Integumentary system PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Integumentary system
1
Integumentary system
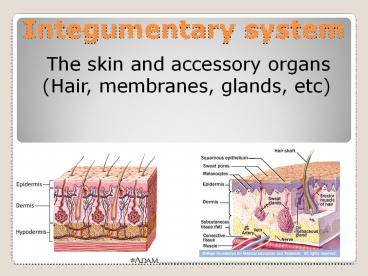
- The skin and accessory organs (Hair, membranes,
glands, etc)
2
Membranes
- Serous membranes Line body cavities that lack
openings to the outside. - is a smooth membrane consisting of a thin layer
of epidermal cells - They line and enclose several body cavities,
where they secrete a lubricating fluid which
reduces friction from muscle movement.
3
Membranes
- Serous membranes Basically they cover
- areas such as the
- thoracic cavity
- the heart and
- lungs area, and
- ventral cavity.
4
Membranes
- Serous membranes
5
Membranes
- Mucous membranesare involved in absorption and
secretion. - They line various body cavities that are exposed
to the external environment and internal organs. - Examples are the nasal and oral cavities, tubes
of the respiratory, digestive and reproductive
tracts.
6
Membranes
- Mucous membranes
- Usually found near or on glands that will help
secrete a mucous. - It is at several places continuous with skin.
- Why would you find mucous membranes continuous or
near or connected to your skin?
7
Membranes
8
(No Transcript)
9
Membranes
- Synovial membranes is the soft tissue that lines
the non-cartilaginous surfaces within joints
(synovial joints). - They secrete a fluid to lubricate the joints.
10
Membranes
- Synovial membranes
11
Membranes
- Cutaneous membranes The skin They consist of
stratified squamous epithelium and the underlying
connective tissues. Cutaneous membranes are
thick, relatively waterproof, and dry. - The skin helps in regulating body temperature and
maintaining homeostasis.
12
Membranes
- Cutaneous membranes
13
THE THREE LAYERS OF SKIN
- EPIDERMIS
- DERMIS
- SUBCUTANEOUS LAYER
14
EPIDERMIS
- The outer layer
- Composed of
- stratified
- squamous
- epithelium
15
EPIDERMIS
Contains five separate layers Stratum Corneum-
outer most layer- mostly dead cells Stratum
Basale- The area where cells divide
rapidly Stratum Spinosum Stratum Granulosum- only
in areas where the skin is thick Stratum lucidum-
only on the palms and soles.
16
- 5 Layers of Epidermis
17
EPIDERMIS
- Here is what happens to make these layers
- 1. The basale layers divide rapidly pushing the
cells and tissues up toward the top. - 2. The closer they get to the top the less
nutrients they have from the connective tissue so
they eventually die (This becomes your Corneum
layer)
18
EPIDERMIS
- The process of these cells hardening and dying is
called KERATINIZATION - This is when they can secrete the protein Keratin
to make the skin tough and water proof.
19
EPIDERMIS
- Your epidermis also contains MELANIN is a dark
pigment that provides your skin color. - Melanocytes are the cells that produce the
melanin. They are found in the deep layers of the
epidermis. - WHY Would you want them in the deep layers
instead of the corneum?
20
EPIDERMIS
- HOW or why do you think people have different
colors of skin then? DISCUSS with your table and
come up with an answer!
21
EPIDERMIS
- Most people have the same number of melanocytes
but the differences are due to the amount of
melanin they produce. - It is genetic!!
- If genes instruct the melanocytes to produce a
lot of melanin then your skin is darker.
22
Epidermis
- How do you think sunlight plays a role in melanin
and skin color? (Obviously sun UVA rays can make
you darker- but why do you think so?) DISCUSS as
a table and come up with an answer to report out.
23
(No Transcript)
24
EPIDERMS
- ANSWER The sun stimulates (Speeds up) production
of the melanin pigment. - Some people depending on how dark their skin is
can turn red or blush and it can be seen.
What do you think is happening there to
temporarily change the skin color?
25
EPIDERMIS
- ANSWER When the blood vessels in the lower
layers of the skin are well oxygenated the blood
pigments appear bright red (hot). When the oxygen
content is low, the skin can appear blueish
(cold). - Remember I said skin has something to do with
regulating body temperature- here is one way it
doe that!
26
DERMIS
- Known as the Inner layer
- Very thick
- Contains Connective tissues, epithelial tissues,
smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue and blood
vessels. - This is where your fingerprints come from.
- Supplies nutrients to the epidermis and regulates
body temperature.
27
DERMIS
- Contains sensory receptors (touch receptors,
temperature receptors- sweat glands, and so
forth) - Also contains the HAIR FOLLICLES, SWEAT GLANDS,
and SEBACACEOUS GLANDS
28
DERMIS
- HAIR FOLLICULE Hair is present everywhere
except palms, soles, nipples, and some external
reproductive parts. - Hair develops from a group of epidermal cells at
the base of a hair follicule that divide and grow
until they are pushed up and out and are dead.
SO HAIR IS DEAD- What type of dead cells do you
think they are? DISCUSS and come up with an
answer.
29
DERMIS
- ANSWER Once the cells get pushed up they become
the keratinized dead epidermal cells. - Think back to what we talked about with Melanin
and skin color. HOW do you think genetics and
melanin determine hair color? DISCUSS as a group
and come up with an answer.
30
DERMIS
- Answer Genes determine the type and amount of
pigment the melanocyte cells will produce. So
your hair follicles have melanocyte cells at the
base of them. - If these cells at the base of the follicle
produce a lot of melanin the hair will be darker.
- When you get older how
- does your hair start to
- turn gray and then white?
31
DERMIS
- ANSWER The melanocyte cells eventually over time
die and stop producing melanin. - A person with RED hair is the
- exception- they have a pigment
- called Trichosiderin.
32
- Arrector Pili muscle a smooth muscle attached to
the hair follicle. - Why do you think your skin would need a muscle
attached to the hair? What does it do? - Answer Causes your hair to stand up when you
have the goosbumps- either emotional response or
cold.
33
DERMIS
- Sebaceous Glands associated with hair follicles.
Secrete oil called sebum through small ducts into
the hair. - Helps keep hair and skin soft and waterproof.
34
DERMIS
- SWEAT GLANDS There are different types of sweat
glands. - Eccrine glands respond to a rise in temperature
and are located on the forehead, neck and back
where they produce droplets of sweat to cool the
body down. - Apocrine glands become active at puberty or when
a person is emotionally upset. (arm pit region or
groin).
35
- Sweat Gland
36
DERMIS
- Sweat glands sweat is more than just water-
contains salts and other wastes. - Sweat glands help regulate body temperature.
37
SUBCUTANEOUS LAYER
- Beneath the dermis
- Consists of Loose Connective tissue and Adipose.
- Contains most of the blood vessels for supplying
the epidermis nutrients - Also insulates- conserving body heat and keeps
too much heat from coming into the body.
38
- THE THREE LAYERS
39
THE SKIN
- LABEL THE
- DIAGRAM