Arrays and Pointers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Arrays and Pointers
Description:
Arrays and Pointers Variables are just names of memory locations An array is a variable (just with many memory locations all contiguous) Address = pointer (in ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:110
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Arrays and Pointers
1
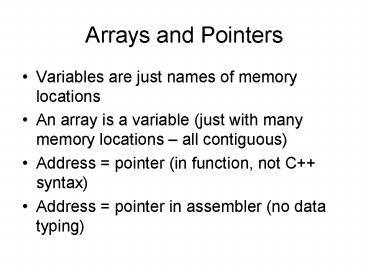
Arrays and Pointers
- Variables are just names of memory locations
- An array is a variable (just with many memory
locations all contiguous) - Address pointer (in function, not C syntax)
- Address pointer in assembler (no data typing)
2
Allocating an Array
- You have to know the size in bytes of each
element of the array - Int 4 bytes
- Float 4 bytes
- Char 1 byte
- Determine the number of bytes needed
- Sizequantity
- Allocate space (in bytes) arr .space 100
3
Memory Access
- Remember, the REAL assembly language can only
access memory via number(R) - Or disp(base) where disp is a number and base is
a register - The address is the value in the base register
added to the displacement
4
The la command
- The la (load address) macro command is very
helpful (especially with arrays) - We will load the address of the data section.
- The data section always starts at memory location
x10010000. - Look at the first 4 hex char (x1001).
- This is 4097 in decimal
5
The lui command
- Used by the assembler a lot
- Some instructions only have a 16 bit operand
- To get a 32 bit value into a register, we need
two instruction - lui load upper immediate
- Loads the upper 2 bytes (16 bits) of the register
with the specified value and places 0s in the
last 16 bits - ori or immediate logically ors the last 16
bits of a register with the immediate operand.
6
Back to the la
- So, to load the 32 bit address of a variable into
t1, the assembler uses - lui t1,4097 now t1 has the addr of the
data section - ori t1,offset the distance the var is from
the beginning of the .data - This replaces the la t1,var instruction
7
Working with Arrays
- First, get the address of the array into a
register - la t1,arr
- To get to element i of an array, you multiply i
by the size of an element and add that to the
base address of the array. - This gives the address of arri
8
Processing an entire array
- If you are looping through an array, rather than
multiply, you could just add the size of an
element to the current address to get the
address of the next element - Example for (i0 ilt25 i) arrii
9
In assembler
- In the .data section
- arr .space 100
- In the .text section la t1,arr li t2,0
i li t3,25 limit - loop beq t2,t3,done sw t2,0(t1) addi t1,4
address increases by 4 - addi t2,1 counter increases by 1 j loop
- done
10
Other examples
- Look at the reverse string example
- Look at the binary search example
- Look at the sorting example