Structure of the Synapse - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Structure of the Synapse
Description:
Structure of the Synapse The Structure and function of the synapse WALT That synapses occur between neurones How the nervous impulse is transmitted across the synapse ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:89
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Structure of the Synapse
1
Structure of the Synapse
2
The Structure and function of the synapse
- WALT
- That synapses occur between neurones
- How the nervous impulse is transmitted across the
synapse - That synapses use different neurotransmitters
3
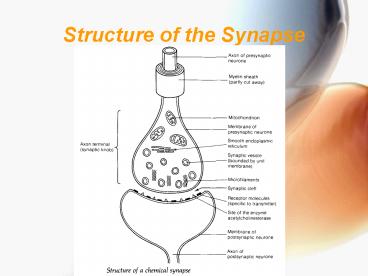
Definitions
- presynaptic neuron before the synapse
- postsynaptic neuron behind the synapse with
receptor molecules - synaptic cleft a narrow gap about 20 nm wide
4
Synapse
- When a nerve impulse arrives at the synaptic knob
it alters the permeability of the presynaptic
membrane to Ca, which therefore enters - Synaptic vesicle fuse with membrane discharge
its transmitter substance
5
Synapse
- The transmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft
fuses with receptor molecules - This alters permeability of postsynaptic
membrane to Na - If excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) EPSP
by summation exceeds threshold - Action potential results
6
Synapses
- Transmitter substance (acetylcholine) is
hydrolysed by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase on
the postsynaptic membrane. - Its breakdown can be reused to synthesize
acetylcholine again at the synaptic knob, with
energy from mitochondria.
7
Synapse
8
Synapse
9
(No Transcript)
10
Neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine - released by all motor neurones,
activating skeletal muscles involved in the
parasympathetic nervous system (relaxing
responses) - cholinergic
synapses - Noradrenaline - involved in the sympathetic
nervous system ('fight or flight'
responses) - adrenergic
synapses
11
Functions of the synapse
- 1. Transmit information between neurons
- 2. Pass impulses in one direction only
- 3. Act as junctions
- 4. Filter out low level stimuli
- 5. Allow adaptation to intense stimulation
12
Task
- Draw and annotate the transmission of an impulse
across the synapse - What is meant by adaptation?
- Where else do synapses occur?
- What name is given to those synapses that use
acetylcholine as neurotransmitter? - Questions 9 and 10 page 61
- Explain summation
13
Types of Synapse
- Excitatory ion channel synapses -neuroreceptors
are Na channels. When Na channels open, local
depolarisaition occurs, if threshold is reached
then action potential is initated - Inhibitory ion channels - neuroreceptors are Cl-
channels. When Cl- channels open,
hyperpolarisation occurs, making action potential
less likely - Non channel synapses - neuroreceptors are
membrane-bound enzymes. When activated, they
catalyse the 'messenger chemical', which in turn
can affect the sensitivity of the ion channel
receptors in the cell
14
Types of Synapse
- Neuromuscular junctions - synapses formed between
motor neurones and muscle cells. Always use the
neurotransmitter acetylcholine, and are always
excitatory - Electrical synapses - the membranes of the two
cells actually touch and they chare proteins.
The action potential can pass directly from one
membrane to the next