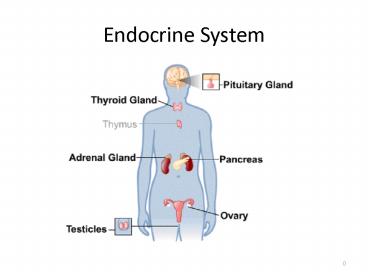
Endocrine System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 72
Title:
Endocrine System
Description:
What is hypocalcemia and what are its effects? * Have students state the potential causes of these abnormalities and whether or not they can be treated. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:340
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Endocrine System
1
Endocrine System
2
Learning Objectives Endocrine System
- Identify the endocrine glands and their hormones.
- Gain an understanding of the functions of these
hormones in the body. - Analyze medical terms related to the endocrine
glands and their hormones.
3
Learning Objectives (contd.)
- Identify abnormal conditions resulting from
excessive and deficient secretions of the
endocrine glands. - Describe laboratory tests and clinical procedures
related to endocrinology, and recognize relevant
abbreviations. - Apply your new knowledge to understanding medical
terms in their proper contexts, such as medical
reports and records.
4
The Endocrine System p. 746
- Glands release hormones
- Hormones regulate the many and varied functions
of an organism - Hormones bind to receptors
- Receptors are recognition sites in the various
target tissues on which hormones act - http//study.com/academy/lesson/hormones-definitio
n-function-intro-to-the-endocrine-system.html
5
(No Transcript)
6
Two Types of Glands
- ENDOCRINE glands
- Secrete their hormones directly into the
bloodstream - EXOCRINE glands
- Send chemical substances (tears, sweat, milk,
saliva) via ducts to the outside of the body. - https//www.youtube.com/watch?vVBwCBdd0ru8
7
Glands page 747
8
Thyroid Gland page 748
9
Thyroid Function page 748
- Two hormones secreted by thyroid
- thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine (T4)
- triiodothyronine (T3)
- Thyroid hormones aid cells in their uptake of
oxygen and regulate metabolic rate
10
Thyroid Gland
- Calcitonin stimulates calcium to leave the blood
and enter the bone - https//www.youtube.com/watch?vbsM5-PV_ObQ
- New hormone recently discovered
11
Thyroid Gland Hormones and Actions
12
Parathyroid Gland - page 749
13
Parathyroid Glands page 750
14
Parathyroid Function
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- causes calcium to mobilize from bones into the
bloodstream
15
Adrenal Glands page 751
16
ADRENAL GLANDS
- Each gland has two parts
- an outer portion, the adrenal cortex
- Secretes corticosteriods or steriods, chemicals
derived from cholesterol - an inner portion, adrenal medulla
- Secretes catecholamines
- chemicals derived from amino acids
17
Adrenal CORTEX Secretes
- Glucocorticoids influence metabolism of sugars,
fats, and proteins (cortisol) and are
anti-inflammatory (cortisone). - Influences--SUGAR
- Mineralocorticoids regulate electrolytes
- Aldosterone reabsorption of sodium/excretion of
potassium. InfluencesSALT (and BLOOD PRESSURE) - Gonadocorticoids androgens and estrogens.
Influences--SEX
18
Adrenal MEDULLA Secretes
- Two types of catecholamine hormones
- Epinephrine (adrenaline) increases heart rate
and blood pressure, dilates bronchial tubes,
releases glucose from storage - Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) constricts
vessels to raise blood pressure
19
The Adrenal Cortexand Adrenal Medulla
20
Pancreas page 752
- Located near and partially behind stomach
- Exocrine and endocrine organ
21
Pancreas Function
- islets of Langerhans produce
- Insulin promotes movement of glucose into cells
and promotes storage as glycogen - Glucagon promotes movement of glucose into the
blood by breaking down glycogen stored in liver
cells
22
Pancreas Function
23
(No Transcript)
24
Pituitary Gland page 753
- Pea-sized gland in depression of skull (sella
turcica) also called the hypophysis - Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis)
- Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis)
- Hypothalmus controls secretions of the pituitary
via releasing factors (hormones)
25
Pituitary Gland
26
Pituitary Function page 754
- Anterior Pituitary secretes the following
hormomes - Growth hormone (GH) increases bone and tissue
growth - Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH thyrotropin)
27
(No Transcript)
28
Pituitary Function
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulates
cortisol secretion - Gonadotropic hormones (FSH, LH)
- Prolactin (PRL)
29
Pituitary Function (contd.)
- Posterior pituitary stores and releases hormones
synthesized in the hypothalamus - Antidiuretic hormone (ADH vasopressin)
increases water reabsorption by kidneys - Oxytocin (OT)
30
Pituitary Gland Hormones and Actions page 755
31
Ovaries and Testes Hormones and Actions page
755-756
32
Table 18-2
- See page 756 for summary of major endocrine
glands, hormones they produce, and their actions.
33
COMBINING FORMS page 760
- GLANDS
- aden/o gland
- adren/o adrenal glands
- adrenal/o adrenal glands
Combining Form Meaning
34
Combining Forms
- Combining Form Meaning
- gonad/o sex glands (ovaries, testes)
- pancreat/o pancreas
- parathyroid/o parathyroid gland
35
Page 760 - Glands
- pituitar/o pituitary gland
- thyr/o thyroid gland
- thyroid/o thyroid gland
Combining Form Meaning
36
Combining Forms - Page 760-761
- andr/o male
- calc/o, calici/o calcium
(hypocalcemia) - cortic/o cortex, outer region
- crin/o secrete (endocrine)
Combining Form Meaning
37
Combining Forms
- Combining Form Meaning
- dips/o thirst (poly dipsia)
- estr/o female
- gluc/o, glyc/o sugar (hyperglycemia
)
38
Glands - Page 761
Combining Form Meaning
- home/o sameness
- hormon/o hormone
- kal/I potassium (an electrolyte)
39
Glands
- Combining Form Meaning
- lact/o milk
- myx/o mucus
- natr/o sodium
40
Glands - Page 762
Combining Form Meaning
- phys/o growing
- somat/o body (somatotropin)
- ster/o solid structure
41
Glands
- Combining Form Meaning
- toc/o childbirth
- toxic/o position
- ur/o urine
42
Suffixes - page 763
Suffix Meaning
- -agon assemble, gather together
- -emia blood condition
- -in, -ine a substance
43
Suffixes
- Suffix Meaning
- tropin stimulating the function of
- -uria urine condition
44
Prefixes - page 763
- eu- good, normal (euthyroid)
- hyper- excessive, above
- hypo- deficient, below
- oxy- rapid, sharp, acid
Prefix Meaning
45
Prefixes
- Prefix Meaning
- pan- all
- tetra- four
- tri three
46
QUICK QUIZ
- Which term means a blood condition of too little
potassium? - hyperkalemia
- hypocalcemia
- hypercalciuria
- hypokalemia
47
Thyroid Abnormalities page 764
- Goiter Enlargement of the thyroid
- https//www.youtube.com/watch?vSVSBo065hmw
48
Thyroid Abmormalities
- Hypersecretion
- Hyperthyroidism
- Graves disease Autoimmune
- Exophthalmos and proptosis
49
Thyroid Abnormalities
- Hyposecretion
- Hypothyroidism
- Myxedemaswelling of the skin and underlying
tissues giving a waxy consistency, typical of
patients with underactive thyroid glands. - Cretinism characterized by physical deformity, dw
arfism, and mentalretardation, and often by goiter
. - Neoplasms
- Thyroid carcinoma
50
(No Transcript)
51
Thyroid carcinoma
52
Parathyroid Abnormalities page 765
- Hypersecretion
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Loss of bone density
- Kidney stones
- Hypercalcemia
- https//www.youtube.com/watch?vsD9st1ZPFrQ
53
(No Transcript)
54
Parathyroid Abnormalities
- Hyposecretion
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Deficient production of parathyroid hormone leads
to hypocalcemia which leads to tetany
55
Abnormalities of Adrenal Cortex page 766
- Hypersecretion
- adrenal virilism excessive androgens
- amenorrhea (absence of menstruation),
hirsutism, acne, voice deepening - Cushing syndrome excessive cortisol
- Obesity, moon-face, thoracic fat deposition
56
hirsutism
57
(No Transcript)
58
Abnormalities of Adrenal Cortex
- Hyposecretion
- Addison disease low cortisol and aldosterone
levels - hyponatremia, fatigue, weakness, low blood
pressure
59
(No Transcript)
60
Abnormalities of Adrenal Medulla page 767
- Pheochromocytoma
- Benign tumor of adrenal medulla
- Excess epinephrine and norepinephrine
- Hypertension, palpitations, severe headaches,
sweating, flushing of the face, and muscle spasms
61
Abnormalities of the Pancreas
- Hypersecretion
- Hyperinsulinism excessive secretion of insulin
causing - Hypoglycemia, convulsions, fainting
62
Pancreas
- Hyposecretion
- Diabetes mellitus
- Lack of insulin secretion or resistance of
insulin in promoting sugar, starch and fat
metabolism in cells - Type 1 childhood onset typically
- Type 2 adult onset typically
63
Comparison of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
64
Abnormalities Pituitary Gland (Anterior Lobe)
- Hypersecretion
- acromegaly
- gigantism
- Hyposecretion
- dwarfism
- panhypopituitarism
65
(No Transcript)
66
(No Transcript)
67
(No Transcript)
68
Abnormalities Pituitary Gland (Posterior Lobe)
- Hypersecretion
- Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH)
- Excess ADH
- Excess water retention
- Hyposecretion
- Diabetes insipidus
- Deficient ADH
- Polyuria and polydipsia
69
Review Abnormal Conditions of Endocrine Glands
page 748
70
Laboratory Tests page 748
- Fasting blood sugar (FBS)
- Measures circulating glucose in a patient who has
fasted at least 4 hours - Serum and urine tests
- Measures hormones, electrolytes, glucose, etc. in
blood and urine as indicators of endocrine
function - Thyroid function tests
- Measures T3, T4, and TSH in the bloodstream
71
Clinical Procedures page 749
- exophthalmometry
- computed tomography (CT) scan
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head
- radioactive iodine uptake
- thyroid scan
- ultrasound examination
72
QUICK QUIZ
- What is the pathologic condition in which
enlargement of the extremities is caused by
hypersecretion of the anterior pituitary after
puberty? - Addison disease
- acromegaly
- Cushing syndrome
- Graves disease