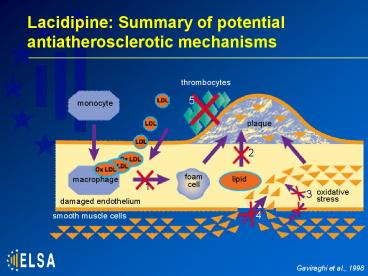
Lacidipine: Summary of potential antiatherosclerotic mechanisms
1 / 12
Title:
Lacidipine: Summary of potential antiatherosclerotic mechanisms
Description:
Lacidipine: Summary of potential antiatherosclerotic mechanisms thrombocytes 5 monocyte plaque 2 foam cell macrophage lipid 1 oxidative stress 3 damaged endothelium –
Number of Views:60
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lacidipine: Summary of potential antiatherosclerotic mechanisms
1
Lacidipine Summary of potential
antiatherosclerotic mechanisms
thrombocytes
5
monocyte
plaque
2
foam cell
macrophage
lipid
oxidative stress
3
damaged endothelium
smooth muscle cells
4
Gaviraghi et al., 1998
2
ELSA Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Major inclusion criteria
- Aged 4575 years
- Systolic and diastolic blood pressure of 150210
mmHg and 95115 mmHg, respectively - Readable ultrasound carotid artery scan with
maximum intima-media thickness (IMT) lt 4.0 mm - Major exclusion criteria
- Fasting serum cholesterol gt 320 mg/dL
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- Myocardial infarction (within previous 12 months)
- Stroke (within previous 6 months)
- Previous carotid endarterectomy
3
Study design
Run-in
Titration
Maintenance
Trial phases
Months
-1 0 1 3
6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 59
days
0 1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Follow up
Visits
25mg
HCTZ (if required)
12.5mg
6mg
Lacidipine
4mg
Placebo
Medication
Atenolol
50mg
100mg
HCTZ (if required)
12.5mg
25mg
Measurements
Clinical examination
Blood pressure
B-mode ultrasound arterial blood pressure
monitoring
Zanchetti, 1996
4
Measurement of IMT and CBMmax
- The primary endpoint for IMT measurement in the
ELSA trial is CBMmax. This is defined as the mean
of the maximum IMT of the four far walls of the
carotid bifurcation and distal common carotid
artery
External carotid
Internal carotid
Stratification
Location
Plaque ?1.3 mm
Internal
Bifurcation
Thickening ?1.0, lt1.3 mm
Common
Normal lt1.0 mm
Common carotid
Zanchetti et al., 1998
5
Study endpoints
- Primary objective
- Comparison of effects of lacidipine and atenolol
on carotid IMT - Primary efficacy outcome
- Change in CBMmax
- Secondary objective
- Comparison of the effects of lacidipine and
atenolol on - cardiovascular events
- blood pressure control
- progression/regression of atherosclerotic plaques
- Secondary efficacy outcomes
- Percentage of patients with increased/decreased
number of carotid plaques - Incidence of fatal/non-fatal major and minor
cardiovascular events, and total mortality - Change in mean maximum IMT (Mmax)
6
Baseline characteristics
Lacidipine
Atenolol
Variable
55.9 7.5
56.1 7.5
Age (years)
Gender ( males)
55.4
54.2
Current smoking ()
18.4
22.6
Body mass index (kg/m2)
27.2 3.6
27.2 3.9
Total cholesterol (mmol/L))
5.84 1.01
5.80 0.98
Serum HDL-cholesterol (mmol/l)
1.34 0.46
1.34 0.43
Serum LDL-cholesterol (mmol/l)
3.73 0.98
3.70 0.94
Serum triglycerides (mmol/l)
1.51 0.77
1.51 0.71
Clinic DBP (mmHg)
101.3 4.9
101.4 5.3
Clinic SBP (mmHg)
163.1 12.5
163.9 12.2
24-h ambulatory DBP (mmHg)
87.6 9.3
88.2 9.3
24-h ambulatory SBP (mmHg)
140.4 14.2
141.4 14.0
CBMmax (mm)
1.1619 0.2480
1.1589 0.2399
IMT-common carotid (mm)
1.0173 0.2152
1.0090 0.1980
IMT-carotid bifurcation (mm)
1.3115 0.3782
1.3131 0.3594
7
Treatment-related changesCarotid wall CBMmax
CBMmax Final vs. baseline scan
0.06
0.05
0.04
Atenolol
Mean change (mm/year)
0.03
Lacidipine
0.02
0.01
0
ITT
PP1
PP2
Completers
Ratio of mean changes (95 CI)
ITT
PP1
PP2
Completers
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
In favour of lacidipine
In favour of atenolol
8
Treatment-related changes Carotid plaque
prevalence
Changes in number of carotid plaques per patient
from baseline to end of study with lacidipine and
atenolol
60
Atenolol
50
Lacidipine
40
of patients
30
20
10
0
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
Less
No change
More
Change in number of plaques
Atenolol (N 937)
Lacidipine (N 947)
9
Treatment-related changesBlood pressure and
heart rate
Blood pressure (SBP, DBP) and heart rate (HR)
changes during randomised treatment (ITT)
Clinic values
24 h Ambulatory values
SBP
DBP
HR
SBP
DBP
HR
0
0
0
0
-2
-2
-4
-4
-4
-4
-8
-8
-6
-6
-12
-12
-8
-8
-16
-16
-10
-10
-20
-20
-12
-12
-24
-24
b/min
mmHg
mmHg
b/min
Lacidipine
Atenolol
10
Safety analysis
Relative risk of adverse events in lacidipine-
and atenolol-treated patients
Events (N)
Relative risk (95 CI)
Lacidipine
Atenolol
Myocardial infarction
17
18
Stroke
14
9
33
Major CV events
27
CV death
8
4
All death
17
13
Hospitalised angina
11
17
Other minor CV events
30
27
All serious AEs
201
186
1.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.5
2.0
4.0
Lacidipine better
Atenolol better
11
Key findings from the ELSA study
- Compared with atenolol, lacidipine is
significantly (P lt 0.001) more effective in
slowing increases in carotid IMT in hypertensive
patients - reduced 4-year CBMmax progression by
- 0.0227 mm (ITT population)
- 0.0281 mm (Completers population)
- reduced yearly carotid IMT progression rate by
2340 (4060 in Completers and PP2) - increased the proportion of patients with
regression of pre-existing plaques by 31
12
The ELSA studySummary
- 4-year, multi-centre study
- Largest study of treatment effects on carotid IMT
to date - Careful design and implementation for highly
reliable results - Clear demonstration of benefits of lacidipine
over atenolol in slowing the progression of
carotid IMT - Clinically significant treatment effect on IMT
- Verifies pre-clinical evidence of
antiatherosclerotic properties of lacidipine - Supports antiatherosclerotic actions of
lacidipine independent of antihypertensive effects