Refraction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: Refraction
1
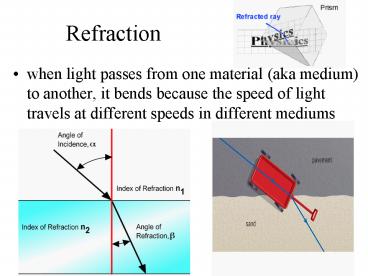
Refraction
- when light passes from one material (aka medium)
to another, it bends because the speed of light
travels at different speeds in different mediums
2
Light bends toward the normal when it slows
down, and away from the normal as it speeds up.
- vacuum 3.0 x 108 m/s - water 2.26 x 108
m/s - acrylic 1.76 x 108 m/s
3
Light travels thru water
- (why we see blue best)
4
- This bending of light can play tricks on our
minds. Ie. Broken/Bend pencil/spoon.
5
- This is why a fish in the water looks just below
the surface, and may be deeper and further away.
6
Another Trick
Light travels faster at higher altitudes because
the air is less dense.
7
- Another example of refraction of light is the
twinkling of a star in the night sky - As starlight travels from space into the Earths
atmosphere, the rays are refracted. - Since the atmosphere is constantly changing, the
amount of refraction also changes.
8
- Light can undergo partial reflection and
refraction at the same time at a surface. - Ex. Sunglasses, two way mirrors (buildings less
air conditioning)
9
Refraction Lab
Purpose To determine relative speeds of light
through different mediums
- Observations
- 1. Trace a petri dish, label the normal and draw
in an incident light ray for you to follow. - 2. Fill the petri dish with water
- 3. Shoot the light ray down the incident ray.
- 4. Trace the light ray coming out of the petri
dish - 5. Remove petri dish and connect the lines and
label water - 6. Repeat steps 2 5 with glycerin in petri
dish. - 7. Use a protractor to label the incident angle
and both of the refracted angles.
10
- Analysis
- Which ray bends most toward the normal air,
water, glycerin? Which ray bends the least? - Which substance is the light travelling the
fastest in and why? - Which substance is the light travelling the
slowest in and why?
11
- Dispersion
- - The refraction of white light into different
colours. (Pink Floyd dark side of the moon) - - Since each colour travels at a different
speeds, it bends at different angles
12
- Ex. Rainbows in order to see a complete
rainbow, you need to stand so that its raining in
front of you, and the sun is directly behind you.
13
Total Internal Reflection
- Sometimes light bends (refracts) so much that
- it hits the inside wall of a substance at 90
degrees, - and totally reflects off (no refraction occurs).
The light gets trapped inside the - object.
14
Ex. Fiber Optics used to send signals quickly
over long distances glasses, phone cables,
surgery
Demo dollar store fibre optics
Demo laser follows stream of water (2L water
bottle)
15
- Ex. Diamonds
- jewellers cut angles surfaces (facets) to
make the light become trapped in diamond, and
reflect out the top, making it sparkle.
16
Prisms
17
- Pg. 503 1 3, 7