why good interface design? - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
why good interface design?
Description:
allows people to learn by using the system. allows the design to suggest the correct process model ... source: Andy Cockburn University of Canterbury NZ ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:21
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: why good interface design?
1
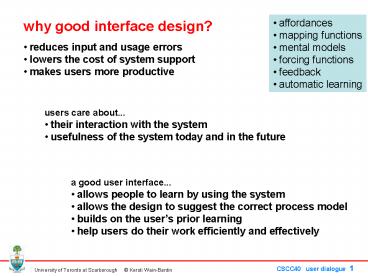
why good interface design?
- affordances
- mapping functions
- mental models
- forcing functions
- feedback
- automatic learning
- reduces input and usage errors
- lowers the cost of system support
- makes users more productive
- users care about...
- their interaction with the system
- usefulness of the system today and in the future
- a good user interface...
- allows people to learn by using the system
- allows the design to suggest the correct process
model - builds on the users prior learning
- help users do their work efficiently and
effectively
2
interface (input and output) design is an
iterative process
design
- inputs to interface design
- understanding of the users
- best-practice considerations
- evaluation with the users
- evaluation without the users
- user involvement
- task analysis
- storyboards
- dialogue charts
- prototyping
- etc.
source Andy Cockburn University of Canterbury NZ
3
design problems
- avoid design inertia - dont let early
- bad design decisions stay bad
- correctly distinguish between problems
- and symptoms in the user domain
- its hard for users to communicate problems
- designers are uniquely unqualified to evaluate
- their own designs
- its not easy to distinguish between the
- designers model and the users model
source Andy Cockburn University of Canterbury NZ
4
design opportunities
- to get a good idea, get lots of ideas
- delay commitment
- try one or more of the following validation
techniques
- storyboards
- dialogue charts
- prototypes
- role-play
- formal empirical evaluation
- focus/test groups
5
input from user /output from system
6
input from user /output from system
7
(No Transcript)
8
designing input
- input design objectives
- select best media and methods
- develop efficient input procedures
- reduce input volume
- reduce input errors
- users and system designers care about
- data entry at source, without delays
- data entered only once
- data verified where/when input
- automated data entry where possible
- controlled access for data adds/changes
- audit trail/log of all data changes
9
input device options
- input decisions
- batch VS online
- centralized or distributed?
- if online, data entry or data capture?
- keyboard
- mouse
- touch screen
- graphic input device (light pen)
- voice input device
- biological feedback device
- terminal
- internet workstation
- telephone
- electronic whiteboard
- digital camera
- video input
- magnetic ink character recognition
- scanner / optical recognition
- data collection device
10
when considering input options
- costs
- security
- volumes
- accuracy
- timing
consider
for
- transaction entry
- status update/adjustment
- information retrieval
- when considering user techniques
- menus
- form fill
- prompt screens
- (questions/answer, dialogue)
- natural language
- GUI
11
input controls
GIGO GIGO GIGO GIGO GIGO GIGO GIGO GIGO
GIGO GIGO
- edits
- repetition
- business rules
- conventions
- totals
- calculations
- visual checks
- audit trails
- encryption
- On error occurrence use
- error messages
- error logs
- error suspense file
12
output classifications and options
summary detail turn-around internal external excep
tion
printer screen plotter audio e-mail the
web fax microform other
13
questions asked when working with output
Whats this about? How recent is the
information? Where does it come from? Is all of
it here? How current is this? What time period
does this information include? How much of the
information is included or excluded? Is this an
internal or external report? If its a turnaround
document, how do I use it? Is this detailed
information, a summary, or both? What do I do
with this? Is the report showing something
unusual? Is there bias imposed by sequence,
limits or graphics?
14
sample output mockup - printed report