Bez nadpisu - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Bez nadpisu
Description:
Visual Computing of Global Postglacial Rebound in a Spherical Domain Ladislav Hanyk1, Ctirad Matyska1 and David A. Yuen2 e-mail: ladislav.hanyk_at_mff.cuni.cz, www: http ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:77
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bez nadpisu
1
Visual Computing of Global Postglacial Rebound in
a Spherical Domain
Ladislav Hanyk1, Ctirad Matyska1 and David A.
Yuen2 e-mail ladislav.hanyk_at_mff.cuni.cz, www
http//geo.mff.cuni.cz/lh 1 Department of
Geophysics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic 2
University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute
and Department of Geology and Geophysics,
Minneapolis
OBJECTIVE visual tour of postglacial rebound
processes PHYSICAL MODEL a pre-stressed
self-gravitating spherical Earth Maxwell
viscoelastic rheology arbitrary parameter
stratification both compressible and
incompressible models cyclic loading and
unloading MATHEMATICAL MODEL initial value
approach (no Laplace transform) 1,2 momentum
equation, Poisson equation, constitutive
relation spherical harmonic decomposition set of
differential equations in time and radial
direction 4,5 pseudospectral discretization in
the radial direction on multi-domain Chebyshev
radial grids 4,5 numerically stiff initial
value problem inversion of sparse (block
diagonal) matrices OUTPUT time-dependent Love
numbers physical fields displacement vector
perturbed gravitational potential stress
tensor components VISUALIZATION HARDWARE Intel
Pentium IV 2 GHz RIMM 512 MB 800 MHz nVIDIA
GeForce4 MX 440 64 MB graphics card VISUALIZATION
SOFTWARE Amira v. 2.3 visualization of scalar
and vector fields in 3-D space and time extensive
set of input data formats easy color scaling,
zooming and adjusting the view direction movies
preparation capability scripting language DATA
PREPARATION time series of binary Amira Mesh
files with curvilinear coordinates and line
segments generated by a fast Fortran-90 code a
coordinate mesh deformed by exaggerated
displacement color rendering of the physical
fields hollow data objects allow to spare a
degree of freedom in the data format for
handling many various models with an
interactive speed MOVIES ON THE
WEB http//www.msi.umn.edu/lilli links to
larry_movies http//geo.mff.cuni.cz/lh
links to references REFERENCES 1 Hanyk L.,
Yuen D. A. and Matyska C., 1996. Initial-value
and modal approaches for transient viscoelastic
responses with complex viscosity profiles,
Geophys. J. Int., 127, 348-362. 2 Hanyk L.,
Matyska C. and Yuen D. A., 1998. Initial-value
approach for viscoelastic responses of the
Earth's mantle, in Dynamics of the Ice Age Earth
A Modern Perspective, ed. by P. Wu, Trans Tech
Publ., Switzerland, pp. 135-154 3 Hanyk L.,
Matyska C. and Yuen D. A., 1999. Secular
gravitational instability of a compressible
viscoelastic sphere, Geophys. Res. Lett., 26,
557-560. 4 Hanyk L., Matyska C. and Yuen D.A.,
2000. The problem of viscoelastic relaxation of
the Earth solved by a matrix eigenvalue approach
based on discretization in grid space, Electronic
Geosciences, 5, http//link.springer.de/link/servi
ce/journals/10069/free/discussion/evmol/evmol.htm.
5 Hanyk L., Matyska C. and Yuen D.A., 2002.
Determination of viscoelastic spectra by matrix
eigenvalue analysis, in Ice Sheets, Sea Level and
the Dynamic Earth, ed. by J. X. Mitrovica and B.
L. A. Vermeersen, Geodynamics Research Series
Volume, American Geophysical Union, pp. 257-273.
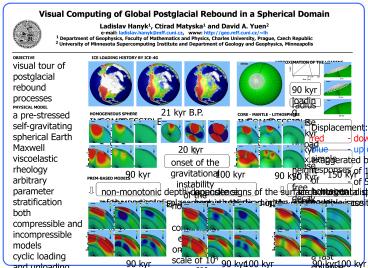
ICE LOADING HISTORY BY ICE-4G
APPROXIMATION OF THE LOADING HISTORY
height
0 90 100 150
0 kyr
time kyr
90 kyr loading phase 10 kyr unloading phase 50
kyr free decay
90 kyr
radius 15? max. height 3500 m
21 kyr B.P. 8 kyr B.P.
present
HOMOGENEOUS SPHERE INCOMPRESSIBLE
COMPRESSIBLE
CORE - MANTLE - LITHOSPHERE INCOMPRESSIBLE
100 kyr
Displacement red - down or from the axis blue -
up or towards the axis exaggerated by a factor
- of 100 vertically - of 500 horizontally
horiz. displacement vertical displacement
horiz. displacement vertical displacement
20 kyr 50 kyr 80 kyr
simple responses of homogeneous
incompressible models a fast collapse of
homogeneous compressible models
onset of the gravitational instability of the
homogeneous compressible sphere on the time scale
of 104 yr 3
90 kyr 100 kyr 150 kyr
90 kyr 100 kyr 150 kyr
PREM-BASED MODELS
non-monotonic depth-dependence of the vertical
displacement in realistic models
opposite signs of the surface horizontal
displacement beneath the load in the
compressible case
large horizontal deformations in the
low-viscosity zone
INCOMPRESSIBLE - isoviscous 1021 Pa s -
120-km lithosphere COMPRESSIBLE
- isoviscous 1021 Pa s - 120-km lithosphere
COMPRESSIBLE - lower mantle 2.1022 Pas -
LVZ 1019 Pas - lithosphere
horiz. displacement vertical displacement
horiz. displacement vertical displacement
horiz. displacement vertical displacement
90 kyr 100 kyr 150 kyr
90 kyr 100 kyr 150 kyr
90 kyr 100 kyr 150 kyr