Poster Template - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Poster Template
Description:
Developing PHEV Charging Load Profile Based on Transportation Data Analyses Student(s): Zahra Darabi, Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty Advisor(s): Dr ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:21
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Poster Template
1
Developing PHEV Charging Load Profile Based on
Transportation Data Analyses
Student(s) Zahra Darabi, Electrical and
Computer Engineering
Faculty Advisor(s) Dr. Mehdi Ferdowsi,
Electrical and Computer Engineering
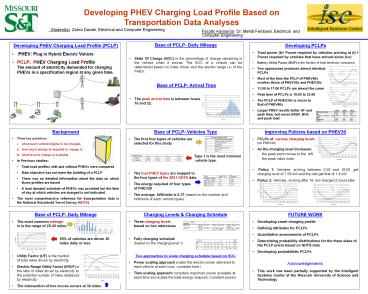
- Base of PCLP- Daily Mileage
- State Of Charge (SOC) is the percentage of charge
remaining in the vehicle when it arrives. The SOC
of a vehicle can be determined based on miles
driven and the electric range (x) of the PHEV. - Base of PCLP- Arrival Time
- The peak arrival time is between hours
16 and 22.
- Developing PHEV Charging Load Profile (PCLP)
- PHEV Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- PCLP PHEV Charging Load Profile
The amount of electricity demanded for charging
PHEVs in a specification region at any given
time.
- Developing PCLPs
- Total power (t) Power required by vehicles
arriving at (t) Power required by vehicles that
have arrived since (t-n) - Battery Utility Factor (BUF) is the fraction of
total electricity consumed. - Two approaches produces almost identical
PCLPs - Most of the time the PCLP of PHEV40s
overlies those of
PHEV30s and PHEV20s - 1100 to 1700 PCLPs are almost the same
- Peak time of PCLPs is 1800 to 2300
- The PCLP of PHEV30s is closer to
that of
PHEV40s - Larger PHEV results better UF and
peak
time, but worse ERUF, BUF,
and peak load
- Background
- Three key questions
- when each vehicle begins to be charged,
- how much energy is required to charge it,
- what level of charge is available.
- In Previous studies
- Total load profiles with and without PHEVs were
compared - Main objective has not been the building of a
PCLP - There was no detailed information about the data
on which those profiles are based - A load demand schedule of PHEVs was provided but
the time of day at which vehicles are charged is
not indicated. - The most comprehensive reference for
transportation data is the National Household
Travel Survey (NHTS)
- Base of PCLP- Vehicles Type
- The first four types of vehicles are
selected for this study -
Type 1 is the most common is
vehicle type. are
-
- The four PHEV types are mapped to
the four types of the
2001 NHTS data - The energy required of four types
of PHEV20 - The average kWh/mile is 0.37 (based on the
number and kWh/mile of each vehicle types).
- Improving Policies based on PHEV30
- PCLPs of various charging levels
(for PHEV30) - As the charging level increases
- the peak point moves to the left
- the peak value rises
- Policy 1 Vehicles, arriving between 000 and
1600, get charging level of 7.68 kW and the rest
get that of 1.4 kW - Policy 2 Vehicles, arriving after 16, are
charged 2 hours later
- Base of PCLP- Daily Mileage
- The most common mileage
is in the range of
25-30 miles. -
55 of vehicles are driven 30 30
miles daily or less - Utility Factor (UF) is the fraction
of total miles
driven by electricity. - Electric Range Utility Factor (ERUF) is
the ratio of miles
driven by electricity to
the potential number of miles displaced
by
electricity. - The intersection of two curves occurs at 30
miles.
- Charging Levels Charging Schedule
- Three charging levels
based on
two references - Fully charging schedule
(based
on the charging level 1) - Two approaches to scale charging schedule based
on SOC - Power scaling approach scales the electric power
delivered to each vehicle at each hour. (constant
time ) - Time scaling approach considers maximum power
available at each time and scales the total
energy required. (constant power)
- FUTURE WORK
- Developing smart charging profile
- Defining attributes for PCLPs
- Quantitative assessments of PCLPs
- Determining probability distributions for the
three sides of the PCLP prism based on NHTS data - Developing probabilistic PCLPs
- This work has been partially supported by the
Intelligent Systems Center at the Missouri
University of Science and Technology
Acknowledgements