The 6 Principles of Second language learning (DEECD,2000) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
The 6 Principles of Second language learning (DEECD,2000)
Description:
The 6 Principles of Second language learning (DEECD,2000) Learner Centred Principle Assessment Principle Immersion Principle Beliefs and Understandings – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:237
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The 6 Principles of Second language learning (DEECD,2000)
1
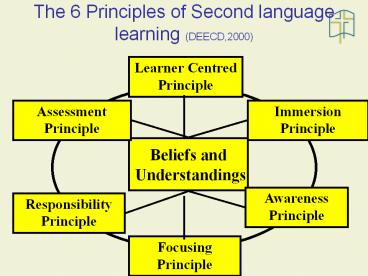
The 6 Principles of Second language learning
(DEECD,2000)
Learner Centred Principle
Assessment Principle
Immersion Principle
Beliefs and Understandings
Awareness Principle
Responsibility Principle
Focusing Principle
2
Principal 1-The Learner Centred Principle
ESL learners learn best when the language input
is relevant to their individual needs, interests
and understandings.
3
Teachers need to
- recognise that students bring a first language to
the learning of a new language, and this provides
the basis for their learning of the second
language - help learners make links between what they
already know and new concepts and knowledge - plan for the sharing of knowledge and experience
of all students - choose resources that are culturally sensitive
and accessible - create an atmosphere that is receptive to, and
tolerant of, cultural similarities and
differences
4
Principal 2-The Immersion Principle
ESL learners learn best when they are provided
with opportunities to communicate in authentic
school and social contexts.
5
Teachers need to
- encourage all students to participate actively
and to take risks in language use - provide a wide range of learning activities using
different groupings, situations and teaching
strategies - provide opportunities for students to produce and
respond to spoken and written text - provide opportunities for students to use English
in authentic contexts so that they may gain an
awareness of how purpose and audience influence
language choices.
6
Principal 3-The Awareness Principle
ESL learners learn best when they are aware of
the reflective use of language and the role and
nature of English.
7
Teachers need to
- create an awareness in students that oral
language can vary according to the audience and
the purpose - create an awareness in students of different
approaches to writing for different purposes and
for different audiences - provide opportunities for students to develop the
language to think and talk about language
8
Principal 4-The Focusing Principle
ESL learners learn best when they are focused on
the structures and features of English in order
to develop an increasing control over
communication in school and social contexts.
9
Teachers need to
- focus on and explicitly teach specific features
of text, such as grammar and vocabulary relating
to a topic or theme - explicitly teach and model the organisation of
the text ( linguistic structure) and the language
choices (linguistic features) relating to the
purpose.
10
Principal 5-The Responsibility principle
- ESL students learn English best when they are
provided with opportunities to develop strategies
that enhance communication.
11
Teachers need to
- foster the development of learning how-to-learn
and social interaction skills - provide opportunities for students to develop
strategies to facilitate their acquisition of
English - help students to become progressively independent
language learners and users - encourage students to take responsibility for
their own learning
12
Principal 6-The Assessment Principle
- ESL students learn English best when they are
provided with appropriate feedback about their
progress.
13
Teachers need to
- set realistic and achievable goals so that
students can experience success, and so promote
self-esteem - support further learning through realistic but
sensitive feedback and encouragement