Light Spectrum - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 62
Title:
Light Spectrum
Description:
Figure 26-1 Wave Fronts and Rays ... Light Spectrum – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:112
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Light Spectrum
1
Light Spectrum
2
Remember when we said that light travels as
electromagnetic waves? Well, what is an
electromagnetic wave?
- EM wave coupled, changing electric and magnetic
field that travels through space - EM radiation energy that is carried, or
radiated, in the form of EM waves - EM spectrum the entire range of frequencies and
wavelengths that make up all forms of EM
radiation - Ex radio waves, microwaves, visible waves, and
x-rays
3
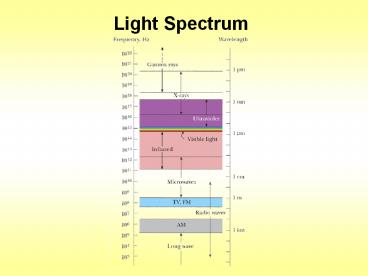
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
4
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- The EMS are transverse waves that carry both
magnetic and electric energy. Each type of EMW
is defined by its wavelength. Wavelengths range
from 104 m (10,000 m) to 10-15 m
(0.00000000000001 m).
5
Radio/TV Waves
- Radio waves come in three types Frequency
modulation (FM), amplitude modulation (AM), and
then there are the lowest frequencies, which are
used by two way radios, etc.
6
- Radio Waves and Electromagnetic Fields Simulation
7
Visible Light
- The part of the spectrum that we can see is
called visible light. It is the smallest portion
of the spectrum.
8
c speed of light in a vacuum 2.9979 x 108
m/s 3.0 x 108 m/s
9
v lf c lf
10
White Light and Color
11
Newtons Light Experiment
- So, Newton figured out that white light is
composite (made up of other colors)but how did
he do it?
12
Not just one prism
13
But TWO!
14
Each color in the spectrum is associated with a
wavelength
15
PRIMARY COLORS
The colors, that when added together, form white
light
(Red, Blue, Green)
16
ADDITIVE COLOR PROCESS
red blue green white
17
SECONDARY COLORS
The colors, that are formed when two primary
colors are added together
(yellow, cyan, magenta)
18
SECONDARY COLORS
19
(No Transcript)
20
What does it really mean to see color?
21
Ray Model
22
Reflection from Smooth and Rough Surfaces
23
Reflection
24
Problem
25
Refraction
26
An Analogy for Refraction
27
The Basic Mechanism of Refraction
28
SNELLS LAW
29
SNELLS LAW
30
Indices of Refraction
31
Example in notes
A beam of light of wavelength 550 nm traveling in
air is incident on a slab of transparent
material. The incident beam makes an angle of
40.0? with the normal, and the refracted beam
makes an angle of 26.0? with the normal. Find
the index of refraction of the material.
32
Refraction Summary
- If there is no change in index of refraction the
light is not deflected.
- As light goes from a low n to a high n it is bent
toward the normal. The greater the difference
the greater the deflection.
- As light goes from a high n to a low n it is bent
away from the normal. The greater the difference
the greater the deflection.
- If the light is incident on the surface of the
material along a normal path, there is no
deflection.
33
Dispersion
34
Index of Refraction Revisited
35
Dispersion in a Raindrop
36
Figure 26-38How Rainbows Are Produced
37
Total Internal Reflection
38
Critical Angle Equation
- sin?cn2/n1
- Try the one in your notes
39
How We See Objects
P
P'
P
40
Locating a Mirror Image
41
Spherical Mirrors
42
Concave and Convex Mirrors
43
Real vs. Virtual
- Real images are formed by converging light rays.
- Virtual images are formed by diverging light rays.
44
Principal Rays Used in Ray Tracing for a Concave
Mirror
45
Image Formation with a Concave Mirror
46
Inside the Focal Point
47
Principal Rays Used in Ray Tracing for a Convex
Mirror
48
Image Formation with a Convex Mirror
49
Refraction and the Bent Pencil
50
How is the ray deflected?
51
Comparing Lenses with a Pair of Prisms
52
Lenses
Converging Lenses
Diverging Lenses
Concave Meniscus
Convex Meniscus
Planoconcave
Doubleconcave
Planoconvex
Doubleconvex
53
The Three Principal Rays Used for Ray Tracing
with Convex Lenses
54
Rules for lens diagrams
- Converging lenses
- P ray starts parallel then heads toward focal
point - F ray starts from or heads toward focal point
then goes parallel - M ray goes straight through the middle
55
Wheres The Image?
56
Wheres The Image?
F
F
57
- Diverging lenses
- P ray starts parallel then heads away from focal
point - F ray starts from or heads toward far focal point
then goes parallel - M ray goes straight through the middle
58
The Three Principal Rays Used for Ray Tracing
with Concave Lenses
59
Wheres The Image?
60
Describe the Image
F
F
61
Two Lenses
62
Thin Lens Equation