2. Atoms and Electrons - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
2. Atoms and Electrons
Description:
2. Atoms and Electrons How to describe a new physical phenomenon? New natural phenomenon Explained Experiments confirm new phenomena Previously existing theory – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:72
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 2. Atoms and Electrons
1
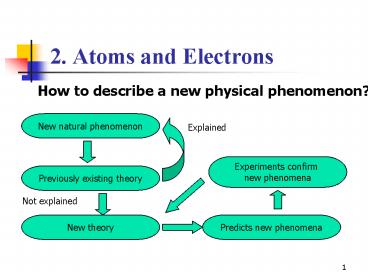
2. Atoms and Electrons
How to describe a new physical phenomenon?
New natural phenomenon
Explained
Experiments confirm new phenomena
Previously existing theory
Not explained
New theory
Predicts new phenomena
2
How to describe a new physical phenomenon?
New phenomenon
Previous Theory
New comprehensive theory
3
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics
Observation Electrons and atoms did not obey the
classical laws of mechanics.
New theory Quantum mechanics predicts the way in
which electrons behave in solids..
Postulate The light is quantized. The smallest
discrete unit of energy is photon.
Ehf
4
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Nobel Prizes 1918 Planck for the discovery of
energy quanta 1921 Einstein for the law of
the photoelectric effect
Wave
Dual nature
Particle
Wave nature electromagnetic wave f1/ T (Hz)
?c/f (m) wavelength
Light
Particle nature photon ph/? momentum of a
photon
5
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Atomic spectra Bohr model of atom
Nobel prize 1922 Niels Bohr for structure of
atoms and radiation emanating from them
- Bohr postulates
- Electron exists in certain stable circular orbits
about the nucleus and does not give off radiation - Electron may shift to an orbit of higher or lower
energy by absorbing or emitting a photon of
energy hf - Angular momentum is quantized p m v r n h/2?
?
6
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Atomic spectra Bohr model of atom
E
e-
3
E
2
hf E3-E1 Emission
31
E
1
e-
hf E2-E1 Absorption
12
7
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (Nobel prize
1932 for the creation of quantum mechanics)
The more precise you know the position of a
particle , the less precise you know the momentum
of the particle ?x ?px
h/2?
The more precise you know the time, the less
precise you know the energy
?E ?t h/2?
8
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Schrodinger Wave Equation
Dual nature of Electron
- Wave
- Wave function ?(x)
- Schrodinger Wave Equation
- ?(x) ?(x) dx is probability that the position
of electron is within (x, x?x)
- Particle
- Mass
- Position
- Momentum
- Energy
9
Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont.
Schrodinger equation and solution for the
potential well problem will be presented in class.