Endocrine System PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Endocrine System
1
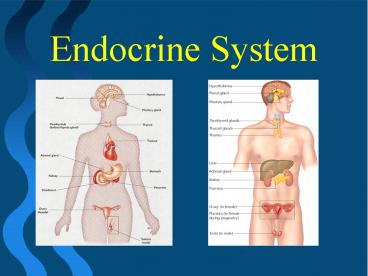
Endocrine System
2
Endocrine SystemGeneral Info
- Works WITH the Nervous system
- Main function is to produce hormoneschemical
messenger influencing other tissues/organs. - Differs from NS with regard to speed
- NSbody will make rapid adjustments to changes
- ESuses chemical messengers (hormones) to affect
change. Hormones travel via bloodstream.
Generally longer lasting.
3
Endocrine vs Exocrine glands
- Endocrine glandssecrete hormones directly into
the blood - anterior pituitary
- thyroid
- adrenal
- Exocrine glandsdeliver hormones into the blood
via tubes leading from the gland - sweat glands
- salivary glands
- mammary glands
4
Major body processes regulated by ES
- Reproduction
- Growth and development
- Maintaining homeostasis of electrolytes, water
and nutrients - Regulation of cellular metabolism
5
Target cells and controlling the ES
- Hormones travels through the entire body via the
blood, but only affect specific target tissues. - The body primarily uses negative feedback loops
to determine when to turn on/shut off hormone
production. - Other ways the body controls the ES is through
the nervous system and biorhythms.
6
ENDOCRINE REGULATION
A fuzzy balancing act Receive, Reaction,
Refine
7
- Sensory/Humoral input
- response to substance in the blood (Iodine,
glucose) - Hormonal regulation
- responds to upstream gland regulation (TSH,
LH...) - Neural regulation
- response short term stress
11
8
Endocrine RegulationREACT
- Hormones travel through the blood and bind to
receptor proteins - Steroid hormones (cholesterol derived)
- Are lipid soluble and cross the plasma membrane,
bind to receptors inside the cell and affect DNA
transcription. - Animation
- Non-steroid hormones (protein based)
- Bind to specific membrane receptors and trigger a
signaling cascade inside the target cell which
activates necessary enzymes. - Animation
9
- Steroids
- Lipid soluble - readily enter cells
- stimulus leads to biosynthesis
- transport in blood assisted by carrier proteins
(serum albumin)
10
- Non steroids
- Water Soluble can travel through blood freely,
but have to interact with membrane receptors
(cant cross lipid bilayer). Once docked, will
set cause changes within cell. - Protein is synthesized, packaged into vesicles
via golgi bodies - vesicles migrate to and collect at release site
- exocytosis to dump contents into bloodstream
11
(No Transcript)
12
REFINE Negative Feedback loops
- Works like a thermostat in your house to maintain
a constant environment of 68oF.
- Turns on the furnace to produce heat if the
temperature is too cold and off when the desired
temp is reached. - Turns on AC to cool the house if temp is too
high and shuts it off when back to the desired
temp.
http//www.endocrinesurgeon.co.uk/endocrine_condit
ions/What-is-negative-feedback.html
13
REFINEHomeostasis
- ensure the body returns to normal conditions
after stimulus.
www.mdmaterials.com
13
14
14
http//www.thetruthisbliss.com/wp-content/uploads/
2009/11/Calcium-Regulation.jpg
15
Endocrine System
- Down Regulation-Negative Feedback loop
Parathyroids
stimulates
Blood Ca2 levels Decrease
inhibits
-
Blood Ca2 levels Increase
PTH
Bone is degraded
16
Glucose Regulation
10
Biology, Campbell. 1987. pg 896
17
- Hypothalamus receives input and reacts to
stimulate specific organs to achieve the desired
effect.
18
Negative Feedback Loop--egs
- Feedback system for the control of ovulation
16
BiologyAn Exploration of Life, McFaddenKeeton.
1995. pg 546
19
Positive Feedback Loop
20
Endocrine System
- Removal of hormones
- The bulk of hormone is cleared by the liver and
kidneys - Only a small fraction is removed by target tissue
- Steroid (and thyroid hormones) are degraded after
hormone-receptor complex binds to DNA - action and elimination are slower (hours-days)
- protein and amine hormones (non steroids) bind to
receptors and are internalized and degraded - action and elimination is usually quicker
(minutes)
20
21
(No Transcript)
22
Endocrine Problems
- Dwarfism
- Characteristics
- -Short stature
- (proportional)
- Cause
- shortage of GH (hypophysial dwarfism)
- or defective receptor (Laron Syndrome).
www.blogsmonroe.com
23
- Gigantism
- Characteristics-
- Extreme height
- (8-9 ft, proportional structures)
- Cause-
- Excessive GH during development
Gigantism is extremely rare (only a few hundred
known cases total). Cause of excess of GH
excess varies but often is linked to Acromegaly
www.endotext.org
24
Endocrine Problems
- Acromegaly-
- Characteristics
- abnormal bone growth joint aches
- thick coarse oily skin impaired vision
- excessive sweating sleep apnea
- abnormal menstruation skin odor
- erectile dysfunction headaches
- fatigue and weakness decreased libido
- enlarged lips nose and tongue skin tags
Acromegaly- Cause-excess GH in adulthood.
Usually benign adenoma
www.addamsfamily.com
25
- Hypothyroidisim
- Characteristics-
- Fatigue, weakness, weight gain or resistance to
weight loss, course dry hair, dry rough pale
skin, hair loss, cold intolerance, muscle cramps
and aches, constipation, depression,
irritability, memory loss, abnormal menstruation,
decreased libido. - High TSH with low T3/T4.
- Cause- Not enough thyroid hormone.
- Hasimotos disease- autoimmune disease
- Medical treatments- hormone replacement
thyroid.about.com
www.datiskharrazian.com
26
- Hyperthyroidism
- Characteristics- palpitations, heat intolerance,
nervousness, insomnia, breathlessness, increased
BM, decreased menstruation, fatigue, fast heart
rate, trembling, weight loss, muscle weakness,
warm moist skin, hair loss, staring gaze. - Low TSH
- high T3/T4 levels
- Causes-
- Graves Disease autoimmune disease (antibodies
attach to thyroid and over stimulate T3
production) - Benign tumor- nodule (few cells)
- out of regulation
- Thyroiditis- temporary swelling
- of gland (postpartum)
pro.corbis.com
www.avondalevet.com
27
Endocrine DisordersHyperthyroidism cont
- Treatment-antithyroid medication, radioactive
iodine and possibly surgery (if trouble
swallowing or initial treatments dont work.
28
- Cushings Disease
- Characteristics-
- central body obesity Osteoporosis
- glucose intolerance kidney stones
- Hypertension excess hair growth
- menstrual irregularity emotional liability
- Buffalo hump moon face
- Cause- Excess Cortisol
- tumor of the lungs, pituitary or adrenal glands
29
- Diabetes-
- Most common Endocrine disorder
- Consistent elevated blood sugar
- Characteristics- frequent hunger, thirst,
urination, blurred vision, fatigue, weight loss,
poor wound healing, dry mouth, dry itchy skin,
impotence, recurrent infections. Erratic blood
sugar. - normal blood glucose 80-120mg/100 ml,
- diabetes as much as 600mg/100ml of blood
ourlatinamerica.blogspot.com
www.malluworld.org
30
Diabetes Causes- Type 1 -insulin deficiency
Type 2 -insulin resistance hormone
disturbance Agromegaly Cushings Gestat
ional diabetes- temporary condition caused by
pregnancy placenta metabolizes insulin quickly.
31
ENDOCRINE DISORDERS
32
Review of Endocrine System
- Quick review of info
- Amazing Podcast!
33
Endocrine System
- Glands and the hormones they produceyou will
need to know these for the test. - Study earlier rather than later!
34
- The pituitary gland secretes hormones that
regulate other glands in the body and therefore
is referred to as the Master Gland.
waukesha.uwc.edu
35
Hypothalamus
a region of the brain, between the thalamus and
the midbrain, that functions as the main control
center for the autonomic nervous system by
regulating sleep cycles, body temperature,
appetite, etc., and that acts as an endocrine
gland by producing hormones, including the
releasing factors that control the hormonal
secretions of the pituitary gland.
36
Hypothalamus Gland Hormones
- TRF
- Responsible for stimulating Pituitary to release
TSH
en.wikipedia.org
37
Hypothalamus Gland Hormones
- Oxytocin
- Responsible for causing uterine contractions
during and after birth.
38
Hypothalamus Gland Hormones
- GHRH (growth hormone releasing hormone)
- Responsible for triggering release of GH from
pituitary
www.uscnk.com
39
Hypothalamus Gland Hormones
- GnRH (gondatropin releasing hormone)
- Triggers release of FSH from pituitary.
commons.wikimedia.org
40
Pituitary
- Known as the master gland as it is not only
responsible for many hormones, it also acts as a
regulator for other glands in the endocrine
system.
41
Pituitary Gland Hormones
- ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone)
- Responsible for maintaining water balance in your
body.
42
Pituitary Gland Hormones
- GH (Growth Hormone)
- Causes growth in humansbig surprise huh?
43
Pituitary Gland Hormones
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
- Influences your thyroid gland
44
Pituitary Gland Hormones
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone)
- Regulates the adrenal glands
45
Pineal Gland
46
Pineal Gland Hormone
- Melatonin
- Helps your body adjust to various amounts of
daylight
47
Thyroid Gland
- Location Surrounds windpipe
48
Thyroid Hormones
- Thyroxine
- If iodine is present, it will control the
metabolism of glucose in the body.
49
Thyroid Hormones
- Calcitonin
- Responsible for depositing blood calcium into
bones
50
Parathyroid Glands
- Locationattached behind the thyroid
- Years ago, they used to remove the parathyroids
with the thyroid if the thyroid was damaged.
This lead to death in patientsOOPS!
51
Parathyroid Hormone
- PTH (Parathyroid hormone)
- Responsible for pulling calcium from bones and
depositing it into the bloodstream.
52
Thymus Gland
- Location Longish gland in the middle of your
chest.
53
Thymus Hormone
- Thymosin
- Assists the immune system
54
Adrenal Glands
- Location Located right on top of kidneys
55
Adrenal hormones
- Aldosterone
- Maintain blood salts (primarily Na, K)
56
Adrenal hormones
- Cortisol
- Kicks in to help body with long term stress.
57
Adrenal hormones
- Epinephrine
- Kicks in when body undergoes short term stress
- Test-taking, car accident, caught in a lieetc.
58
Pancreas
- Location Found right behind the stomach
59
Pancreas hormones
- Insulin
- Decreases blood sugar
60
Pancreas hormones
- Glucagon
- Increases
- blood sugar
61
Ovaries
- Small, almond shaped organs on the ends of the
fallopian tubes.
62
Ovary hormones
- Estrogen and Progesterone
- Responsible for sex characteristics and
controlling the menstrual cycle
63
Testes
- Testosterone
- Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics
64
Other structures and the ES
- Heart
- ANP will increase the Na excretion and inhibit
smooth muscle contraction
65
Other structures and the ES
- Kidney
- Renin will cause vasoconstriction of the blood
vessels (increases blood pressure)
66
Other structures and the ES
- G.I. Tract
- There are many polypeptide hormones that act on
the GI tract. - Most hormones will increase intestine motion and
enzyme production
67
Other structures and the ES
- Placenta
- HCG maintains embryo growth in first 90 days
gestation
68
Other structures and the ES
- Placenta
- Estrogen and Progesterone help maintain uterus
health - Lactogenic Growth hormone help with milk
production after birth of baby
69
www.abbottdiagnostics.com.