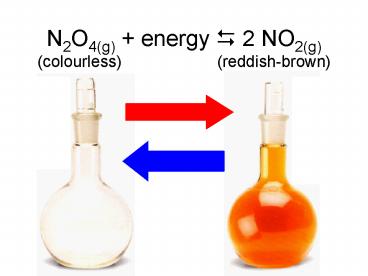
N2O4(g) energy ? 2 NO2(g) (colourless) (reddish-brown) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
N2O4(g) energy ? 2 NO2(g) (colourless) (reddish-brown)
Description:
N2O4(g) + energy 2 NO2(g) (colourless) (reddish-brown) Le Chatelier s Principle When a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed by a stress ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:69
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: N2O4(g) energy ? 2 NO2(g) (colourless) (reddish-brown)
1
N2O4(g) energy ? 2 NO2(g)(colourless)
(reddish-brown)
2
Le Chateliers Principle
- When a chemical system at equilibrium is
disturbed by a stress, the system adjusts
(shifts) to oppose the change - Stresses include
- Change in concentration
- Change in pressure (or volume)
- Change in temperature
3
Change in Concentration
A(g) 3B(g) ? 2C(g) heat
- Increasing the concentration of the reactants OR
- Decreasing the concentration of the products
- Will favour the forward reaction, causing the
equilibrium to shift to the RIGHT - Decreasing the concentration of the reactants OR
- Increasing the concentration of the products
- Will favour the reverse reaction, causing the
equilibrium to shift to the LEFT - RECALL Addition or removal of solid or liquids
does not change the concentration. Therefore does
not cause a shift. I.e. only applies to gases and
aqueous solutions.
4
Change in Concentration
5
N2(g) 3H2(g) ? 2NH3
6
Change in Pressure
? volume ? pressure ? volume ? pressure
A(g) 3B(g) ? 2C(g) heat
- Increasing the volume of the container OR
- Decreasing the pressure
- Will cause a shift to the side with MORE gas
molecules - In our example, it will shift left (4
molreactants gt 2 molproducts) - Decreasing the volume of the container OR
- Increasing the pressure
- Will cause a shift to the side with LESS gas
molecules - In our example, it will shift right (4
molreactants gt 2 molproducts)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Change in Temperature
- In an exothermic reaction
- Increasing the temperature will cause a shift to
the LEFT - Decreasing the temperature will cause a shift to
the RIGHT
9
Change in Temperature
- In an endothermic reaction
- Increasing the temperature will cause a shift to
the RIGHT - Decreasing the temperature will cause a shift to
the LEFT
10
Change in Temperature
Recall Keq is temperature dependent. Therefore,
changes in temperature will also affect Keq Shift
right ? products, ? Keq Shift left ?
reactants, ?Keq
11
Variables that do NOT Affect Equilibrium
- Catalysts
- Increases reaction rate by lowering activation
energy (of BOTH the forward and the reverse
reactions equally) - Decreases the time required to reach equilibrium
but does not affect the final position of
equilibrium - Inert Gases
- Increases the pressure, which will increase
reaction rate - Increases the probability of successful
collisions for BOTH products and reactants
equally - Decreases the time required to reach equilibrium
but does not affect the final position of
equilibrium
12
Practice!
- Read p. 450-456
- P. 457 1-6
- P. 459 1-6