Getting info from R(r) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Getting info from R(r)
Description:
Getting info from R(r) Identify the general form of the radial functions R = (constant)(eqn in )( x)(e- /y) What do the plots show you about nodes? – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:36
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Getting info from R(r)
1
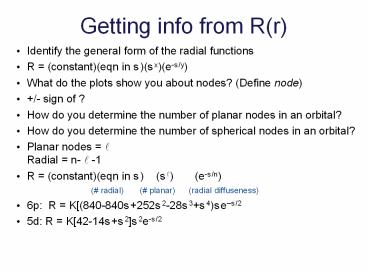
Getting info from R(r)
- Identify the general form of the radial functions
- R (constant)(eqn in s)(sx)(e-s/y)
- What do the plots show you about nodes? (Define
node) - /- sign of ?
- How do you determine the number of planar nodes
in an orbital? - How do you determine the number of spherical
nodes in an orbital? - Planar nodes ?Radial n- ? -1
- R (constant)(eqn in s) (s?) (e-s/n)
( radial) ( planar)
(radial diffuseness) - 6p R K(840-840s252s2-28s3s4)ses/2
- 5d R K42-14ss2s2e-s/2
2
Orbital Pictures
- Many ways to represent electron densityFigure
2.8 (p. 32) - Constant Electron Density
SurfacesValues are fraction of maximum electron
density - Terms used in describing orbitals gerade (d
orbitals), ungerade (p orbitals) - Figure 2.6 - Boundary surfaces (calculated
probability surfaces, 90) - Dot pictures - Photograph of electron location
over time
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Orbital Phases
7
(No Transcript)
8
Electrons in Orbitals
- Recall ms, spin quantum number (1/2)
- Aufbau principle building up electrons in
atoms, continuous increase in quantum numbers - Pauli exclusion principle each electron has a
unique set of quantum numbers
9
(No Transcript)
10
Electrons in Orbitals
- Hunds rule of maximum multiplicity
(multiplicity n 1 number of possible
energy levels that depend on the orientation of
the net magnetic moment in a magnetic field) - Why maximize multiplicity?Repulsion energy (?c -
coulombic, increases energy)Exchange energy (? e
- negative, lowers energy) - 2 electrons in p orbitals
- Degenerate orbitals favor maximum
multiplicity
11
Orbital Energy and Shielding
- Hydrogen atom (single electron) vs.Multi-elect
ron atoms - Why does this happen?Why does 1s fill before
2s?Why does 2s fill before 2p? - Radial functions, superimpose 1s, 2s, 2p
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Orbital Energy and Shielding
- Hydrogen atom (single electron) vs.Multi-elect
ron atoms - Why does this happen?Why does 1s fill before
2s?Why does 2s fill before 2p? - Radial functions, superimpose 1s, 2s, 2p
- Shielding, Slaters Rules (page 39)
- Do calculation for Li-Kr, main group elements
only - Transition metals - Cr, Fe, Ni (4s vs. 3d)
- Shielding and atomic size, IE, EA, orbital
energies
15
(No Transcript)
16
Slaters Rules of Shielding
- Z Z- S Z atomic S Shielding
- Write electron configuration in order of
increasing quantum - numbers n and l, grouping as follows
- (1s)(2s, 2p)(3s, 3p)(3d)(4s,4p)(4d)(4f)(5s, 5p),
etc. - 2. Electrons in groups to the right in this list
do not shield electrons to their left. - 3. The shielding constant S for electrons in
these groups are determined as - follows
- a. Each electron in the same group
contributes 0.35 to S. - (exception 1s electron
contributes 0.30 to another 1s electron) - b. Each electron in n-1 groups contribute
0.85 to S. - c. Each electron in n-2 or lower groups
contribute 1.00 to S. - 4. For nd or nf valence electrons
- a. Each electron in the same group
contributes 0.35 to S (same as for s and p) - b. All electrons in groups to the left
contribute 1.00 to S.
17
Examples
18
Electron configurations
- Transition, lanthanide, and actinide elements
19
Covalent radii
- Difficult to obtain consistent data - covalent,
atomic, van der Waals radii all frequently used
20
Atomic radii
21
Ionization energy and Electron affinity
- Define
- Explain the trends and the exceptions