Topic 1: Lecture 3 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 48
Title:
Topic 1: Lecture 3
Description:
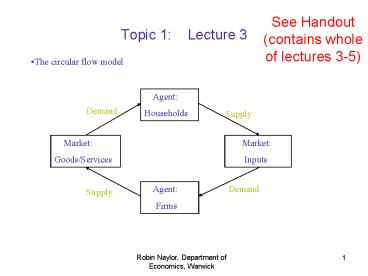
See Handout (contains whole of lectures 3-5) Topic 1: Lecture 3 The circular flow model Agent: Households Demand Supply Market: Goods/Services Market: – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:68
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Topic 1: Lecture 3
1
Topic 1 Lecture 3
See Handout (contains whole of lectures 3-5)
- The circular flow model
Agent Households
Demand
Supply
Market Goods/Services
Market Inputs
Agent Firms
Demand
Supply
2
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Demand
- Consider a Demand Relation
- What are the influences on Demand for a good . .
. ?
How does a change in some other influence affect
the demand curve?
px
a
po
What does the slope of the demand curve tell us?
b
D
X
Xo
3
Topic 1 Lecture 3
4
Topic 1 Lecture 3
5
Topic 1 Lecture 3
6
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Supply
- Consider a Supply Relation
- What are the influences on Supply a good . . . ?
How does a change in some other influence affect
the Supply curve?
px
S
What does the slope of the Supply curve tell us?
a
po
b
X
Xo
7
Topic 1 Lecture 3
8
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Putting together Supply and Demand
What is meant by the market equilibrium?
px
S
What are the possible properties of a market
equilibrium?
pe
D
X
Xe
9
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Comparative Statics
What is the effect on market equilibrium of a
shift in demand?
px
S
pe
D
X
Xe
10
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Comparative Statics
What is the effect on market equilibrium of a
shift in supply?
px
S
pe
D
X
Xe
11
Topic 1 Lecture 3
- Uniqueness of equilibrium and price bubbles
Suppose D is the Willingness to Pay for housing.
Its likely to depend on Consumer Confidence
(CC). (i) What happens if CC rises? (ii) What
might cause CC to rise? What is the implication
of this?
px
S
pe
D
X
Xe
12
Topic 1 Lecture 3
13
Topic 1 Lecture 3
14
Topic 1 Lecture 3
15
Topic 1 Lecture 3
16
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis (or analysis of Consumer
Choice) Choice is based on . . . . . .
Preferences and . . . Constraints Well
analyse each of these in turn.
17
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences Suppose your
happiness depends on just 2 commodities (that
you might buy in the market) e.g., ???
18
Topic 1 Lecture 4
- Demand Analysis Preferences
- E.g., Books and Food
- We assume that you have preferences over these
goods and that the nature of your preferences
satisfies various properties - Non-satiation . . . . . . in words
- Ordinal Ranking
- Transitivity
- Completeness
19
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences Non-satiation .
. . in a diagram.
B
a
b
B1
F
F1
F2
20
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences Our assumptions
about the properties of preferences imply that we
can represent preferences using Indifference
Curves. These ICs will have properties which
depend upon the properties of the underlying
preferences.
B
We can show that an IC must slope downwards
because of non-satiation.
a
b
B1
F
F1
F2
21
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences We can show that
ICs cannot cross under the assumptions we have
made about preferences
IC1
B
IC2
a
c
b
F
22
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences The slope of the
IC is the MRS between the 2 goods (refer to
earlier slides).
B
a
b
IC1
F
23
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences If the IC is
linear, this means that the MRS is constant.
B
a
b
IC1
F
24
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences It is more common
to assume that the MRS is diminishing why is
this and what does it imply about the IC?
B
a
b
F
25
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences It is more common
to assume that the MRS is diminishing why is
this and what does it imply about the IC?
B
IC1
F
26
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences What would it
mean if the IC was upward-sloping?
B
IC1
F
27
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences What would this
mean?
B
IC1
F
28
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences Under the
assumption of completeness, there is an IC
passing through every possible point
B
b
a
IC2
IC1
F
29
Topic 1 Lecture 4
Demand Analysis Preferences The consumer
would like to get to the highest possible IC
what limits this?
c
ICn
B
b
a
IC2
IC1
F
30
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints We said that our
understanding of Consumer Choice rests on the
analysis of Preferences and Constraints. Lets
now turn to consider Constraints.
Y
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
31
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints We can represent
a budget set and a budget frontier (or
constraint)
Y
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
32
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints We can represent
a budget set and a budget frontier (or
constraint)
Y
What equation can we give this constraint?
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
33
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints The equation
tells us that if we spend all our money income,
M, on X and Y, our spending be equal to
34
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints Re-arranging,
the equation for the budget constraint
is How do you interpret this equation? And
Graphically?
35
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints The equation of
the budget constraint
Y
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
36
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constraints Given the
position of the budget constraint, what will be
the consumers choice of X and Y? This will
depend on their preferences
Y
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
37
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constrained choice Given the
position of the budget constraint, what will be
the consumers choice of X and Y? This will
depend on their preferences
IC3
Y
IC1
IC2
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
38
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constrained choice Given the
position of the budget constraint, what will be
the consumers choice of X and Y? This will
depend on their preferences
ICmax
Y
Ymax
X
0
Xmax
39
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constrained choice Given the
position of the budget constraint, what will be
the consumers choice of X and Y? This will
depend on their preferences
Y
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
40
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Constrained choice So, by
bringing together preferences and constraints, we
have a model which predicts/explains the
consumers choices (demands) for X and Y . . .
given . . .?
Y
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
41
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Comparative Statics What will
happen to the optimal choices of X and Y if there
are relevant changes to the parameters of the
model?
Y
What are the relevant parameters?
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
42
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Comparative Statics What will
happen to the optimal choices of X and Y if there
are relevant changes to the parameters of the
model?
Y
Consider a change in money income. How do we show
this?
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
43
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
44
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
What can you say about the demand for X as
M?? And the demand for Y?
Ymax
â
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
45
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
What can you say about the demand for X as
M?? And the demand for Y?
â
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
46
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
What can you say about the demand for X as
M?? And the demand for Y?
â
Ymax
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
47
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
What can you say about the demand for X as
M?? And the demand for Y?
Ymax
â
a
Y
X
0
X
Xmax
48
Topic 1 Lecture 5
Demand Analysis Change in money income
Y
What can you say about the demand for X as
M?? And the demand for Y?
Ymax
a
Y
â
X
0
X
Xmax