Determining the Physical Properties of DNA in Microarrays Using Optical Tweezers PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Determining the Physical Properties of DNA in Microarrays Using Optical Tweezers
1
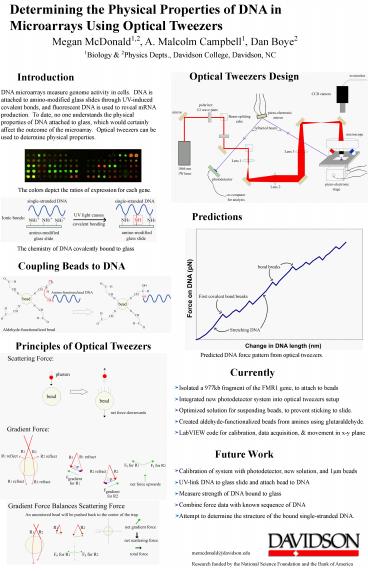
Determining the Physical Properties of DNA in
Microarrays Using Optical Tweezers
Megan McDonald1,2, A. Malcolm Campbell1, Dan Boye2
1Biology 2Physics Depts., Davidson College,
Davidson, NC
Optical Tweezers Design
Introduction
DNA microarrays measure genome activity in cells.
DNA is attached to amino-modified glass slides
through UV-induced covalent bonds, and
fluorescent DNA is used to reveal mRNA
production. To date, no one understands the
physical properties of DNA attached to glass,
which would certainly affect the outcome of the
microarray. Optical tweezers can be used to
determine physical properties.
The colors depict the ratios of expression for
each gene.
Predictions
The chemistry of DNA covalently bound to glass
Coupling Beads to DNA
Principles of Optical Tweezers
Predicted DNA force pattern from optical tweezers.
Currently
Isolated a 977kb fragment of the FMR1 gene, to
attach to beads Integrated new photodetector
system into optical tweezers setup Optimized
solution for suspending beads, to prevent
sticking to slide. Created aldehyde-functionalized
beads from amines using glutaraldehyde. LabVIEW
code for calibration, data acquisition,
movement in x-y plane
Future Work
Calibration of system with photodetector, new
solution, and 1µm beads UV-link DNA to glass
slide and attach bead to DNA Measure strength of
DNA bound to glass Combine force data with known
sequence of DNA Attempt to determine the
structure of the bound single-stranded DNA.
memcdonald_at_davidson.edu
Research funded by the National Science
Foundation and the Bank of America
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.