Trp Operon Overview PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title: Trp Operon Overview
1
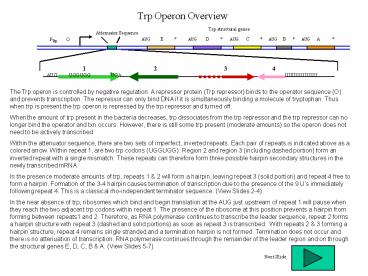
Trp Operon Overview
Trp structural genes
Attenuator Sequence
AUG E AUG D
AUG C AUG B
AUG A
PTrp O
The Trp operon is controlled by negative
regulation. A repressor protein (Trp repressor)
binds to the operator sequence (O) and prevents
transcription. The repressor can only bind DNA if
it is simultaneously binding a molecule of
tryptophan. Thus when trp is present the trp
operon is repressed by the trp repressor and
turned off. When the amount of trp present in
the bacteria decreases, trp dissociates from the
trp repressor and the trp repressor can no longer
bind the operator and txn occurs. However, there
is still some trp present (moderate amounts) so
the operon does not need to be actively
transcribed Within the attenuator sequence, there
are two sets of imperfect, inverted repeats. Each
pair of repeats is indicated above as a colored
arrow. Within repeat 1, are two trp codons
(UGGUGG). Region 2 and region 3 (including dashed
portion) form an inverted repeat with a single
mismatch. These repeats can therefore form three
possible hairpin secondary structures in the
newly transcribed mRNA. In the presence moderate
amounts of trp, repeats 1 2 will form a
hairpin, leaving repeat 3 (solid portion) and
repeat 4 free to form a hairpin. Formation of the
3-4 hairpin causes termination of transcription
due to the presence of the 9 Us immediately
following repeat 4. This is a classical
rho-independent terminator sequence. (View Slides
2-4) In the near absence of trp, ribosomes which
bind and begin translation at the AUG just
upstream of repeat 1 will pause when they reach
the two adjacent trp codons within repeat 1. The
presence of the ribosome at this position
prevents a hairpin from forming between repeats1
and 2. Therefore, as RNA polymerase continues to
transcribe the leader sequence, repeat 2 forms a
hairpin structure with repeat 3 (dashed and solid
portions) as soon as repeat 3 is transcribed.
With repeats 2 3 forming a hairpin structure,
repeat 4 remains single stranded and a
termination hairpin is not formed. Termination
does not occur and there is no attenuation of
transcription. RNA polymerase continues through
the remainder of the leader region and on through
the structural genes E, D, C, B A. (View Slides
5-7)
Next Slide
2
Attenuation occurs in the presence of moderate
amounts of trp
Ultimately, this is the secondary structure which
will form if Trp is present
Next Slide
3
Attenuation is overcome when Trp levels are very
low
2
3
2
3
1
AUG
UGA
UGGUGG
Stalled Ribosome
Ultimately, this is the secondary structure
formed at low concentrations of Trp
Next Slide
4
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Transcription of the Trp operon has begun. RNA
polymerase has transcribed from the 1 into the
trp leader sequence. The line and boxes represent
newly synthesized mRNA from the trp operon.
The following 8 slides will play automatically to
animate the process of attenuation. To begin,
click the button below
5
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
A ribosome has bound to the 1st AUG of the leader
sequence and begun translation. RNA polymerase
has continued transcription into region 2
6
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
7
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Termination factor
1
2
3
AUG
UGA
UGGUGG
Since trp is present, translation continues
through the two trp codons on to the stop codon.
Transcription has continued into region 3.
8
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Translation terminates once the ribosome reaches
the stop codon. RNA polymerase has continued
transcription into region 4.
9
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Once the ribosome dissociates, regions 1 2 can
and will form a hairpin structure.
1-2 hairpin
10
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
With regions 1 2 in a hairpin, regions 3 4 can
form a similar structure
2
1
3
4
11
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Attenuation occurs at moderately low levels of Trp
Formation of the 3-4 hairpin, results in
transcription termination
Next
12
Attenuation Animation
Click the button to see a faster animated
sequence of steps for attenuation just showing
the events without all the text.
13
Attenuation Animation
14
Attenuation Animation
15
Attenuation Animation
16
Attenuation Animation
17
Attenuation Animation
1
2
3
4
RP
AUG
UGA
UGGUGG
18
Attenuation Animation
19
Attenuation Animation
AUG
3
RP
UGGUGG
1
2
UGA
20
Attenuation Animation
AUG
UGGUGG
RP
2
1
UUU
3
4
UGA
21
Attenuation Animation
22
Attenuation Animation
RP
23
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
The following 5 slides show lack of attenuation
in the near absence of TrpClick the button below
to view
24
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Ribosome begins translation, but stalls when it
reaches 2 trp codons in leader sequence
25
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
RNA polymerase continues to transcribe the leader
sequence
26
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
27
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Since the ribosome is stalled on region 1, region
2 3 are avialable to form a hairpinstructure
while RNA polymerase finishes transcribing region
4
28
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
Very low levels of Trp prevent attenuation
allowing Trp EDCBA genes to be transcribed
With the formation of the 2-3 hairpin, there is
hairpin formed immediately upstream of the poly U
stretch.This allows RNA polymerase to continue
transcription of the remainder of the operon
Replay