Cell Structure PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Cell Structure
1
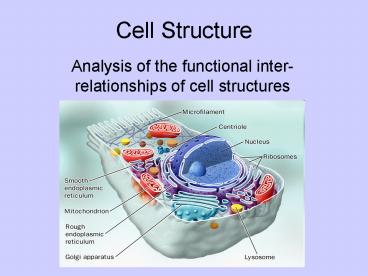
Cell Structure
- Analysis of the functional inter-relationships of
cell structures
2
Cell Biology the study of cells the structural
and function units of all living organisms
morphologically cells vary in shape and size
red blood cells
human sperm cells
bacteria
white blood cells
nerve cell
platelets
cancer cells (myeloma)
cells also vary physiologically
portion of skeletal muscle cells
12
3
Cell Theory
- Cells
- Cells come from cells
4
13
5
Nucleus and Nucleoid
a nucleoid (which consists of the organisms DNA)
is NOT enclosed in a membrane prokaryotic cell
eukaryotic cell DNA contained within a membrane
15
6
Eukaryotic Cells
- Bounded by cell
- Cytoplasm inside cells composed of aqueous
solution, organelles and molecules - Various fibres compose a to give shape and
structure
7
Nucleus
- Contains genetic material which controls/directs
the activities of the cell - function brain of cell, i.e. determines
metabolism, growth, differentiation,
reproduction of cell - Nucleus enclosed in a nuclear envelope
- Within is chromosome/chromatin, nucleoplasm
and nucleoli - are long strands of DNA wrapped around
protein molecules which make up genes (units of
heredity) - nucleoplasm is a highly viscous liquid
- is the site where rRNA is assembled (rRNA then
travels to the cytoplasm for protein syntheis)
8
DNA packed in Chromosomes
9
Chromatin vs. Chromosome
10
Ribosome
- consist of 2 nonidentical subunits formed from
rRNA proteins - function protein synthesis
- found attached to endoplasmic reticulum or free
in cytoplasm - group of ribosomes simultaneously
synthesizing same protein
11
Membranous Canals
- Includes endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus,
vacuoles and lysosomes
12
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Series of canals exist in cytoplasm
- Can extend from envelope to cell membrane
- rough endoplasmic reticulum
- ribosomes attached to surface
- function synthesize proteins for secretion
- NOTE unlike free ribosomes that synthesize
proteins for use within cell - smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- no ribosomes attached to surface
- functions
- synthesis of lipids, e.g. cell membrane
hormones - metabolism of carbohydrates, e.g. synthesis of
glycogen - detoxify drugs wastes in cell, e.g. alcohol
13
Golgi Apparatus
- resembles stack of hollow tubes,
- i.e. similar to smooth endoplasmic reticulum,
but closer to cell membrane - function sorting, modification (assembly),
packaging of substances for storage or - e.g. produces glycolipids by joining
carbohydrates to lipids - receives vesicles from endoplasmic reticulum that
contain newly synthesized proteins/lipids - proteins/lipids sorted, modified, packaged
into new vesicles that bud off - transported within cell or moved to cell
membrane for export by exocytosis
14
Vacuoles
- large, membrane enclosed sac
- vesicle small
- storage or transport
- formed by
- 1. budding (pinching off) from Golgi apparatus
- 2. endocytosis of
- 3. extension of endoplasmic reticulum membrane
15
Lysosomes
- vesicle formed by Golgi apparatus, which contains
hydrolytic enzymes - functions
- 1. cellular digestion of food particles, i.e.
fuses with food vacuoles enzymatically digests
proteins, carbohydrates, lipids - 2. disposal of damaged cell organelles, e.g.
mitochondria - 3. breakdown of whole cell, i.e. releases
contents into cell cytoplasm
16
Energy related organelles
17
Mitochondria
- function cellular respiration (aerobic
metabolism), i.e. converts glucose
(carbohydrates) to energy (ATP) - chemical reaction
- cristae (singular crista) shelflike structures
formed from folded inner membrane with enzymes on
surface for cellular respiration - Provides lots of surface area for cell. resp.
reaction. - matrix solution surrounded by
- cristae contains DNA
18
Choloroplast
- function in plant cells, i.e. converts
sunlight energy to carbohydrates - Made up of membranous stacks called grana, which
contain chlorophyll pigments - chlorophyll chemical that absorbs sunlight
energy allows photosynthesis to occur
19
Basic Photosynthesis
- Works hand in hand with cellular respiration
20
Organelles made up of Membranes
- Nuclear envelope
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Vacuoles
- Vesicles
- Cell membrane
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Note Membranes are composed of phospholipids
21
Cell Shape
22
Other Organelles
- Cell wall
- rigid cellular layer that the cell membrane in
plant cells - Provides , shape, and for the cell
- Composed of cellulose
- Cytoskeleton
- network of protein fibres
- functions cell shape, anchor organelles,
involved in
23
Characteristics of Living Things
- Living are made of cells.
- Living things obtain and use energy.
- Living things grow, reproduce and repair.
- Living things produce .
- Living things to their environment.
- Living things a life span.
24
By the end of this section you should be able to
- Prokaryotic cell verses a eukaryotic cell
- Describe the following cell structures and their
functions - Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- Chloroplast
- Cytoskeleton
- Cytoplasm
- Golgi bodies
- Lysosomes
- Mitochondria including cristae and matrix
- Nucleus - including nuclear pore, nucleolus,
chromatin, nuclear envelope, and chromosomes - Ribosomes (and polysomes)
- Smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Vacuoles
- Vesicles
- State the balanced chemical equation for cellular
respiration and photosynthesis - Describe how the following organelles function to
compartmentalize the cell and more materials
through it - Rough ER and smooth ER
- Vesicles
25
(No Transcript)