Systems Development Lifecycle PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Systems Development Lifecycle
1
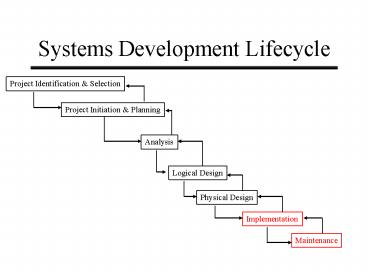
Systems Development Lifecycle
Project Identification Selection
Project Initiation Planning
Analysis
Logical Design
Physical Design
Implementation
Maintenance
2
System Implementation
- Coding and Integration
- Testing
- Installation
- Documentation
- Training
- Support
3
Coding and Integration
- Start with the design products
- data flow diagrams, structure charts, logic
models, interface and database designs - Get the components
- write from scratch
- buy packaged
- generate
- Integrate the components
- parameterize and tailor the components
- write wrappers and glueware
4
System Integration
Glueware
Tailoring
Wrapper
5
Testing Terms
- Coverage
- ideally, testing will exercise the system in all
possible ways - not possible, so we use different criteria to
judge how well our testing strategy covers the
system - Test case
- consists of data, procedure, and expected result
- represents just one situation under which the
system (or some part of it) might run
6
Test Planning
- A test plan includes
- test objectives
- schedule and logistics
- test strategies
- test cases
- procedure
- data
- expected result
- procedures for handling problems
7
Testing Phases
- Unit testing - does this piece work by itself?
- Integration testing - do these two pieces work
together? - System testing - do all the pieces work together?
- Alpha acceptance testing - try it out with
in-house users - Installation testing - can users install it and
does it work in their environment? - Beta acceptance testing - try it out with real
users
In development/ maintenance organization
In user organization
8
Testing Techniques
- Structural testing techniques
- white box testing
- based on statements in the code
- coverage criteria related to physical parts of
the system - tests how a program/system does something
- Functional testing techniques
- black box testing
- based on input and output
- coverage criteria based on behavior aspects
- tests the behavior of a system or program
9
System Testing Techniques
- stress testing - test larger-than-normal capacity
in terms of transactions, data, users, speed,
etc. - execution testing - test performance in terms of
speed, precision, etc. - recovery testing - test how the system recovers
from a disaster, how it handles corrupted data,
etc. - operations testing - test how the system fits in
with existing operations and procedures in the
user organization - compliance testing - test adherence to standards
- security testing - test security requirements
10
System Testing Techniques (cont.)
- requirements testing - fundamental form of
testing - makes sure the system does what its
required to do - regression testing - make sure unchanged
functionality remains unchanged - error-handling testing - test required
error-handling functions (usually user error) - manual-support testing - test that the system can
be used properly - includes user documentation - historical test data - tests until the number of
defects found approaches the average number of
defects in the products produced under similar
circumstances
11
Unit Testing Techniques
- input domain testing - pick test cases
representative of the range of allowable input,
including high, low, and average values - equivalence partitioning - partition the range of
allowable input so that the program is expected
to behave similarly for all inputs in a given
partition, then pick a test case from each
partition - boundary value - choose test cases with input
values at the boundary (both inside and outside)
of the allowable range
12
Unit Testing Techniques (cont.)
- statement testing - ensure the set of test cases
exercises every statement at least once - branch testing - each branch of an if/then
statement is exercised - path testing - every path is exercised
(impossible in practice) - fault seeding - put a certain number of known
faults into the code, then test until they are
all found
13
Manual Testing Techniques
- Attempt to evaluate a program without executing
it - Techniques
- inspections and reviews
- walkthroughs and desk checking
- mathematical correctness proofs
- safety analysis
- program measurements
- data flow and control flow analysis
14
Installing the System
- Installation process
- must be analyzed and designed, too
- needs to be tested
- needs to be scheduled and managed
- need to have a conversion plan
- Consider business cycle
- Organizational change process
15
Conversion
- Refers to the process of switching from the
previous system to the new one - Conversion strategies
- direct
- parallel
- single location
- phased
- Have to consider conversion of data, hardware,
documentation, work methods, physical spaces,
business forms, etc.
16
Types of User Documentation
- Users manuals
- Operators manuals
- Conversion manuals
- Tutorials
- Automated Demos
- Programmers Guide
- Failure Message Reference Guide
- On-line Help
- Quick Reference Guides
17
Documentation in the SDLC
- Often left to the most junior members of the team
- Or the most incompetent (can do less damage
documenting rather than coding) - Devote 5 effort at the last minute
- Result inadequate documentation
- Exception when system success depends on
satisfaction of general population users
18
How It Should Happen
- Should be managed properly, staffed
appropriately, monitored according to schedule - Get started early - before implementation
- Use professionals
- Thorough review of all documentation
- Provide mechanisms for feedback from users
- Revise regularly
19
Documentation Evaluation
- informal reviews by a variety of reviewers
- features checklists
- automated metrics
- information walkthroughs with users
- controlled experiments with users
- field trials with users
20
Documentation Audiences
- Users, operators, programmers, customers,
maintainers - Level of technical expertise and experience
- What they want to know
- I want to buy it
- I want to learn it
- I want to use it
- I want to fix it
- How much time they have to spend
21
Training and Support
- Often overlooked
- Cant leave it entirely to documentation
- Training - upfront instruction, usually intensive
- Support - long-term assistance, often for
occasional users - On-line training and support more and more
expected
22
Success Factors
- Management support of new system
- User involvement during development
- Commitment to the project from all parties
- Organizational commitment to change
- Quality of project definition and planning
- User expectations
23
Evolving the System
- In an ideal world
- The system, once installed, is continuously
monitored to determine areas for improvement, to
immediately correct problems, and to quickly
adapt to changing circumstances. - In reality
- The system, once installed, is largely ignored
unless it has a catastrophic failure or someone
complains loudly enough, in which case it is
modified as quickly as possible with the minimum
amount of effort.
24
Maintenance vs. Evolution
- Maintenance - individual changes that must be
made to a system after installation - Evolution - the long-term change in structure and
quality that occurs in a system due to the
overall effect of maintenance changes - Evolution results in system deterioration unless
it is managed - Managing evolution requires managing maintenance
25
Systems must be changed because...
- A defect had to be corrected
- The user changed their mind
- The user thought of something new (that theyre
willing to pay for) - The environment changes
- Changes can be made to make future changes easier
26
Categories of Maintenance Changes
- Corrective - fixing bugs
- Adaptive - no change to functionality, but now
works under new conditions - Perfective - adds something new makes the system
better - Preventive - enhances internal structure of
system without affecting external behavior
Enhancements
27
Maintenance Terms
- Configuration Control Board (CCB) -
organizational unit that makes decisions about
what proposed maintenance changes will actually
be made - Releases - planned collections of maintenance
changes that are applied to a system before it is
delivered to customers - Patches - emergency fixes to a system that are
delivered to customers between scheduled releases - Configuration management - the process of keeping
track of different versions of a system that have
been supplied to different customers and that
must be maintained separately
28
Maintenance Terms (cont.)
- Ripple effect - the (usually unintended) effects
that a change in one part of a system has on
other parts of the system - Impact analysis - analysis of a planned
modification to a system in an effort to
determine all of the components of the system
that will be affected by the modification,
including ripple effects - System decay - a degradation of system structure
and quality over time due to poorly planned and
executed changes - Program comprehension - the human process of
understanding a piece of software code - Porting - a type of adaptive maintenance in which
a system is translated from one operating system,
language, or platform to another
29
Why is Maintenance Hard?
- System maintainers have limited sources of
information about the system - Systems are complex and interdependent
- Systems are not developed for maintainers
- Maintenance is not very glamorous
- Maintenance is not very well respected