Hydrological Cycle PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
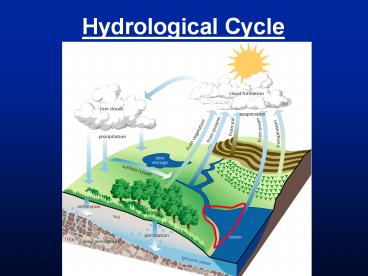
Title: Hydrological Cycle
1
Hydrological Cycle
2
Estuaries
- Estuary semi-enclosed body of water where
freshwater from land drainage dilutes sea water. - Fresh ? Brackish ? Marine extent of salinity
types varies with stream discharge, wave action,
tidal action, evaporation, etc. - VARIABLE
3
(No Transcript)
4
Types of Estuaries
partially mixed
salt wedge
well mixed
fjord-type estuary with a sill
5
Estuary Substrates
- Substrates is estuaries usually are dominated by
the sediment and FPOM transported by the stream
input. (low tide may revel mud flats) - Sedimentation may form
- a delta if tidal and wave
- action is low enough.
- Mississippi delta
6
Estuary Sides
STREAM-SIDE Stream Discharge Freshwater Higher
Turbidity (FPOM, DOM, Sediment)
OCEAN-SIDE Waves Tides Marine Water Lower
Turbidity (usually)
7
Drought, Floods, Tides
- Drought less freshwater estuary becomes more
saline and less sediment w/ FPOM. - High Tide more marine water estuary becomes
more saline. - Floods lots of freshwater estuary becomes
much less saline and sediment with FPOM may be
deposited less in the estuary itself (blown out
of the estuary) - Low Tide less marine water estuary becomes
less saline.
8
In-Estuary Primary Production
- High turbidity often reduces (or eliminates)
in-estuary submerged photosynthesis closer to the
stream input. - Salt-tolerant marginal emergent macrophytes
undergoes significant production, especially in
higher order streams. (e.g., Spartina) - Periphyton (microphytes) may be able to undergo
in-stream photosynthesis on the substrate (mud)
surface (often at low tide). - Phytoplankton often important in more protected
estuaries and at the seaward side.
9
Allochthonous Inputs
- In most estuaries the most nutrients come from
surrounding terrestrial environments via stream
discharge (allochthonous materials) - Most enters as FPOM or DOM. Limited CPOM, but
some from surrounding emergent macrophytes. - Detritivores and decomposers are very important
in most estuaries. - The flats (mud flats) of estuaries often are very
productive. - Deoxygenation of sediments often occurs.
10
Estuary Food Web
11
Salt Marsh
12
Salt Marsh(Protected Shallow Estuary with
Spartina)
13
(Tropical) Mangrove Swamp Estuary(Shallow
Estuary with Rhizophora)
14
Estuary Animals
- Freshwater Animals Most have a low
salinity-range tolerance (stenohaline) and are
restricted to the upper estuary (salinity lt7). - Stenohaline Marine Animals have a low range of
salinity tolerance are restricted to the outer
estuary (salinity gt25). - Euryhaline Marine Animals have a high range of
salinity tolerance and are found in most of the
estuary (salinity gt15). - Estuarine Animals All have a wide range of
salinity tolerance and many can inhabit much of
the estuary (including hypersaline isolated
areas). Most in salinity 5-18.
15
ChesepeakeBay Species OxygenTolerances
16
Human Impacts Development
- Low land in the estuary protected from flood or
tidal inundation and developed. - Increases sedimentation in channel, water
velocity, and estuary cleaning of water before
it reaches the ocean. - Similar to stream
- channelization.
17
Human Impacts Barrages
- Barrages block tidal and other increased water
flow from entering from seaward. - -May protect from storm or flooding surges.
- -May keep water fresh for use locally.
- Increase sedimentation.
- Change to more freshwater environment.
- May prevent or impede spawning migrations.
18
Human Impacts Pollution
- Many human population centers are in or drain to
estuaries (sewage and other pollution). - Heavy metals in sediments are of concern.
- Estuaries can be nutrient overloaded. Red
Tides and other algal blooms.