INTERPHASE PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: INTERPHASE
1
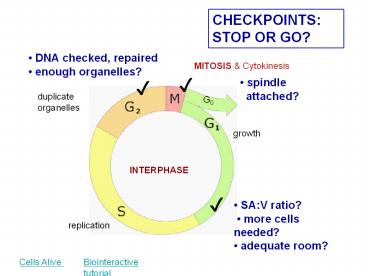
CHECKPOINTS STOP OR GO?
DNA checked, repaired enough organelles?
MITOSIS Cytokinesis
spindle attached?
?
?
duplicate organelles
G0
growth
INTERPHASE
INTERPHASE
?
SAV ratio? more cells needed? adequate
room?
replication
Biointeractive tutorial
Cells Alive
2
REGULATING THE CHECKPOINTS
proto-oncogenes trigger cell division, direct
cell to continue in the cycle turn on the
gas! tumor-suppressor genes shut down the
cycle hit the brakes!
3
EFFECTS OF MUTATIONS
In proto-oncogenes gt less division
therefore too few cells more division,
creating too many cells, increasing likelihood of
mutation In tumor-suppressor genes gt
loss of inhibition too many cells
creates TUMORS
Animation 1
4
More division increases likelihood of more
mutations What else causes mutations?
5
normal cells
Cells stop dividing when they should Cells die
when damaged
mutation gt cell death
cancer cells
Abnormal growth Abnormal DNA
6
TUMOR DIRECTS MORE GROWTH
Tumor that can grow and spread
tumor
angiogenesis
signals
blood vessel
Signal molecules
cell releases signal molecules that cause blood
vessels to grow
blood vessels bring in nutrients and removes
waste products
7
CANCER SPREADS via blood vessels
tumor breaches organ wall
1. Cancer cells invade surrounding tissues and
vessels
Blood vessel
cells lodge, grow in other organs
Metastasis
blood transports cancer cells
8
DIFFERENT TYPES OF CANCERSDIFFERENT TYPES OF
TREATMENTS
- Radiation use EM waves to disrupt tumor cell
DNA - Chemotherapy - toxic chemical cocktail
- problem both therapies kill mitotic cells,
cancerous AND healthy - Disrupt signal molecules produced by tumor cells
- Block growth of blood vessels to tumors
- Use immune system to attack cancer like it does a
virus - Vaccines for microbe-caused cancers (HPV)
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.