ADDIE Model - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
ADDIE Model
Description:
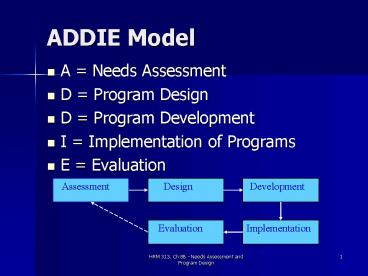
ADDIE Model Implementation Evaluation A = Needs Assessment D = Program Design D = Program Development I = Implementation of Programs E = Evaluation Assessment – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:3667
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: ADDIE Model
1
ADDIE Model
- A Needs Assessment
- D Program Design
- D Program Development
- I Implementation of Programs
- E Evaluation
2
A Needs Assessment
- Reasons why organizations do not conduct needs
assessment - Lack of support for the needs assessment process
- Time-consuming
- Managers may prefer action over research.
- Training fads and demands from senior managers
sometimes take precedence. - Benefits of needs assessment
- Allows for content decisions to be made on the
basis of fact rather than intuition - Provides base-line information for use in
evaluating effectiveness - Permits HR professionals to develop and implement
cost-effective programs
3
Levels of Needs Assessment
- Organizational needs analysis
- Assess short-and long-term strategic objectives
(Human resource needs, Efficiency indices,
Training climate, Resources and constraints) - Job needs analysis
- Identify specific skills, knowledge and behavior
needed in present or future jobs (competency
modeling) - Person needs analysis
- Identify the gap between current capabilities and
those that are necessary or desirable (output
measures, self-assessed training needs, career
planning discussions, attitude surveys)
4
Five Steps in Needs Assessment
- Step 1 Gather data to identify needs
- Beginning Sources for needs assessment
- Skills inventories, exit interviews,
organizational climate indexes, labor-management
data, turnover and absenteeism rates, employee
suggestions, productivity rates, attitude
surveys, customer complaints, efficiency indexes - Methods of needs assessment
- Surveys/questionnaire, interviews, performance
appraisals, observations, tests, assessment
centers, focus groups/group discussions, document
reviews, advisory committees
5
- Step 2 Determine needs that can be met by
- TD interventions
- Identify problems that cannot be solved by TD.
- Refer these to top management or other functions
of HRM. - Step 3 Propose solutions
- Develop all possible alternatives.
- Step 4 Calculate potential cost of TD
- interventions
- Compare cost (total cost of training/number of
people trained) with benefits. - Step 5 Choose and implement an
- intervention
- Choose an intervention.
6
Potential Costs and Benefits
- Costs
- Trainers salary
- Trainees salary
- Materials and supplies
- Consultants services
- Living expenses
- Cost of facilities
- Transportation
- Equipment
- Lost production
- Development costs
- Support costs
- Benefits
- Reduction in errors
- Increase in production
- Reduction in turnover
- Less supervision necessary
- Ability to advance
- Ability to perform wider range of jobs
- Attitude changes
- Employee/organization alignment
- Facilitation of organizational change
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Increase in organizational competencies
7
D Design
- Setting goals and objectives
- Goals Who is the training for? What is the
training about? Why is the training being
conducted? - Objectives The situation surrounding the desired
behavior, the skill to be learned, the object of
that behavior, any qualifiers, such as tools to
be used while doing the behavior - S(pecific), M(easurable), A(ction-oriented),
R(ealistic), T(imely) - Defining the target audience
- Aptitude, prior knowledge and skills, attitudes
and perceptions - Selecting an instructional design
- In-house vs. off-the-shelf
8
In-House vs. Off-the-Shelf
- In-house
- Advantages
- Knowledge of company culture is useful.
- Learning objectives can be tailored to specific
needs. - Management may buy in more quickly.
- Disadvantages
- Development time may be lengthy.
- Training staff often already overloaded with
administrative duties - Expertise needed is often not on staff.
- Assumption that experts are always somewhere
else.
- Off-the-shelf
- Advantages
- Training is immediately available.
- Developers expertise is usually available to
company. - It is often less expensive.
- Disadvantages
- Training doesnt always target specific needs.
- There is usually a need for company orientation
on the corporate culture. - It may not be possible to truly customize the
product. - It can sometimes be expensive.
9
D Content Development
- Cognitive knowledge
- Orientation, basic skills (three Rs)
- Skill development
- Technical, interpersonal, quality, managerial,
executive - Affective outcomes
- Work/family issues, team spirits, harassment,
emotional intelligence, wellness, diversity
10
Choosing Formats
- On-the-job (job instruction training,
apprenticeship training, internships and
assistantships, job rotation and developmental
job assignments, supervisory assistance and
mentoring, coaching) - On-site, but not on-the-job (programmed
instruction on intranet or internet, videos and
CDs, teleconferencing, corporate universities and
executive education) - Off the job (formal courses, simulation,
assessment centers, role-playing, business board
games, sensitivity training, wilderness trips and
outdoor training) - Methods
- Case study, demonstration, group discussion,
reading, structured exercise, presentation