Cells PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title: Cells
1
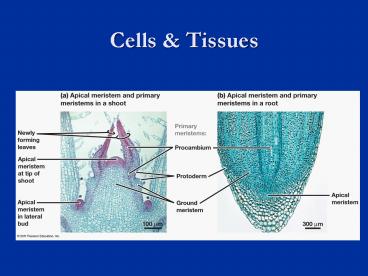
Cells Tissues
2
Apical Meristems
- Tips of roots and shoots
- Extension of plant body
- Initials
- One cell remains as initial maintaining
meristem - Other cell is derivative new body cell
3
Primary Meristems
- Multiple divisions before differentiation
- Partly differentiated tissue
- Primary growth
- Extension of the plant body
- Secondary growth
- Thickening of the plant body
- Indeterminate growth
- Formation of new organs during their entire life
4
Growth, Morphogenesis Differentiation
- Development sum total of events that form an
organisms body - Driven by genetics
- In response to environment day length, light
quality/quantity, temperature, gravity - Development 3 processes
- Growth
- Morphogenesis
- Differentiation
5
Growth
- Combination of cell division and elongation
- Cell division alone only increases number!
- Most growth elongation enlargement
6
Morphogenesis
- Primary event expansion of tissue
- Subdivided by cell division
- Cell/tissue differentiation follow morphogenesis
7
Differentiation
- Often begins while cell is still enlarging
- Depends on gene expression
- Ultimate fate positional
- Not dependant on cell lineage
- Determination
- Commitment to specific course of development
- Competency
- Ability of cell to develop in response to
specific signal
8
Differentiation
9
Internal Organization
- Cells ? tissues ? tissue systems
- Tissue Systems
- Ground
- Vascular
- Dermal
10
Tissue Systems
- Ground
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Vascular
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Dermal
- Epidermis ? periderm
11
Tissue Systems
- Characteristic Distribution Patterns
- Primary difference vascular/ground tissue
12
Fig 12.1
13
Dicot vs Monocot
ROOT
STEM
14
Tissues
- Functionally/ structurally distinct cells
- Simple tissues one type of cell
- Ground tissues
- Complex tissues more than 1 type of cell
- Vascular tissues
- Dermal tissues
15
Ground Tissues -- Parenchyma
- Living at maturity
- Capable of cell division
- Some have 2º cell walls
- Adventitious roots
- Photosynthesis, storage secretion
- chlorenchyma
- Movement of water and food
16
Parenchyma Transfer Cells
- Increased surface area
- Facilitates movement of solutes over short
distances - Intensive solute transfer
- Common
- Associated with xylem/phloem of minor veins
- Cotyledons
- Leaves in herbaceous Eudicots
- Leaf traces
- Reproductive tissues placentae, endosperm
- Glandular structures nectaries, salt glands
17
Ground Tissues -- Collenchyma
- Living at maturity
- Discrete strands of elongated cells
- Continuous cylinders in stems and petioles
- Borders veins in Eudicot leaves
- Unevenly thickened, nonlignified cell walls
- Supports young growing organs
18
Ground Tissues -- Sclerenchyma
- Continuous masses or small groups
- Hard, lignified cell walls
- Strengthening and supporting plant parts
- Fibers
- Long, slender cells
- strands or bundles
- Bast fibers
- Sclerids
- Variable in shape
- Seed coats, nut shells, endocarp
19
Vascular Tissue
- Xylem and Phloem
- Conducts water and nutrients
20
Vascular Tissues -- Xylem
- Conducts water
- Also conducts minerals
- Support
- Food storage
- 1º growth procambium
- 2º growth vascular cambium
- Dead at maturity
21
Vascular Tissues -- Xylem
- Trachery elements
- Tracheids
- Vessel elements
- May have wall pits
22
Xylem Vessel Elements
- Vessel elements perforation plate
- End rims
23
Xylem -- Tracheids
- Less specialized
- No perforations
- Seedless vascular plants Gymnosperms
- Only water conducting cells
- Less efficient because of lack of perforations
- Safer because of pit membranes
- Stop air bubbles
24
Xylem -- Tracheids
- Variety of 2º wall thickenings
- During elongation spiral or annular
- Allow for extension after differentiation
- Programmed cell death
- Only cell walls retained
25
Xylem Miscellany
- Parenchyma stores stuff
- Vertical strands
- In rays -- 2º xylem
- Fibers
- Storage and support
- May be living
- Sclerids
26
Vascular Tissue -- Phloem
- Principal food-conducting tissue
- Not just sugars!
- Long distance signaling molecules
- 1º or 2º growth
- Sieve elements principal conducting cells
- Sieve areas connecting adjacent sieve elements
- Sieve cells only phloem tissue in gymnosperms
- Sieve-tube elements only angiosperms
27
Phloem
- Sieve Cells
- Narrow pores
- Uniform sieve areas
- Sieve-tube elements
- Sieve Plate
- Some areas ? larger pores
28
Phloem
- Sieve Cells
- Sieve Tube Elements
- Narrow pores
- Uniform sieve areas
29
Sieve Elements
- Living at maturity
- Differentiation
- Trachery elements complete breakdown
- Sieve elements partial breakdown
- Breakdown of nucleus, loss of ribosomes, Golgi
cytoskeleton - Remainder distributed along wall ? plasma
membrane, SER, some plastids mitochondria - P-protein except in some monocots
30
Sieve Tube Elements
Arrows show P-protein bodies
31
Sieve-tube Elements
- Companion Cells specialized parenchyma
- Same mother cell
- Deliver stuff to sieve-tube elements
- Hormones, proteins, ATP, etc.
- Life support system for STE
- Companion cell dies when sieve element cell dies
32
Sieve-Tube Element Differentiation
33
Gymnosperm Sieve Cells
- Associated with albuminous cells
- Have nucleus, etc.
- Similar function to companion cells
- Also dies when sieve element cell dies
34
Dermal Tissue
- Epidermis outermost layer
- Variable functionally structurally
- Unspecialized or specialized!
- Guard cells
- Trichomes
- Protects plant
- cuticle
35
Epidermis Guard Cells
- Contain chloroplasts
- Regulate stomatal opening
36
Epidermis -- Trichomes
- Root hairs
- Increased reflection of radiation
- lower temps
- Lower water loss
- Absorption of water and minerals
- Secretory functions
- Protection against herbivory
- Carniverous plants
37
Trichomes
38
Carnivorous Plants
Nepenthes
Drosera
Dionaea
39
Periderm
- 2º protective tissue
- Replaces epidermis in 2º growth
- Cork (phellem) ? nonliving
- Cork cambium (phellogen)
- Cork outer surface
- Phelloderm -- inner
- Phelloderm living parenchyma tissue
40
Periderm -- Lenticels
- Loosely arranged
- Gas exchange across the cork
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)