Mass Spectrometry PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Mass Spectrometry
1
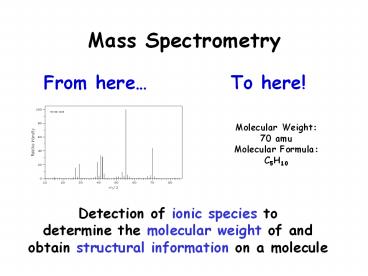
Mass Spectrometry
To here!
From here
Molecular Weight 70 amu Molecular Formula
C5H10
Detection of ionic species to determine the
molecular weight of and obtain structural
information on a molecule
2
Mass spectrometry
3
Fig. 12-1, p. 410
4
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectromety (GC-MS)
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectromety (LC-MS)
5
Base peak Molecular ion (M)
-CH3
6
Mass Spectrum of Hexane
Chemical Formula C6H14 Exact Mass
86.1095 Molecular Weight 86.1753
Fig. 12-4, p. 413
7
Fig. 12-5, p. 413
8
methylcyclohexane or ethylcyclopentane ?
Fig. 12-6, p. 414
9
(No Transcript)
10
Isotope effects
Molecular weight Br 79.9040
Br isotopic abundance 79Br 50.5 81Br 49.5
CH379Br
CH381Br
11
(No Transcript)
12
Fragmentation by a-cleavage
- a-cleavage (cleavage of bond one removed from
radical or radical cation) - Carbonyl compounds
13
-CH3
-CH3
14
Fragmentation by a-cleavage
- a-cleavage (cleavage of bond one removed from
radical or radical cation) - Carbonyl compounds
- Amines and alcohols
- Alkenes
15
Fragmentation by a-cleavage
- a-cleavage (cleavage of bond one removed from
radical or radical cation) - Carbonyl compounds
- Amines and alcohols
- Alkenes
16
Fragmentation by a-cleavage
- a-cleavage (cleavage of bond one removed from
radical or radical cation) - Methyl benzene (toluene) compounds
17
18
m/z 102
Fig. 12-8, p. 416
19
Determination of FormulaRule of 13
Assumes CnHn and amu equivalent (13 for n1) is
present in all molecular fragment ions Step 1
Divide M mass by 13, this gives n Step 2 Any
remainder represents count of additional
H's example 1 for M 78 78 13 6 ? n 6
? C6H6 example 2 for M 92 92 13 7.077
? n 7 7 x 13 91 ? 1 extra H is
present Formula is C7H71 C7H8
20
Determination of FormulaRule of 13
example 3 for M 161 161 13 12.385 ? n
12 12 x 13 156 ? 5 extra H's are
present Formula is C12H125 C12H17 What
about heteroatoms? Step 1 First derive formula
as above Step 2 Next, modify using CnHm
equivalents
21
Problem
An unknown compound subjected to mass
spectrometry gave the parent ion at m/z 114.
The parent ion quickly undergoes homolytic
?-cleavage to give fragment ions with m/z 99
(100 ) and m/z 45 (45 ). No other significant
peaks are seen the in spectrum. The unknown does
not react when treated with H2, Pd/C. The
infrared spectrum of the unknown shows a strong,
broad peak at 3500 cm-1. Show the reaction and
the electron pushing mechanism that accounts for
the fragmentation of the parent ion to give
either of the observed fragments.
22
MS Ionization Techniques
- Electron Impact (EI)uses beam of electrons
- Fast Atom Bombardment (FAB)uses beam of atoms
- Chemical Ionization (CI)uses chemical reactions
- Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption (MALDI)uses
lasers to ionize molecules - Electrosprayuses compounds which are already
ionic