Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Description:
Sensory (afferent): sense organs to CNS Motor (efferent): CNS to the muscles or glands ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:108
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
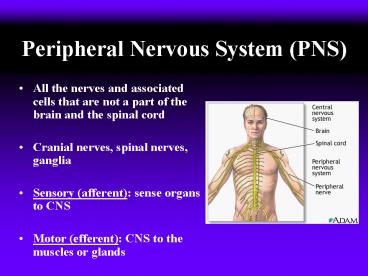
- All the nerves and associated cells that are not
a part of the brain and the spinal cord - Cranial nerves, spinal nerves, ganglia
- Sensory (afferent) sense organs to CNS
- Motor (efferent) CNS to the muscles or glands
2
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Somatic Nervous System regulates activities that
are under conscious control - Autonomic Nervous System regulates activities
that are automatic, or involuntary - Parasympathetic
- Sympathetic
3
(No Transcript)
4
Example Autonomic Nervous System
5
Physiological Effects of the Autonomic Nervous
System
6
The Senses
- Sensory Receptors located throughout the body
but are concentrated in the sense organs - Pain Receptors
- Thermoreceptors
- Mechanoreceptors
- Chemoreceptors
- Photoreceptors
7
Types of Sensory Receptors
8
The Senses
- Vision
- Hearing and Balance
- Smell
- Taste
- Touch and Related Senses
9
Vision
- Pupil small opening in the middle of the iris
through which light enters the eye - Lens transparent object behind the iris that
changes shape to help adjust the eyes focus to
see near or distant objects
10
Vision
- Retina innermost layer of the eye
- Rod photoreceptor in eye that is extremely
sensitive to light - Cone in the retina of the eye, a photoreceptor
that responds to light of different colors,
producing color vision
11
Hearing and Balance
- Cochlea fluid-filled part of the inner ear
sends nerve impulses to the brain through the
cochlear nerve - Semicircular Canal one of three structures
within the inner ear that help an organisms
maintain balance
12
Smell and Taste
- Both an ability to detect chemicals
- Taste Bud sense organ that detects the flavor of
a substance
13
Touch and Related Senses
- Your largest sense organ SKIN!
- Skin has sensory receptors that respond to
- Temperature
- Touch
- Pain
- The greatest density of touch receptors is found
on your fingers, toes and face
14
Drugs That Affect The Synapse
- Stimulants
- Depressants
- Cocaine
- Opiates
- Marijuana
- Alcohol
- Alcohol and Disease
15
Stimulants
- Increase the actions regulated by the nervous
system - Increase heart rate
- Raise blood pressure
- Increase breathing rate
- Increase the number of neurotransmitters at some
synapses in the brain - Examples amphetamines, cocaine, nictotine,
caffeine
16
Depressants
- Decrease the rate of functions regulated by the
brain - Decrease heart rate
- Decrease breathing rate
- Lower blood pressure
- Relax muscles
- Relieve tension
- Example alcohol
17
Cocaine
- Causes the sudden release in the brain of a
neurotransmitter DOPAMINE - Addiction uncontrollable craving for more of a
drug - Powerful stimulant
18
Cocaine
19
Opiates
- Opium poppy produces a powerful class of
painkillers opiates - Mimic natural chemicals in the brain known as
endorphins, which normally help to overcome
sensations of pain
20
Marijuana
- The most widely abused illegal drug
- Species of hemp plant
- THC active ingredient (tetrahydrocannabinol)
21
Alcohol
- One of the most dangerous and abused depressant
drugs - Slows down the rate at which the CNS functions
- Can lead to the DISEASE Alcoholism
22
Effects of Blood Alcohol Concentration
23
Psychoactive Drugs of Abuse
24
Drug Abuse
- Use of any drug in a way that most doctors would
not approve