Population Health Curriculum for Health Professionals - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title: Population Health Curriculum for Health Professionals
1
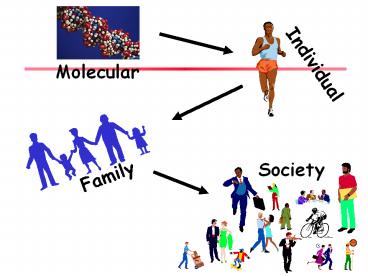
Individual
Molecular
Society
Family
2
(No Transcript)
3
Measurements of disease factors influencing health
4
Objectives
- To understand the importance of parameters
measuring healthy conditions social, cultural
and economical. - You students should also be capable to understand
the role of human genetics, food and nutrition,
infectious agents, environment and education in
health status.
5
What is Health?
6
Individual
Molecular
Society
Family
7
Health is a state of complete Physical, Mental,
and Social well-being and not merely the absence
of disease or infirmity. WHO, 1948
The Metaphysical Context of the Universe
Physical
Mental
Social
The Secular Dimensions of Health
8
Two Major Aspects ofHealth
- Feeling Well
- Ability to Function
9
Determinants of Health
- the complex inter-relationships of
- genetics
- social environment
- physical environment
- behavior
- health/illness services
- that determine the level of health and sense of
well-being in an individual
10
Genetics
- Body Size
- Special Abilities
- Disease Resistance
- Disease Susceptibility
- Genetic Diseases
- General Robustness
11
Physical Environment
- Macro-environment
- Food and Water
- Air Pollution
- Micro-environment
- Home
- Workplace
12
Social Environment
- Religion
- Race/Gender
- Socioeconomic Status
- Education
- Occupation
- Family Composition
13
Socioeconomic Status, Income and Health
- Socioeconomic Status
- As GDP increases, the health of a nation
increases - In times of economic hardship, the incidence of
disease increases
14
Health Care
- Quality
- Availability
- Health has improved NOT because of steps taken
while we are ill, but because we are ill less
often.
Thomas McKeown, 1978
15
Primary Prevention
- Measures taken to prevent the disease from
occurring such as - healthy lifestyle habits
- Immunizations
16
Secondary Prevention
- Measures undertaken to facilitate early detection
- Screenings
- Diagnostic tests
17
Tertiary Prevention
- Measures to minimize complications or
exacerbation of injury or disease. - Rehabilitation Therapy
- Patient counseling
18
Rising Life Expectancy
Source United Nations (U.N.) Population
Division, Demographic Indicators, 1950-2050 (The
1996 Revision) (U.N., New York, 1996).
19
Prevention and Religion
- Washing Hands
- Hands should be washed when one touches something
polluted or unclean likewise, before or after
eating. - The Prophet, Peace Be Upon Him, said Whoever
sleeps and his hands are not clean from fat and
thereby gets harmed should blame no one but
himself - The Prophet, Peace Be Upon Him, used to wash his
hands before eating
20
Historical Examples of Global Prevention
Activities
Model for acute infectious agents
21
Death rate for Tuberculosis, 1860-1960, United
States, Source US Bureau of the Census,
Historical Statistics of the United States
Colonial Times to 1970 (Washington, D.C
Government Printing Office, 1975), Part 1
pp58,63. Note Data between 1860 and 1900 for
Massachusetts only.
Koch identified tubercle bacillus
Streptomycin introduced
Vaccination available
22
The Sanitary Revolution and the Ascendancy of
Public Health
- The sanitary revolution produced the greatest
transformation in the pattern of disease that the
world had known since nomadic hunter-gatherers
settled in permanent villages, and ultimately
developed modern urban industrial communities
23
Death Rates for Measles in Children Under Age 15,
England and Wales, 1850-1970
Source Thomas McKeown, The Modern Rise of
Population (Academic Press, San Francisco, 1976),
pp. 93, 96.
24
Epidemiologic Transition, MexicoDecline in
Communicable, Rise of NCDs
25
(No Transcript)
26
Example of successful prevention program in
Cuba VACCINATION PROGRAM RESULT
POLIO ELIMINATED SINCE
1962 DIPHTHERIA ELIMINATED SINCE 1969 NEWBORN
TETANUS ELIMINATED SINCE 1972 CONGENITAL
RUBELLA ELIMINATED SINCE 1989 MENINGITIS POST
MUMPS ELIMINATED SINCE 1989 MEASLES
ELIMINATED SINCE 1993 WHOOPING COUGH
TRANSMISSION INTERRUPTED SINCE 1994 RUBELLA
TRANSMISSION INTERRUPTED SINCE
1995 MUMPS TRANSMISSION
INTERRUPTED SINCE 1995 MORBIDITY MENINGOCOCCICA
L DISEASE REDUCTION 93 TYPHOID
FEVER REDUCTION 75 B
HEPATITIS REDUCTION 52
27
Introduction
- Cervical cancer is the 2nd most common cancer
among women globally - Higher cervical cancer mortality in developing
countries due to lack of effective screening
programs
28
Estimated impact of AIDS on under-5 child
mortality rates Selected African countries, 2010
Source US Bureau of the Census
29
Death Rates for Coronary Heart Disease by Country
Men Ages 35-74, 1970 and 1993 (Rate/100,000)
750
FIN
USA
AUST
SCOT
NZ
CAN
500
SING
USSR
250
ITY
SPN
FRAN
JPN
HK
CHN
0
30
Lifestyle Factors
Genes load the gun.Lifestyle pulls the trigger
Dr. Elliot Joslin
31
(No Transcript)
32
What is the future of prevention?
- Globalization of Prevention
- Networking of people in prevention
- Sharing of data, knowledge and wisdom
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
Objectives
- To understand the importance of parameters
measuring healthy conditions social, cultural
and economical. - You students should also be capable to understand
the role of human genetics, food and nutrition,
infectious agents, environment and education in
health status.