Nervous Systems PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title: Nervous Systems
1
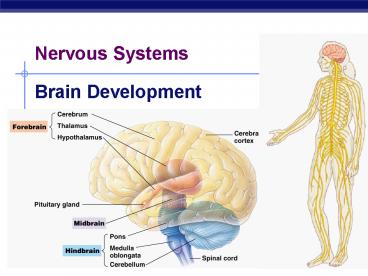
Nervous Systems
Brain Development
2
Nervous system
Centralnervoussystem
Peripheralnervoussystem
Spinalcord
Motorpathways
Sensorypathways
Brain
Somatic(voluntary)nervous system
Autonomic(involuntary)nervous system
- Sympathetic
- arousal energy production
- fight or flight
- Parasympathetic
- calming back to maintenance
- rest digest
Sympatheticdivision
Parasympatheticdivision
3
Types of neurons
cell body
sensory neuron
cell body
axon
interneuron
associative
dendrites
dendrites
cell body
motor neuron
4
Cephalization Brain evolution
- Cephalization clustering of neurons in brain
at front (anterior) end of bilaterally
symmetrical animals
?? where sense organs are
More organization but still based on nerve nets
supports more complex movement
Simplest, defined central nervous system more
complex muscle control
Simplest nervous system no control of complex
actions
5
Cephalization Brain evolution
- increase in interneurons in brain region
Further brain development ganglia neuron
clusters along CNS
More complex brains connected to all other parts
of body by peripheral nerves
More complex brains in predators most
sophisticated invertebrate nervous system
6
Evolution of vertebrate brain
?forebrain
???forebraindominant cerebrum
hindbrain
??forebrain
7
Human brain
8
Functional divisions of brain
- Hindbrain
- evolutionary older structures of the brain
- regulate essential autonomic integrative
functions - brainstem
- pons
- medulla oblongata
- midbrain
- cerebellum
- thalamus, hypothalamus
9
Brainstem
- The lower brain
- medulla oblongata
- pons
- midbrain
- Functions
- homeostasis
- coordination of movement
- conduction of impulses to higher brain centers
10
Medulla oblongata Pons
- Controls autonomic homeostatic functions
- heart blood vessel activity
- breathing
- swallowing
- vomiting
- digestion
- Relays information to from higher brain
centers
11
Midbrain
- Involved in the integration of sensory
information - regulation of visual reflexes
- regulation of auditory reflexes
12
Reticular Formation
- Sleep wakefulness produces patterns of
electrical activity in the brain - recorded as an ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG)
- most dreaming during REM (rapid eye movement)
sleep
13
Cerebrum
- Most highly evolved structure of mammalian brain
- Cerebrum divided
- hemispheres
- left right side of body
- right left side of body
- Corpus callosum
- major connection between 2 hemispheres
14
Lateralization of Brain Function
- Left hemisphere
- language, math, logic operations, processing of
serial sequences of information, visual
auditory details - detailed activities required for motor control
- Right hemisphere
- pattern recognition, spatial relationships,
non-verbal ideation, emotional processing,
parallel processing of information
15
Cerebrum specialization
- Regions of the cerebrum are specialized for
different functions - Lobes
- frontal
- temporal
- occipital
- parietal
16
(No Transcript)
17
Limbic system
Mediates basic emotions (fear, anger), involved
in emotional bonding, establishes emotional memory
Amygdala involved in recognizing emotional
content of facial expression
18
Simplest Nerve Circuit
- Reflex, or automatic response
- rapid response
- automated
- signal only goes to spinal cord
- no higher level processing
- adaptive value
- essential actions
- dont need to think or make decisions about
- blinking
- balance
- pupil dilation
- startle
19
Eye Blink or Pain Withdrawal Reflex
Gray matter
Interneuron
Stimulus
White matter
Receptor in skin
Sensory neuron
Motor neuron
Spinal cord
Effector (muscle)
20
Any Questions??