Stacks PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title: Stacks
1
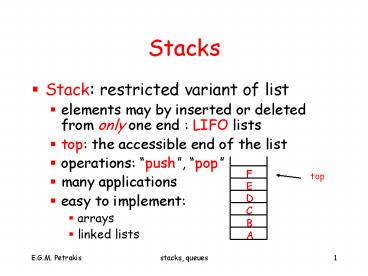
Stacks
- Stack restricted variant of list
- elements may by inserted or deleted from only one
end LIFO lists - top the accessible end of the list
- operations push, pop
- many applications
- easy to implement
- arrays
- linked lists
2
Array Implementation
- A simplified version of list implementation
- array of fixed size
- top always the first element
- current is always the top element
- push insert at top !
- pop remove from top !
3
Stack ADT
- interface Stack
- public void clear( ) //remove all ELEM's
- public void push(Object it) //push ELEM onto
stack - public Object pop( ) // pop ELEM from top
- public Object topValue( ) // value of top ELEM
- public bool isEmpty( ) // TRUE if stack is
empty
4
class AStack implements Stack // Array based
stack class private static final int
defaultSize 10 private int size //
Maximum size of stack private int top //
Index for top Object private Object
listarray // Array holding stack AStack()
setup(defaultSize) AStack(int sz)
setup(sz) private void setup(int sz) size
sz top 0 listarray new Objectsz
public void clear() top 0 // Clear all
Objects public void push(Object it) // Push
onto stack Assert.notFalse(top lt size,
"Stack overflow") listarraytop it
public Object pop() // Pop Object from top
Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "Empty stack")
return listarray--top public Object
topValue() // Return top Object
Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "Empty stack")
return listarraytop-1 public boolean
isEmpty() return top 0
5
Dynamic Memory Implementation
- Simplified version of the linked list
implementation - the head and tail pointers of the list
implementation are not used
6
class LStack implements Stack // Linked stack
class private Link top // Pointer to list
header public LStack() setup() //
Constructor private void setup() //
Initialize stack top null // Create
header node public void clear() top null
// Clear stack public void push(Object it)
// Push Object onto stack top new Link(it,
top) public Object pop() // Pop Object
from top Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "Empty
stack") Object it top.element() top
top.next() return it public Object
topValue() // Get value of top Object
Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "No top value")
return top.element() public boolean
isEmpty() // True if stack is empty return
top null // Linked stack class
7
Applications
- Checking mathematical expressions
- Equal number of left/right (, , , ), ,
8
Algorithm
- Read the expression from left to right
- p next symbol in expression
- Repeat until (empty(stack) )
- read(p)
- if p ( or or then push(stack,p)
- loop
- if p ) or or then c pop(stack)
- if c ! p then error!!
- if (not empty(stack) ) then error!!
9
(No Transcript)
10
More Applications
- Evaluation of arithmetic expressions
- convert infix to postfix or prefix
- evaluate postfix or prefix expression
- infix, prefix, postfix refer to the relative
position of the operator with respect to the
operands - infix AB
- prefix AB
- postfix AB
11
Infix to Postfix or Prefix
- Read from left to right
- First convert operations of higher precedence
- parenthesis have the highest precedence
- have precedence over
- , / have the same precedence but higher
than - , - which all have the same precedence
- The converted prefix or postfix part is treated
as a single operand - If all operators have the same precedence then
convert from left to right
12
Infix to Postfix or Prefix
- ABC gt
- A(BC) equivalent
- ?(?C) BC to postfix
- ABC postfix
- (AB)C () gt
- (AB)C AB to postfix
- (AB)C (AB)C to postfix
- ABC postfix
- Postfix and Prefix have no parenthesis !!
13
Infix to Postfix or Prefix
- AB-C ??C- postfix
- (AB)(C-D) ABCD-
- ??C-DE/F/(GH) ABCD-EF/GH/
- A-B/(CDE) ABCDE/-
- AB-C -ABC prefix
- (AB)(C-D) AB-CD
- ABC-DE/F/(GH) -ABCD//EFGH
- A-B/(CDE) -A/BCDE
14
Convert infix to postfix
- Read expression from left to right
- output operands
- push operators to stack
- higher precedence operators must be above lower
precedence operators - before pushing an operator into the stack check
the precedence of operators already in the stack - if operator in stack has higher precedence ?
output this operator and then insert the current
operator in the stack - (, , have higher precedence, push in
stack - if ), , pop stack until (, , is
found - dont output (, , , ), ,
15
Infix to Postfix Example
- (A B)C
- push ( in stack
- output A
- push in stack
- output B
- dont push ), pop all operators
- output , ignore (, )
- push in stack
- output C
- output
16
Example (A B)C
17
Algorithm
- stack NULL
- while (not end of input)
- symbol read next symbol
- if (symbol operand) output(symbol)
- else
- while(!empty(stack) (preced (stack(top)) gt
preced(symbol)) - top symbol pop(stack) output(top
symbol) - push(stack, symbol)
- while not_empty(stack)
- top symbol pop(stack)
- output(top symbol)
18
Evaluation of Postfix
- While (not end of expression)
- read symbols from left to right
- result 0
- if (symbol operand) push (stack)
- else
- operand1 pop(stack)
- operand2 pop(stack)
- result operand1 operator operand2
- push(stack, result)
- result pop(stack)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Queue
- Queue elements may only be inserted at the rear
and removed from the front - restricted form of list
- FIFO first in first out
- insert enqueue operation
- remove dequeue operator
21
(No Transcript)
22
Array Implementation
- If the elements are the first
- n elements of array and the
- front element is at position 0
- enqueue requires T(1) operations but,
- dequeue requires T(n) operations (all elements
must be shifted) - Condition of empty queue?
23
Front next available position Rear last
position Condition of empty queue rear front
Initial values rearfron LIST_SIZE - 1
front points to the position proceeding the first
element
front 4 rear 4
front 4 rear 0
input A
24
front 4 rear 2
front 4 rear 3
The condition of empty queue is true but the
queue is not empty ? E cannot be inserted The
last array position must be left empty
front 4 rear 4
25
(No Transcript)
26
Queue ADT
- public interface Queue // Queue ADT
- public void clear() // Remove all
Objects from queue - public void enqueue(Object it) // Enqueue
Object at rear of queue - public Object dequeue() // Dequeue
Object from front of queue - public Object firstValue() // Return value
of top Object - public boolean isEmpty() // Return TRUE
if stack is empty
27
class AQueue implements Queue // Array-based
queue class private static final int
defaultSize 10 private int size
// Maximum size of queue private int front
// Index prior to front item private
int rear // Index of rear item
private Object listArray // Array holding
Objects AQueue() setup(defaultSize) //
Constructor default size AQueue(int sz)
setup(sz) // Constructor set size void
setup(int sz) // Initialize queue
size sz1 front rear 0 listArray
new Objectsz1 public void clear()
// Remove all Objects from queue front
rear 0
28
- public void enqueue(Object it) // Enqueue
Object at rear - Assert.notFalse(((rear1) size) ! front,
"Queue is full") - rear (rear1) size // Increment
rear (in circle) - listArrayrear it
- public Object dequeue() // Dequeue
Object from front - Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "Queue is
empty") - front (front1) size // Increment
front - return listArrayfront // Return value
- public Object firstValue() // Return value
of front Object - Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty(), "Queue is
empty") - return listArray(front1) size
- public boolean isEmpty() // Return true
if queue is empty - return front rear
29
Dynamic Memory Implementation
- Simple adaptation of the linked list
implementation - current always points to the first element
- the head pointer of the list implementation is
not used
30
class LQueue implements Queue // Linked
queue class private Link front
// Pointer to front node private Link rear
// Pointer to rear node public
LQueue() setup() // Constructor
public LQueue(int sz) setup() //
Constuctor Ignore sz private void setup()
// Initialize queue front rear
null // Remove all Objects from queue
public void clear() front rear null
public void enqueue(Object it) // Enqueue
Object at rear of queue if (rear ! null)
// Queue not empty add to end
rear.setNext(new Link(it, null)) rear
rear.next() else front rear new
Link(it, null) // Empty queue
31
public Object dequeue() // Dequeue
Object from front Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty())
// Must be something to dequeue Object it
front.element() // Store dequeued Object
front front.next() // Advance
front if (front null) rear null //
Dequeued last Object return it
// Return Object public
Object firstValue() // Return value of top
Object Assert.notFalse(!isEmpty()) return
front.element() public boolean isEmpty()
// Return true if queue is empty return
front null // classes LQueue
32
Priority Queue
- Ascending elements in any order but dequeue
removes the minimum - Descending dequeue removes the maximum
33
Example Dequeue
34
Array Implementation
- Problem dequeue creates empty slots
- Solution(1) move elements T(n) operations on
dequeue - Solution(2) store elements in ascending
(descending) order T(n) operations on enqueue