Membrane Notes Review - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Membrane Notes Review
Description:
Structure of the Plasma Membrane Lipid bilayer two sheets of lipids (phospholipids). Found around the cell, the nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:138
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Membrane Notes Review
1
Membrane Notes Review
2
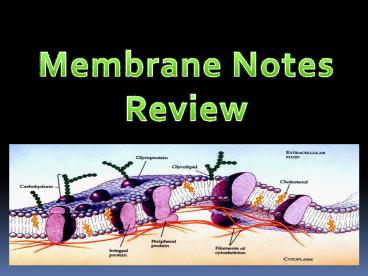
Structure of the Plasma Membrane
- Lipid bilayer two sheets of lipids
(phospholipids). - Found around the cell, the nucleus, vacuoles,
mitochondria, and chloroplasts. - Embedded with proteins and strengthened with
cholesterol molecules.
3
Membrane Proteins
- 1. Determine what particles can pass through the
membrane. - 2. Serve as enzymes (may speed reactions).
- 3. Act as markers that are recognized by
chemicals and molecules from the inside and the
outside of the cell (the immune system).
4
Types of Transportation
Active
Passive
5
(No Transcript)
6
Three Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
7
Passive Transport
- Simple Diffusion
- Doesnt require energy
- Moves high to low concentration
- Example Oxygen or water diffusing into a cell
and carbon dioxide diffusing out.
8
Cell Concentrations
- Hypertonic solutions more dissolved solute.
- Hypotonic solutions less dissolved solute.
- Isotonic solutions the same dissolved solute.
- Solventdoes the dissolving
- Solutesolid(usually) which is dissolved
9
There are three types of solutions (1)
Hypotonic - a solution which is more dilute
(i.e., less solutes) than the cytosol. The cell
gains water and swells.
(2) Hypertonic - a solution which is
more concentrated (i.e., more solutes) than the
cytosol. The cells loses water and
shrinks. (3) Isotonic - a solution which has
the same concentration of solutes as the cytosol.
The cell neither gains nor loses water and
remains unchanged.
10
TONICITY the relative amount of solute
11
HYPERTONIC Concentration outside cell is
____________________ inside cell More water
leaves cell than enters so cell ____________
12
- HYPOTONIC Concentration outside cell is
________________ inside the cellMore water
enters than leaves cell so cellwill
___________________
13
ISOTONIC Concentration outside cell
__________ concentration inside cell Water
entering water leavingso cell
_____________________
14
Osmosis
- Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable
membrane. - Occurs until water is balanced on both sides of
the membrane.
15
Passive Transport
- Facilitated diffusion
- Doesnt require energy
- Uses transport proteins to move high to low
concentration - Examples Glucose or amino acids moving from
blood into a cell.
16
Active Transport
- Requires energy or ATP
- Moves materials from LOW to HIGH concentration
- AGAINST concentration gradient
17
Sodium-Potassium Pump
3 Na pumped in for every 2 K pumped out
creates a membrane potential
18
(No Transcript)
19
Endocytosis Phagocytosis
Used to engulf large particles such as food,
bacteria, etc. into vesicles
Called Cell Eating
20
Exocytosis The opposite of endocytosis is
exocytosis. Large molecules that are manufactured
in the cell are released through the cell
membrane.
Inside Cell
Cell environment
21
Pinocytosis
Most common form of endocytosis.
Takes in dissolved molecules as a vesicle.