What is central dogma? From DNA to Protein - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
What is central dogma? From DNA to Protein
Description:
What is central dogma?From DNA to Protein. All proteins consist of polypeptide chains. A linear sequence of amino acids. Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:286
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: What is central dogma? From DNA to Protein
1
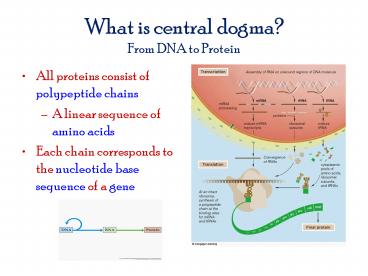
What is central dogma?From DNA to Protein
- All proteins consist of polypeptide chains
- A linear sequence of amino acids
- Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base
sequence of a gene
2
What is the first step?
- 1. Transcription Enzymes uses base sequence of
a gene as template to make strand of RNA - Two DNA strands unwind in a specific region
- RNA polymerase assembles strand of RNA
- Covalently bonds RNA nucleotides (adenine,
guanine, cytosine, uracil) according to
nucleotide sequence of exposed gene
3
What is the second step?
- 2. Translation
- Information in the RNA strand is decoded
(translated) into a sequence of amino acids
4
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- In prokaryotic cells (no nucleus)
- Transcription and translation occur in cytoplasm
- In eukaryotic cells
- Genes are transcribed in the nucleus
- Resulting mRNA is translated in the cytoplasm
5
Three types of RNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Carries protein-building codes from DNA to
ribosomes - Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- Forms ribosomes (where polypeptide chains are
assembled) - Transfer RNA (tRNA)
- Delivers amino acids to ribosomes
6
RNA and DNA compared
- DNA
- exists as double-stranded molecules
- hereditary information
- double helix
- contains deoxoyribose sugar
- RNA
- Disposable copies of hereditary information and
some are catalytic - exists as a single stand.
- contains ribose instead of deoxyribose
- contains uracil in place of thymine
7
RNA Modification Alternative Splicing
- Before mRNA leaves the nucleus
- Introns are removed
- Some exons are removed along with introns
remaining exons are spliced together in different
combinations - Poly-A tail is added to 3 end of new mRNA
8
What is the genetic code?
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries DNAs
protein-building information to ribosomes for
translation - mRNAs genetic message is written in codons
- Sets of three nucleotides along mRNA strand
9
Codons
- Codons specify different amino acids
- A few codon signals stop translation
- Sixty-four codons constitute a highly conserved
genetic code