be
perfectly ordered at 0K.
As T?, the substance will have increased motion
which means it has increased disorder and S?.
Data regarding the heat capacity can be used to
determine the entropy that a substance will have
at standard T (298K). This allows values of
standard entropies to be added to tables of
standard enthalpies of formation.
17
Enthalpy of Reaction
DHrx S n DHf,products S n DHf,reactants
Entropy of Reaction
DSrx S n Sproducts S n Sreactants
CH4(g) 2O2(g) ? CO2(g) 2H2O(l)
DHrx -890 kJ mol-1
Predict the sign of DSrx
Calculate the value of DSrx
18
Spontaneity Factors
DG DH - TDS
- Reduce Enthalpy (H)
- (release heat)
- (form bonds that are stronger than the ones
broken) - (processes for which DH is (-) are favored.)
- Increase Entropy (S)
- (make a system more disordered)
Problem stronger bonds usually make molecules
more ordered! So H S often oppose each other.
3. Decrease Free Energy (G) A combination of
enthalpy (H) and entropy (S) effects.
19
DG DH - TDS
DG is the indicator of spontaneity for a chemical
process.
Will a chemical reaction or physical change occur?
If DG lt 0 (-) yes The products will increase
and reactants will decrease
If DG 0 the system is at equilibrium There
will be no change in reactants or products
If DG gt 0 () no The reaction will proceed in
the opposite direction as written The reactants
will increase and products will decrease
20
DG DH - TDS
CH4(g) 2O2(g) ? CO2(g) 2H2O(l)
DHrx -890 kJ mol-1 DSrx -243 J
mol-1 K-1
DGrx -890 298 (-0.243) -818 kJ mol-1
Which factor, enthalpy or entropy dominates
spontaneity? The heat released however, will
disorder the surroundings so the 2nd law is
upheld!
DGrx S n DGf,products S n DGf,reactants
-394.4 (-237.2) (-50.75) -2(0) -818 kJ
mol-1
21
DG DH - TDS
Temperature Trends for chemical and physical
processes
?T favors disorder As T? then entropy change
becomes a greater factor in determining
spontaneity.
Phase changes solid ? liquid ? gas Weaker
bonding with more disorder favored as T?. In
solid bond formation wins out over disorder. In
gas, disorder wins out over bond formation.
22
DG DH - TDS
CH4(g) 2O2(g) ? CO2(g) 2H2O(l)
DHrx -890 kJ mol-1 DSrx -243 J
mol-1 K-1
DGrx -890 298 (-0.243) -818 kJ mol-1
Entropy favors reactants so as T? DGrx will go
down.