ENVI 30 Environmental Issues PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: ENVI 30 Environmental Issues
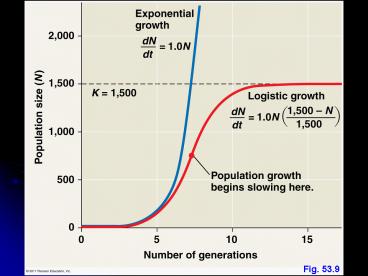
1
Fig. 53.9
2
Fig. 53.10
3
Soay Sheep Hirta Island
4
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Life History Strategies
- Finite amount of energy to allocate among growth,
reproduction, metabolism - Some species maximize reproduction others
maximize survival - r-selection
- Opportunistic species in variable environments
- Population usually much higher or much lower than
carrying capacity - Many weed/pest species
- K-selection
- Usually in stable environments
- Population usually at/near carrying capacity
- Many endangered species Why?
5
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Factors Affecting Population Growth/Size
- Density-Independent Factors
- Catastrophic events
- Ex Floods, fires, drought, storms, extreme
weather - Some aggregated organisms and social animals can
enhance resistance to density-independent factors - Ex Emperor penguins, clustered plants/animals
- Density-Dependent Factors
- Effects increase as population size increases
- Competition Limit resources (food, water,
etc.) - Territoriality Limit space availability
- Health Includes disease
- Predation Selective by predator(s)
- Wastes Toxic at higher concentrations
- Other Factors Ex Aggression at higher densities
6
(No Transcript)
7
Soay Sheep Hirta Island
Fig. 53.16
8
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Factors Affecting Population Dynamics
- Density-Independent Factors
- Catastrophic events
- Ex Floods, fires, drought, storms, extreme
weather - Some aggregated organisms and social animals can
enhance resistance to density-independent factors - Ex Emperor penguins, clustered plants/animals
- Density-Dependent Factors
- Effects increase as population size increases
- Competition Limit resources (food, water,
etc.) - Territoriality Limit space availability
- Health Includes disease
- Predation Selective by predator(s)
- Wastes Toxic at higher concentrations
- Other Factors Ex Aggression at higher densities
9
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Population Stability
- Stability usually related to lifespan,
reproductive rate - Environmental factors
- Resource availability
- Recruitment
10
Isle Royale
Fig. 53.18
11
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Population Stability
- Stability usually related to lifespan,
reproductive rate - Environmental factors
- Resource availability
- Recruitment
- Immigration
- Metapopulations may be more stable than isolated
populations
12
Glanville Fritillary
Fig. 53.21
13
- Population Ecology
- Population Dynamics
- Population Stability
- Stability usually related to lifespan,
reproductive rate - Environmental factors
- Resource availability
- Recruitment
- Immigration
- Metapopulations may be more stable than isolated
populations - Combined factors
- Resources, predation, etc.
14
Fig. 53.19
15
- Community Ecology
- Focus on interspecific interactions
- May be direct or indirect
- Competition
- Two or more species competing for scarce resource
- Ex Two plant species competing for water
- May be detrimental to one or both species
- Competitive exclusion
- No two species can use same set of resources in
same area at same time - Competitively dominant species tend to force
extinction of competitively inferior species
16
- Community Ecology
- Competition
- Ecological niche
- Species ecological role in a community
- Includes use of abiotic and biotic resources
- Niche occupied by a species may be narrower than
range of conditions tolerated by species - Fundamental niche vs. realized niche
17
Fig. 54.3
18
- Community Ecology
- Competition
- Resource partitioning
- Competitive exclusion can be minimized if
competing species modify niches to reduce overlap - Usually involves dividing resource
19
Anolis Dominican Republic
Fig. 54.2
20
- Community Ecology
- Competition
- Character displacement
- Resource partitioning may lead to directional
selection on one or both species - Directional selection may lead to divergence in
traits
21
Fig. 54.4
22
- Community Ecology
- Predation
- Involves consumption of prey by predator
- Predator usually has adaptations to facilitate
capture of prey - Natural selection acts on both predator and prey
- Coevolution
- Strategies
- Pursuit predation
- Predators chase prey to capture them
- Predator usually faster, stronger, /or more
agile than prey - Some species hunt in groups
- Ambush predation
- Predators lie in wait for prey
- Predators usually camouflaged or concealed
- May involve lures
- Aggressive mimicry
- Ex Bolas spider mimics odor of female moths to
attract male moths
23
(No Transcript)
24
- Community Ecology
- Predation
- Predator avoidance
- Escape
- Running/Swimming/Flying away
- Mechanical defenses
- Ex Porcupine quills, armadillo armor
- Social behavior
- Ex Schooling, standing watch
- Chemical defenses
- Ex Poison dart frog, skunk
- Defensive coloration
25
Cryptic coloration - Canyon tree frog
Aposematic coloration - Poison dart frog
Müllerian mimicry
Batesian mimicry Fig. 54.5
26
- Community Ecology
- Herbivory
- Consumption of plants by animals
- Most herbivores are small
- Ex Insects, snails/slugs
- Herbivores adapted to consume plants
- Some plants have anti-herbivore defenses
- Physical Ex Thorns, spines
- Chemical Ex Nicotine in tobacco, pyrethrins in
chrysanthemums - Coevolution has affected herbivore evolution
- Ex Monarch butterfly caterpillars can eat
milkweed - Toxic to most herbivores
- Nearly exclusive access to food source
- Can sequester noxious compounds for defense
27
- Community Ecology
- Parasitism
- Parasite benefits at expense of host
- Host harmed in process
- Ex Tapeworm absorbs nutrients from host
digestive system - Endoparasites Live within body of host
- Ectoparasites Live outside body of host
- Parasitoids Lay eggs on/in host larvae feed on
host, eventually killing host - Many parasites have complex life cycles
Fig. 33.12
28
Fig. 33.11
Schistosoma mansoni
29
- Community Ecology
- Disease
- Widespread disease outbreaks may alter community
composition and dynamics - Ex Dutch elm disease
- Ex Sudden oak death
- Ex Avian flu
- Ex West Nile virus