Cochlear Implants - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Cochlear Implants
Description:
Cochlear Implants Andrew Rosenberg Department of Electrical, Computer, and Biomedical Engineering BME 181 The Healthy Human Ear Three Sections: (Outer ear, Middle ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:544
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cochlear Implants
1
Cochlear Implants
Andrew Rosenberg
Department of Electrical, Computer, and
Biomedical Engineering BME 181
2
The Healthy Human Ear
- Three Sections
- (Outer ear, Middle ear, and Inner ear)
- Sound waves are picked up by the outer ear
- and channeled to the middle ear
- The middle ear relays and amplifies the sound
- waves headed towards the inner ear
- The sound waves enter the inner ear and
- are translated into electrical impulses that
- The brain can interpret
3
Types of Hearing Impairments
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- -Usually deals with the middle ear and sound
amplification - -Hearing aids often help in sound amplification
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- -Deals with damage to the hair cells throughout
the cochlea - -Hearing aids generally do not help sensorineural
damage - -Cochlear implants are an innovative way to
compensate for the - damaged cochlea
4
How Does the Cochlear Implant Work?
- Microphone picks up sound waves
- Waves are translated into digital code by the
speech processor - The receiver/stimulator sends correct amount of
electrical energy to - electrodes implanted in the cochlea
- Electrodes directly stimulate remaining nerve
fibers in cochlea - Resulting electrical information is processed by
the brain
5
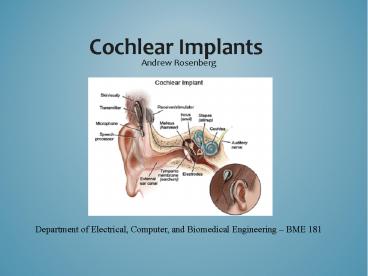
Parts of the Cochlear Implant
External Parts 1. Microphone 2. Speech
Processor 3. Transmitting Coil 5.
Transmitter Internal Parts 1.
Receiver/Stimulator 2. Internal Coil 3.
Electrodes
6
Candidates for a Cochlear Implant
Adults and Children 1. Severe to profound
hearing loss in both ears 2. Receive limited
benefit from hearing aids 3. No medical
problems that would complicate surgery 4.
Strong willingness to participate 5. Realistic
expectations (both patient and parents)
7
Internal and External Procedure
- 2-3 hour surgical procedure (under anesthesia)
- -small incisions made to insert
receiver/stimulator and electrodes - -patient usually leaves after surgery
- After 4-6 weeks
- -patient returns for external fitting and
activation - -adjusting and programming can take up to several
months - -rehabilitation with audiologists, speech
pathologists, and counselors
8
Cost-Effectiveness
- Considered one of the most cost-effective medical
procedures - Average cost between 50-60,000 for surgery,
programming, and - rehabilitation altogether
- Cochlear implants can eliminate much of the 1
million lifetime cost - cost to society for a child w/o a cochlear
implant - Insurance companies help more as time goes on due
to the increasing - societal benefit as cochlear implants improve
- Foreign Outlook Cochlear implants completely
covered by - U.K. government for its citizens
- Medicare in Australia
- Seguridad Social in Israel and Spain
9
Future
- As time goes on
- -implants become smaller
- -the magnets do not interfere with as much
technology - -external parts become less of a burden
- -batteries maintain longer life
- -implants are upgradable, so when new software
comes out - more surgery is unnecessary
Advanced Bionics newest implant
Older version of a cochlear implant
10
Works Cited
Information American-Speech-Language-Hearing
Association. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
lthttp//www.asha.org/public/hearing/Cochlear-Impla
nt/gt. "Cochlear Implants." NIDCD, n.d. Web. 08
Feb. 2013. lthttp//www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hearin
g/pages/coch.aspxgt. "Cochlear Implant." Wikipedia
. Wikimedia Foundation, 27 Jan. 2013. Web. 09
Feb. 2013. lthttp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cochlear_
implantgt. "How Hearing Works." HowStuffWorks.
N.p., n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013. lthttp//science.hows
tuffworks.com/life/human-biology/hearing.htmgt. W
hat Is a Cochlear Implant? University of Miami
School of Medicine, n.d. Web. 08 Feb. 2013.
lthttp//cochlearimplants.med.miami.edu/implants/in
dex.aspgt.
Pictures Kidshealth.org/parent/general/eyes/cochl
ear.htmlgt www.advancedbionics.com/us/en/products/
hires_90k_implant.html www.tinnitusformula.com/li
brary/cochlear-implants-and-electrical-stimulation
/ www.european-hearing.com




![[PDF] DOWNLOAD EBOOK Made to Hear: Cochlear Implants and Raising Deaf PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10132065.th0.jpg?_=202409170810)

























