Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint PPT Presentation
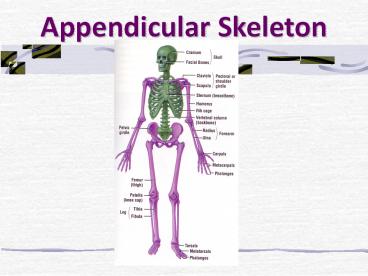
Title: Appendicular Skeleton
1
Appendicular Skeleton
2
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
3
Pectoral Girdle
- Attach the bones of the upper limbs to the axial
skeleton - Consist of two bones clavicle and scapula
- The joints are freely movable in many directions
4
Clavicle
- Also known as the collarbone
- Long, slender S-shaped bone that is horizontally
above the first rib - Transmits mechanical force from the upper limb
to the trunk
5
Scapula
- Also known as the shoulder blade
- Large, flat triangular bone situated in the
posterior part of the thorax
6
- A sharp ridge, the spine, runs diagonally across
the back portion of the scapula body - The lateral end of the spine is the acromion,
where the scapula articulates with the clavicle
7
- The glenoid cavity is a depression inferior to
the acromion. It articulates with the humerus
head to form the shoulder joint. - The coracoid process is where muscles attach.
8
Upper Limb
9
Upper Limb
- Consists of 30 bones (all paired up)
- Humerus in the arm
- Ulna and radius in the forearm
- 8 carpals, 5 metacarpals, and 14 phalanges in the
hand
10
Humerus
- Longest and largest bone of the upper limb
- Articulates with the scapula at the shoulder and
both the ulna and radius at the elbow
11
Ulna
- Located on the medial side of the forearm (pinky
side) - Longer than the radius
12
Radius
- Located on the lateral side of the forearm (thumb
side)
13
Humerus Bone Surface Markings
- Proximal end consists of a head that articulates
with the scapulas glenoid cavity and an
anatomical neck where the epiphyseal plate used
to be
14
- The body contains the deltoid tuberosity, a
roughened V-shaped area where the deltoid muscle
attaches
15
- At the distal end, the capitulum articulates with
the head of the radius. - The radial fossa is a depression that receives
the head of the radius when the forearm is bent.
16
- The trochlea is a spool-shaped surface that
articulates with the ulna. - The coronoid fossa receives part of the ulna when
the forearm is bent. - The olecranon fossa is a depression on the back
of the bone that receives the ulna when the
forearm is straightened.
17
Ulna Bone Surface Markings
- The olecranon forms the prominence of the elbow
on the proximal end. - The coronoid process along with the olecranon
receives the trochlea of the humerus in the
trochlear notch.
18
- The radial notch is a depression for the head of
the radius. - A styloid process is at the distal end.
19
Radius Bone Surface Markings
- Disc-shaped head at the proximal end articulates
with the capitulum of the humerus and radial
notch of the ulna - Radial tuberosity is a raised, roughened area
that is where the biceps brachii muscle attaches
to the bone
20
- The distal end of the radius articulates with
three carpal bones - Theres a styloid process at the distal end
(similar to the ulna)
21
Carpus (Wrist)
- 8 carpals
- Held together by ligaments with four bones in
each row - Named for their shapes
- Short bones
22
- The carpals in the top row are the
- Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, and Pisiform
- The carpals in the bottom row are the
- Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate
23
Metacarpus (Palm)
- 5 metacarpals
- Each consists of a proximal base, an intermediate
body, and a distal head - Numbered I-V starting with the thumb
- Long bones
24
Phalanges (Fingers)
- 14 in each hand
- Thumb has two (proximal and distal)
- In each of the other four digits, there are three
(proximal, middle, and distal)
25
Disorders of the Upper Limb
26
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Narrowing of the carpal tunnel causes compression
of the median nerve - The nerve compression causes pain, numbness,
tingling, and hand muscle weakness
27
Rotator Cuff Injury
- Tears or inflammation of ligaments and tendons of
the shoulder near the humerus - Results in pain and loss of shoulder mobility
28
Fractures
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
Checkpoint Questions
- Which bones make up a pectoral girdle? What is
the function of the pectoral girdle? - With which part of the scapula does the humerus
articulate? - What part of the ulna is called the elbow?
- What part of which bones are commonly called the
knuckles? - What bones form the upper limb, from proximal to
distal?